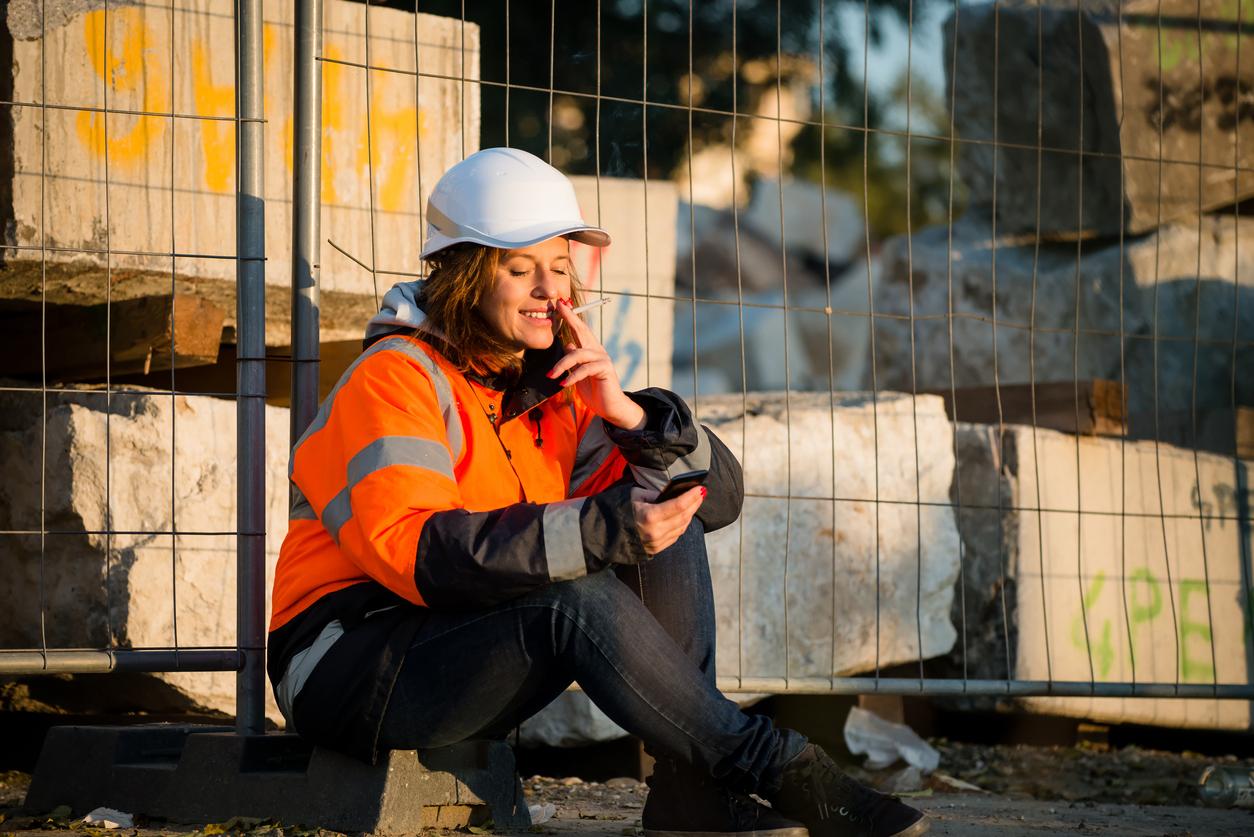
Regular physical activity is associated with better lung function in smokers, according to results of a study published in the medical journal Thorax.
Researchers from the ISGlobal Institute in Barcelona, Spain conducted a study with 3,912 adults, smokers and non-smokers, aged 27 to 57, in 11 countries. Over a 10-year period, these participants were considered active if they exercised twice or more per week and longer than an hour.
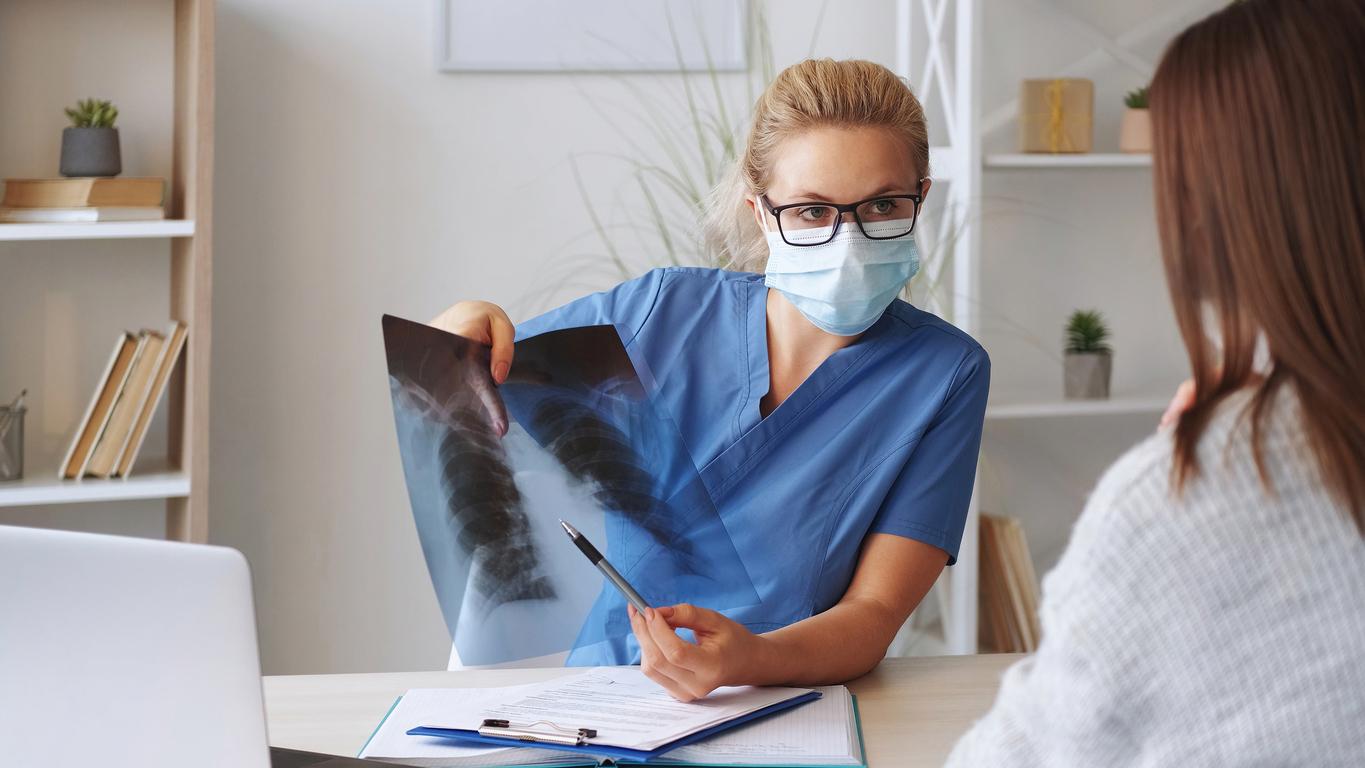
The findings of the study showed that lung functions at the second scan were poorer in smokers than in non-smokers.
Corn, smokers sportspeople on their first examination showed good breathing capacity in both analyzes than sedentary smokers.
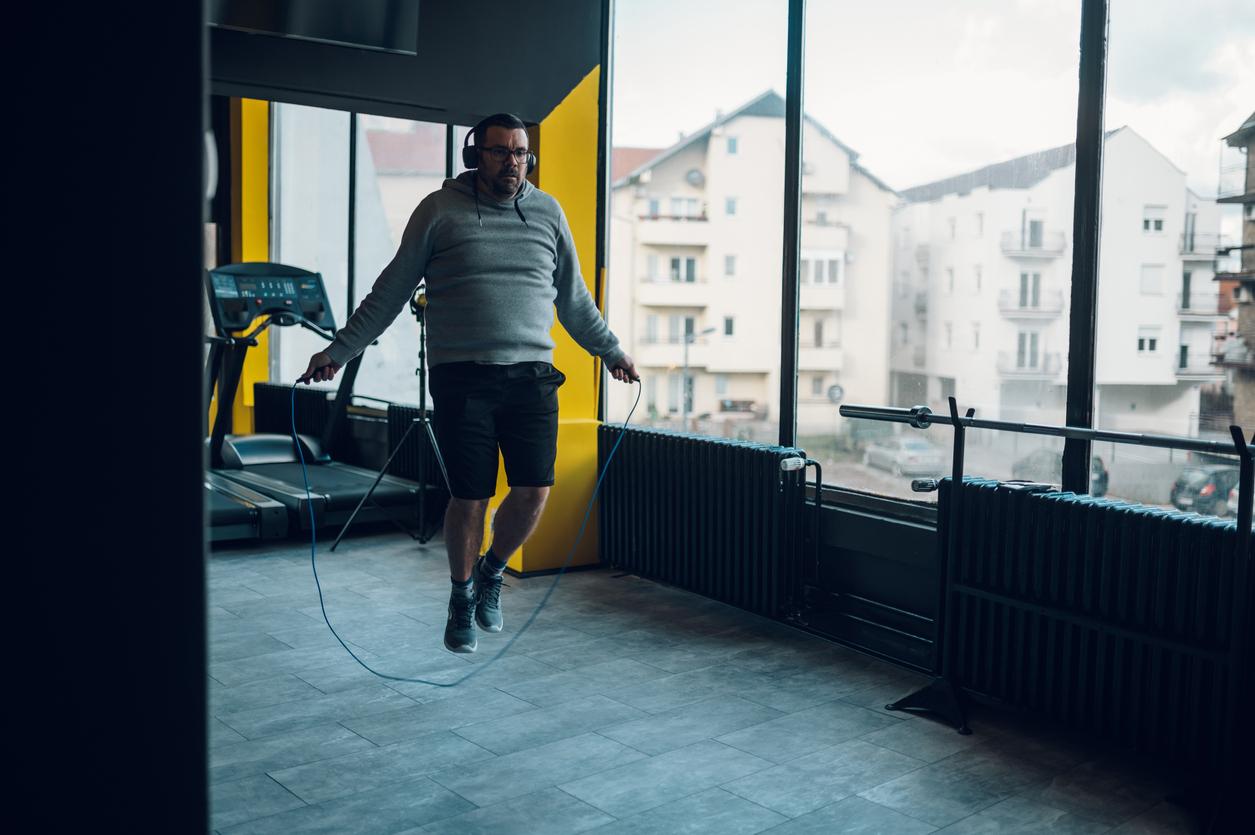
The researchers also observed that people who were athletic at the end of the study, and those who had never stopped exercising, had better lung capacity than sedentary volunteers.
“The results of this study strengthen the epidemiological evidence supporting an association between physical activity and respiratory health“said Judith Garcia-Aymerich, author of the study.
“These results should be used to” inform and encourage public health messages that advocate increased physical activity to maintain respiratory health in adults. “
Read also:
Smoking: Great Britain illustrates the immediate effects of tobacco
Just one cigarette is bad for your heart’s health
10 years without tobacco for healthy sinuses