Young people abuse painkillers and sedatives. This is the result of a study conducted in the United States on patients admitted to the emergency room. These figures reflect the current crisis in the country.

Drug abuse is at epidemic level in the United States, where overdoses kill as much as traffic accidents. According to a study published on October 29 in Pediatrics, nearly one in ten young people misuse painkillers and / or sedatives. The survey, conducted by the University of Michigan, was conducted among 2,135 people aged 14 to 20 who visited the emergency room in 2010 and 2011. The authors considered the use of opioid painkillers and sedatives all subject to prescription.
Non-compliance with prescriptions
Of the total number of emergency room visits, 10% of adolescents and adults admit to misusing an opioid or sedative during the year. For some, the purpose of taking medication was to “get high”, for others it was a higher dose than prescribed or taking medication for a loved one.
The majority of drug diversions are illegal, that is, users do not have a prescription. For sedatives, this concerns 88% of respondents and 85% of opioid users. In the general young population, other studies estimate drug misuse at 8%.
100 deaths per day
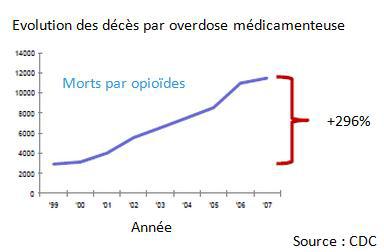
The danger is very real: according to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), 100 people die a day from a drug overdose. Emergencies register around 700,000 visits each year for this reason. The United States records a constant increase in cases of overdoses, opioids or sedatives. The cases of suicide are frequent, but the strong tendency goes to the errors of dosage.
Illicit uses of painkillers or sedatives are also associated with increased risks of drug addiction behavior. Bad users are more likely to be alcoholic, to have abused non-prescription drugs (such as cough syrup), or to have used marijuana. They are also at high risk of being in a car with a drunk driver.
Young people who divert drugs also seem to develop resistance to painkillers. During an emergency room visit, more of these patients receive intravenous opium-based painkillers.
Crisis in the United States
According to the study’s authors, prescribing practices must change, especially in emergency rooms. This service should become the privileged framework of a prevention policy. Drug abuse is a public health problem in the United States. However, emergency physicians often prescribe opioid painkillers urgently and for lack of anything better to their patients.
In France, the situation is far from being as worrying. The DRAMES study (death related to drug and substance abuse) by the Medicines Safety Agency (ANSM) reports 376 deaths in 2010. This figure cumulates overdoses by heroin, opioid substitution treatment and painkillers. The data are not exhaustive and lack precision as to the drugs that cause them. However, we observe that the taking of drugs is well managed in France, even if it is necessary to remain attentive to the evolution of overdoses.
.