In October 2017, 4 staff members of a clinic in Montauban were infected. In August of the same year, 5 Parisian police officers had been infected. No doubt, scabies is well and truly back. According to Public Health France estimates, in 2010 there were 300 to 350 cases of scabies per 100,000 inhabitants*. This dermatological disease is very contagious and does not depend on hygiene or the social environment, contrary to popular belief. Learn to recognize it to better protect yourself from it.
A contagious disease… and shameful
Cases of scabies in a clinic in Montauban, others at the Paris courthouse… For some time now, and most often in the fall, scabies has been making a comeback. A disease in full recrudescence, this pathology which affects men and women of all ages and all conditions, nevertheless remains surrounded by a feeling of shame because we still think (wrongly) that it is linked to a lack of hygiene.
Scabies is actually a skin disease caused by a parasite from the mite family: the sarcoptic. The parasite, which is not visible to the naked eye, settles in the upper layers of the skin and digs furrows there where the female lays her eggs. This skin condition is most often benign, but a delay in treatment can cause difficulties because the disease is highly contagious (scabies is transmitted by contact with the skin) and it cannot heal on its own.
Read also
Scabies progresses in Paris
Symptoms of scabies
First of all, you should know that there is not one but several scabies. Indeed, there are different forms of the disease, the most common being common scabies. Its incubation period is 2 to 3 weeks, that is to say, it takes at least two weeks between contamination and the appearance of the first itching.
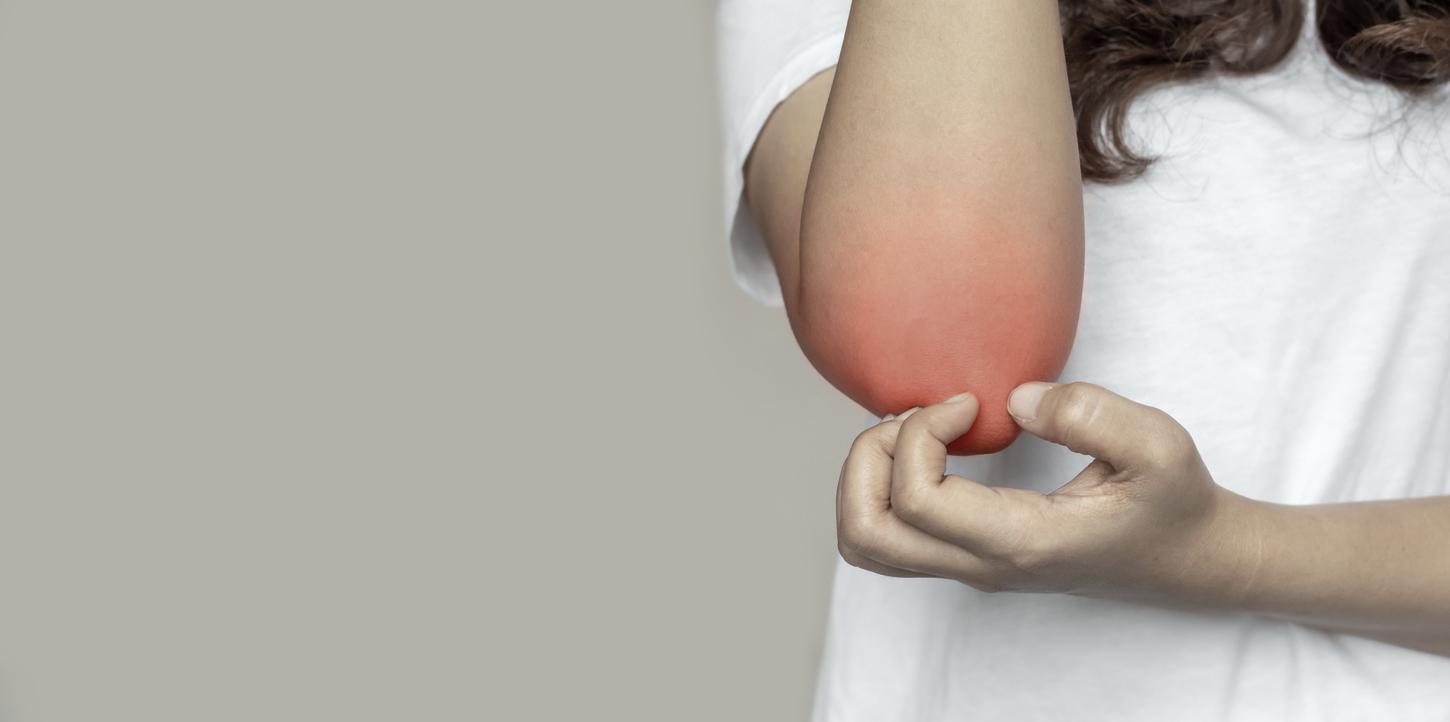
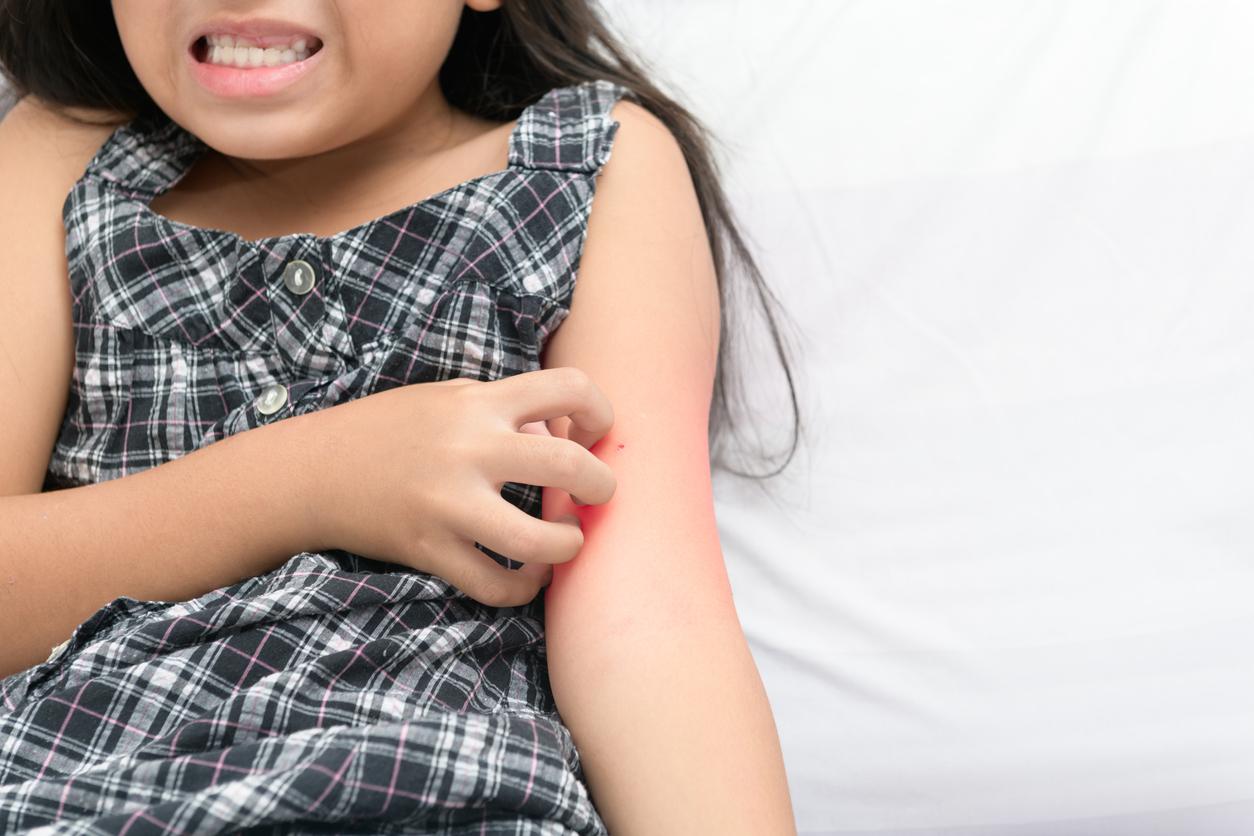
This intense itching (called pruritus) often occurs at night, in skin folds (between the fingers, under the armpits, between the buttocks, around the genitals, inside the wrists or ankles).
To calm them, we tend to scratch, which causes alteration and inflammation of the skin which can then degenerate into a secondary infection.
Another specific symptom of scabies is the appearance of a red skin furrow, which corresponds to the path of the parasite under the skin.
Read also
Scabies back in France
How to care for and protect yourself?
The diagnosis of scabies is mainly clinical, based on the presence of suggestive lesions. In case of doubt, it can be confirmed by a parasitological examination: a sample is taken in the laboratory by a biologist who chooses the lesions likely to contain parasites. When the disease is identified, the one and only treatment is to eradicate the parasite with an antiparasitic product because there is no spontaneous cure.
As for the lice, it is a question of attacking the adults initially and then renewing the treatment 7 to 10 days later to target the eggs. Within the family, sick or not, it’s the same, everyone must be treated otherwise Sarcoptes scabiei hominis – the name of this mite responsible for scabies – will take advantage of this to proliferate…
To avoid the transmission of scabies, it is necessary, at the same time, to apply strict hygiene rules:
- Inform staff of the communities you frequent and all the people with whom you have been in prolonged and repeated contact (including your sexual partner). Recommend that these people also consult their doctor.
- Avoid all skin contact with those around you during the three days following the first intake of medication. Also, abstain from sex during the entire treatment (scabies is considered a sexually transmitted infection).
- Vacuum throughout the house and dispose of used vacuum bags immediately.
- Wash all linen that may have been contaminated in the machine at 60° and dry it at high temperature if possible. Linen that cannot be washed should be locked up for at least a week in an airtight plastic bag because mites do not survive for more than four days without skin contact.
- If your child hashe will not be able to live again in the community (school, crèche) until 3 days after the start of treatment.
More information on the site Dermatos-Info