Citrus fruits are recommended for their vitamin C intake but should be consumed in moderation to limit the risk of melanoma. Their richness in furocoumarins, sensitive toxic agents would reduce the protection of the skin to ultraviolet rays and increase the risk of melanoma.
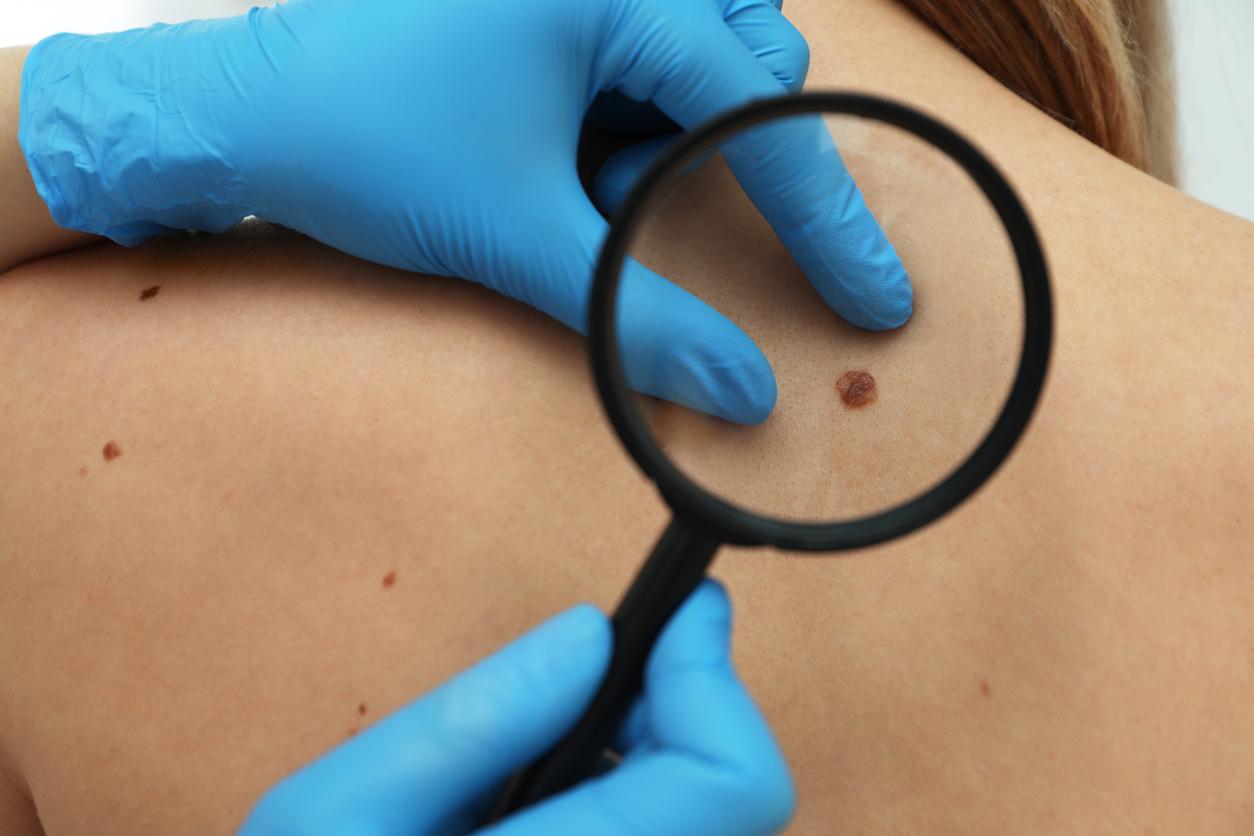
Melanomas are the most dangerous skin cancers because they can spread to other organs and have fatal consequences. When diagnosed at a metastatic stage, they have what is called “poor prognosis”: 5-year survival rates not exceeding 20% for patients.
Researchers from Brown University (United States) analyzed the composition of the plates and the lifestyle (sports activity, smoking, alcohol consumption) of 100,000 participants over 26 years.
After adjusting for risk factors, the results of their study found that people who ate a grapefruit and an orange and a half (or 270 ml in juice) each day had a 36% higher risk of cancer than those who ate less. twice a week.
In question, furocoumarins, sensitive toxic agents present in citrus fruits. These photosensitizing molecules would prevent protection of the skin from ultraviolet rays.
“Further investigations must be put in place to determine whether these are the most dangerous fruits or fruit juices,” said Shaowei Wu, an epidemiologist at Brown University.
The importance of prevention
Skin melanoma is affecting more and more people. With 11,176 new cases estimated in 2012, this skin cancer is ranked 9th among cancers, all sexes combined. 9,780 cases were estimated in 2011 and more and more people are affected in those under 40. This type of cancer can be easily cured if it is detected in time, but most of the time, these melanomas go unnoticed, because they are mistaken for benign moles.
Read also:
Infographic: the places on the body where melanoma hides
Skin cancer: carcinoma or melanoma?
Melanoma: beware of impotence treatments