Intermittent fasting may be as effective as a tailored diet in helping diabetic patients regulate their blood sugar, according to a team of researchers.
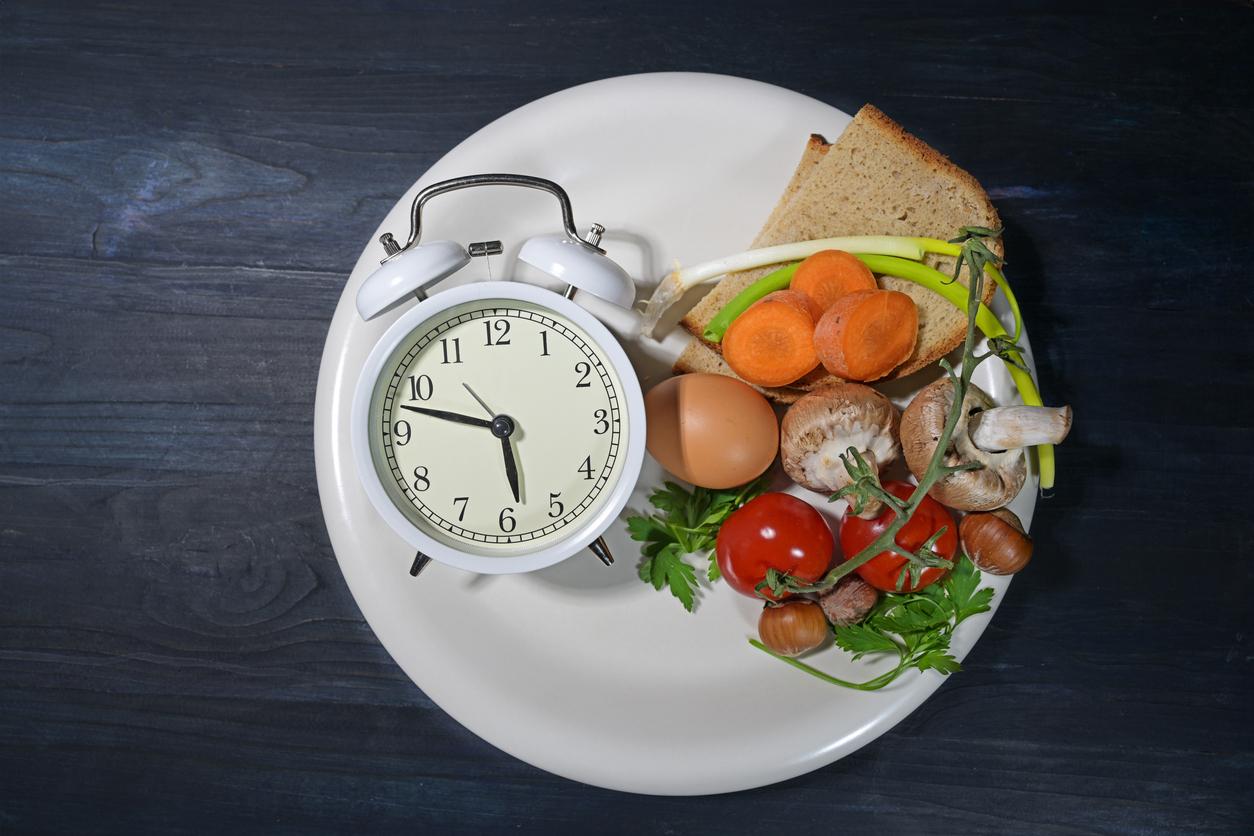

- Researchers compared the effects of intermittent fasting to those of a personalized diet supervised by a dietitian to help people with type 2 diabetes better control their blood sugar levels.
- They saw similar results over six months, with improvements in their blood glucose levels and weight loss for some participants. Patients following intermittent fasting also noted benefits on the quality of their sleep.
- By limiting meals to a window of a few hours, such as 11 a.m. to 7 p.m., this method aligns with the body’s circadian rhythms. However, it is not suitable for everyone and requires the advice of a doctor.
Affecting more than 3.5 million people in France, type 2 diabetes – which represents 90% of cases – leads to high blood glucose levels, increasing the risk of serious complications such as heart disease and kidney failure. or vision problems. Like physical activity and certain drug treatments, diet remains one of the most effective ways to manage chronic illness.
A new study, published in the journal Diabetes Research and Clinical Practicelooked in particular at the impact of intermittent fasting to help diabetic people regulate their blood sugar: it would be as effective as a personalized diet supervised by a nutritionist.
The benefits of intermittent fasting on diabetes
Unlike diets based on the type or quantity of food, intermittent fasting involves limiting food intake to a window of a few hours, such as 11 a.m. to 7 p.m., leaving the body to fast for the rest of the day. “By synchronizing meals with the circadian rhythm, the body benefits from a digestive break, which can promote better metabolism”explain the researchers in an article published in The Conversation. For people with type 2 diabetes, this method offers specific benefits: knowing that their blood glucose levels are often higher in the morning, delaying breakfast while being active beforehand helps reduce their blood sugar levels.
As part of their work, the scientists recruited 52 participants with type 2 diabetes and divided them into two groups: one following a diet supervised by a dietician and the other, the intermittent fasting method (window of 9 hours for all meals). As a result, after six months, both groups saw their blood sugar levels drop, measured by the HbA1c test, the key marker for diabetes management. Some participants even lost between 5 and 10 kilos. Patients following intermittent fasting also noted benefits on the quality of their sleep and their ability to follow the method on a daily basis.

Consult your doctor before embarking on a food fast
The participants, however, mentioned some obstacles to applying intermittent fasting, in particular social and family constraints which can make it difficult to respect this “food window”. But one of the major advantages of dietary restriction lies in its simplicity: by focusing only on meal times, this method seems easier to integrate for people who do not have access to specialized nutritional advice. It could also be adaptable to various cultural contexts, since the types of food remain unchanged, only the time of consumption is changed.
However, this method is not suitable for everyone, the researchers point out: people taking medication that is contraindicated for fasting must consult a health professional before adopting it. In addition, it is recommended to follow classic dietary advice, such as consuming vegetables, fruits, whole grains and good fats.