Mozambique announces the eradication of polio from its soil. Two countries are still affected by the disease which causes paralysis.
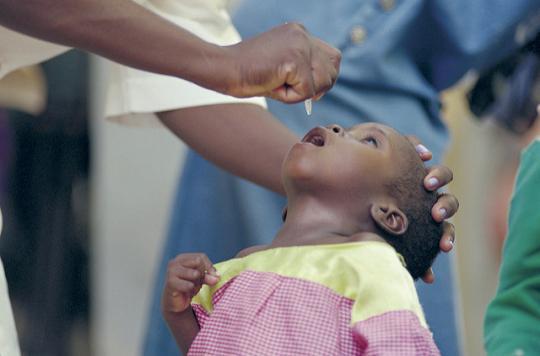
Mozambique has eradicated polio from its territory. The Minister of Health compared the news to the elimination of leprosy in this country in 2008. The announcement follows a gathering of the African regional certification commission for polio eradication.
According to experts, this disease could be eradicated completely by next year by continuing the action taken for more than thirty-five years. In 1988, 125 countries were affected by the epidemic with 350,000 cases, against 75 in 2015. Today, only Afghanistan and Pakistan remain endemic.
The importance of vaccination
One of the three forms of poliovirus was completely eradicated in 1999. For the remaining two, the strategic plan started in 2013 aims for total eradication by 2018. This would prevent 200,000 new cases each year and save 40 to $ 50 million in twenty years.
The World Health Organization recalls that eradication strategies only work if they are fully implemented. They aim to develop or maintain vaccination to stop transmissions and prevent epidemic outbreaks.
In the absence of treatment, prevention by vaccines remains the only means of health action.
In France, vaccination is compulsory with two injections at the age of 2 and 4 months, then compulsory reminders up to 13 years. In adulthood, boosters are recommended at 25, years, 45 years and 65 years, then once every ten years.
Paralysis in children
The disease is indeed very contagious: it is transmitted by the fecal-oral route. The virus spreads in the intestine, reaches the nervous system and causes paralysis in 1 in 200 cases. 5 to 10% lead to death by stopping the respiratory muscles. The other paralyzes are often permanent.
The infection can be asymptomatic, but it often causes fever, headache, asthenia (physical fatigue and weakening of the body), vomiting, and stiffness in the neck and limbs.
The poliovirus mainly affects children under five, in areas with poor sanitary conditions, at war, or with an inadequate health system. The actions taken (surveillance and vaccination in the first place) at the global level are therefore necessary to overcome the virus, especially as these measures help to fight against other diseases.
.