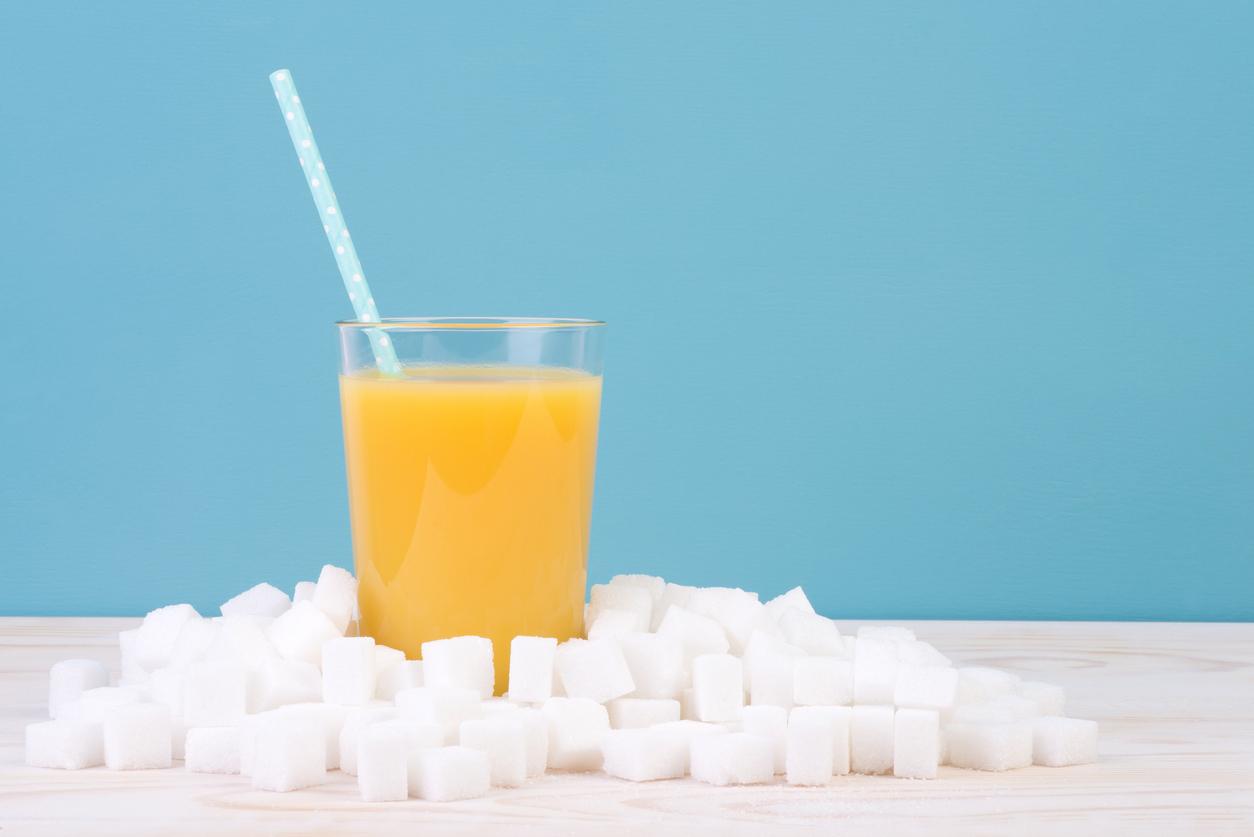
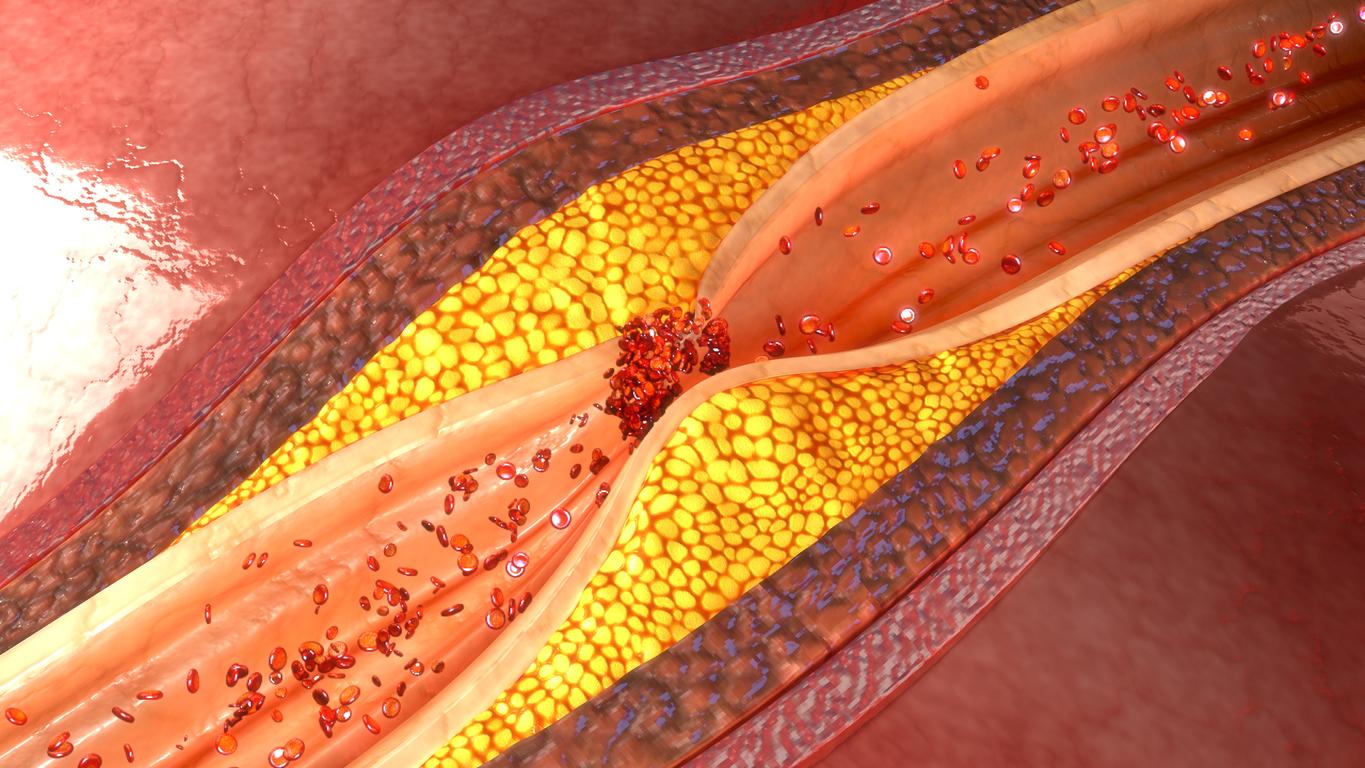
Too much sugar harms metabolism, even when consuming too much sugar does not lead to weight gain. It raises cholesterol and blood pressure.

Good for the taste buds, less for cardiovascular health. Eating too much sugar, even without gaining weight, is associated with several risk factors. This is the result of a meta-analysis to appear in the July edition of theAmerican Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Sugar directly influences cardiovascular risk factors and blood pressure, regardless of weight gain. The concentrations of triglycerides, total cholesterol, LDL and HDL are increased by a diet too rich in sugars. These elements, often associated with weight gain, appear even in patients with a stable and normal weight. Researchers also note a strong relationship between sugar intake and lipids in the body. Last risk factor but not the least: blood pressure is boosted by overconsumption of sugars.
A different assimilation
The cardiovascular risks of sugars had already been suggested, especially in a study conducted on sugary drinks and adolescents. On the other hand, they did not establish any difference in the evolution of the metabolism according to the BMI of the patients. This study “suggests that our bodies assimilate sugar in a different way from other carbohydrates,” said Dr. Lisa Te Morenga, co-author of this meta-analysis.
“Even though the effects of sugar on blood pressure and lipids are relatively modest, our results support public health recommendations for reducing added sugars in our diets as one of the measures that can be expected to reduce the burden of cardiovascular disease around the world, ”says Dr Te Morenga. She believes there is a need for a long-term study, even as the evidence for reducing added sugars in industrial products is mounting.
.