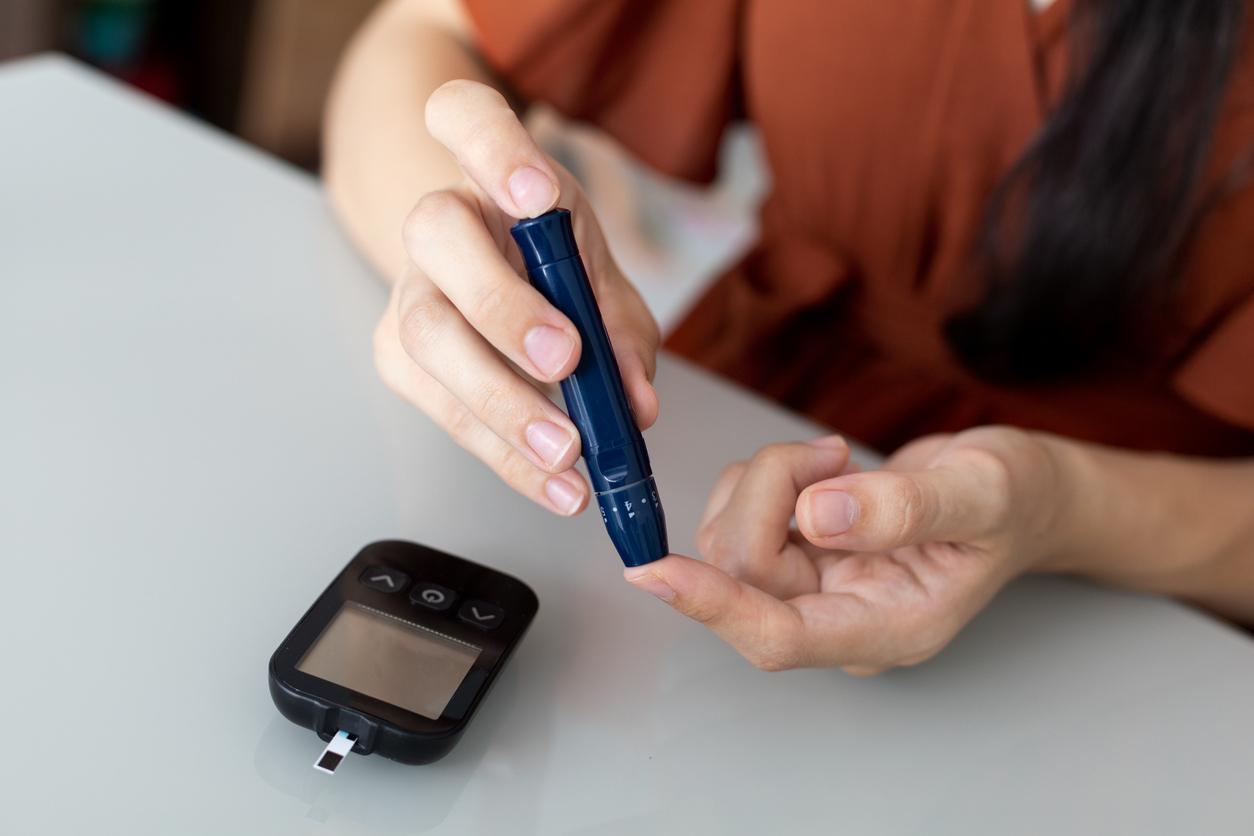
A large number of influencers popularize the idea of monitoring his blood sugar, including in non -diabetic people. Is it really useful? Inserm dissected the question.

- Glucose is an essential source of energy for the body, and its natural variations, such as peaks after a meal, are normal and adapted in healthy people.
- Inserm warns against the diverted use of blood sugar sensors by non-diabetics, which risks encouraging obsessive behavior.
- It is useful to favor scientifically validated recommendations, such as those of the National Health Nutrition Program (PNNS).
Before taking an interest in trends relayed on social networks, let’s not forget that glucose is a key player to run the machine that is our body. As the Inserm specifies, ” Glucose from our diet is necessary for the proper functioning of the body. It serves as an energy substrate for a large number of cells, which use it to produce energy ».
In a healthy person, the normal values of blood sugar vary during the day, oscillating around 1 g/l depending on meals or physical activity. After a meal, for example, a temporary increase – a “peak” of blood sugar – is a perfectly normal and suitable physiological response.
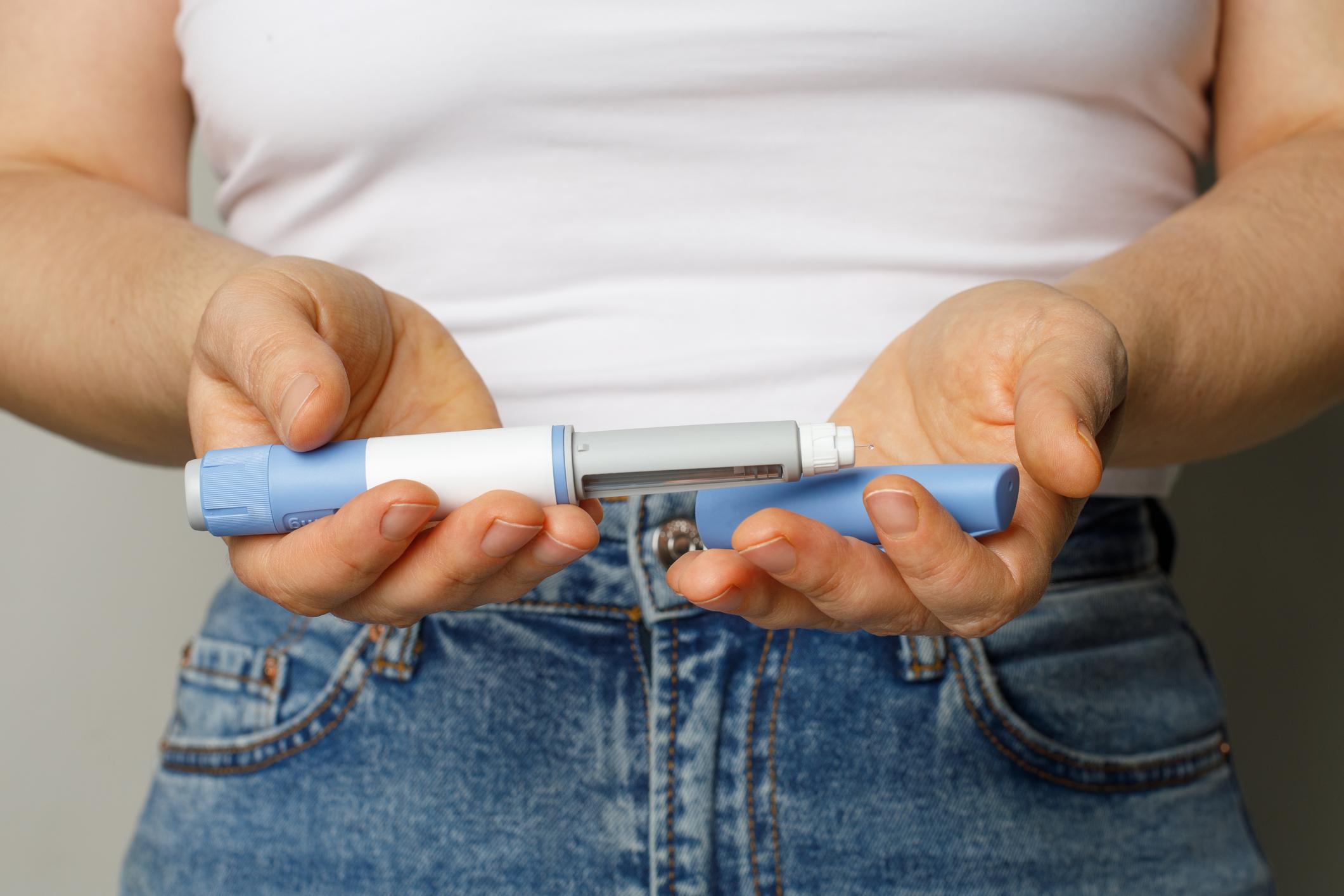
On the other hand, people with type 1 or 2 diabetes must regularly monitor their blood sugar to adjust their treatments, such as insulin, and avoid complications related to episodes of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
The risks of a diverted use of blood sugar sensors
These sensors, although precious for diabetic people, have no scientifically proven utility for non -sick individuals, insists Inserm. However, some influencers continue to promote them as a method to better know your metabolism or adapt your diet.
Risk? These devices, used without medical follow-up, can lead to erroneous interpretations and a “pathologization” of normal body reactions, such as variations, called “post-Prandial” (after a meal). Inserm also warns that these practices can cause obsessive behavior, increasing the risk of eating disorders.
Nutritional advice not always reliable
Advice for ” Limit blood sugar peaks »Multiply on social networks. Among them: Start your meals with fruits and vegetables or walk immediately after eating. If these practices can encourage overall healthy behavior – consume more plants or fight sedentary lifestyle – they are often based on fragile or non -existent scientific justifications.

According to Inserm, there is no solid evidence showing that specific order in food consumption or physical activity at a specific time would be particularly beneficial for glycemic health.
Watch out for “miracle theories”
What worries experts is the spread of excessive demonization of glucose on social networks. Some influencers present sugar as an enemy to eradicate at all costs, fueling a quest for “miracle” solutions to lose weight or stay healthy.
However, as the Inserm reminds us, ” Metabolic health and weight loss depend on many factors, both genetic and environmental ». A balanced diet, in accordance with the recommendations of the National Nutrition Health Program (PNNS), remains the key to preventing chronic diseases (type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, certain cancers).