Women in heavy jobs have a 17% increased chance of having a baby with fetal macrosomia.

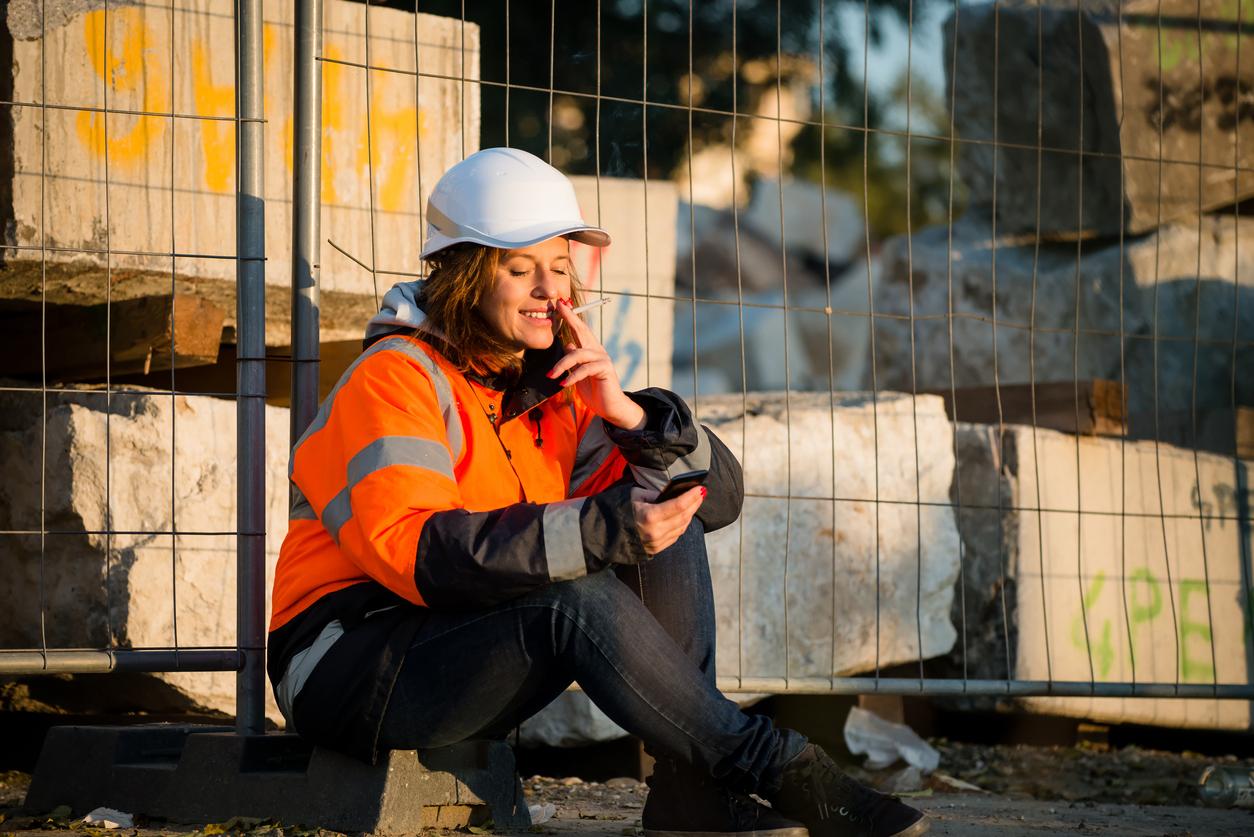
- Lifting heavy loads, standing for a long time or bending repeatedly are considered strenuous tasks.
- The proportion of women working while pregnant rose from 44% in 1967 to 68% in 2018.
According to a new study, women who work too hard during pregnancy are more likely to deliver a large baby, putting her at risk of being overweight in her teenage years. Fetal macrosomia, which refers to infants weighing more than 4 pounds at birth, is also associated with a higher risk of breast cancer for the mother.
Lift heavy loads
Specifically, the researchers found that women who work strenuous jobs have a 17% increased chance of having a baby with fetal macrosomia, in part due to lack of sleep. Lifting heavy loads, standing for a long time or bending repeatedly are considered strenuous tasks.
“Our results also shed light on an understudied link between gestational diabetes, which is a known risk factor for fetal macrosomia, and high-intensity physical activities at work during pregnancy.”adds research director Muzhe Yang.
68% of women work during pregnancy
In the United States, the proportion of women working while pregnant rose from 44% in 1967 to 68% in 2018. “Mothers-to-be also work later in their pregnancy, making it particularly important to understand how drudgery of work impacts pregnancy outcome,” continues the scientist.
In France, the duration of maternity leave includes prenatal and postnatal leave (i.e. 4 months in all), and can be adapted to your family situation, the course of your pregnancy and the birth conditions of your child.
.