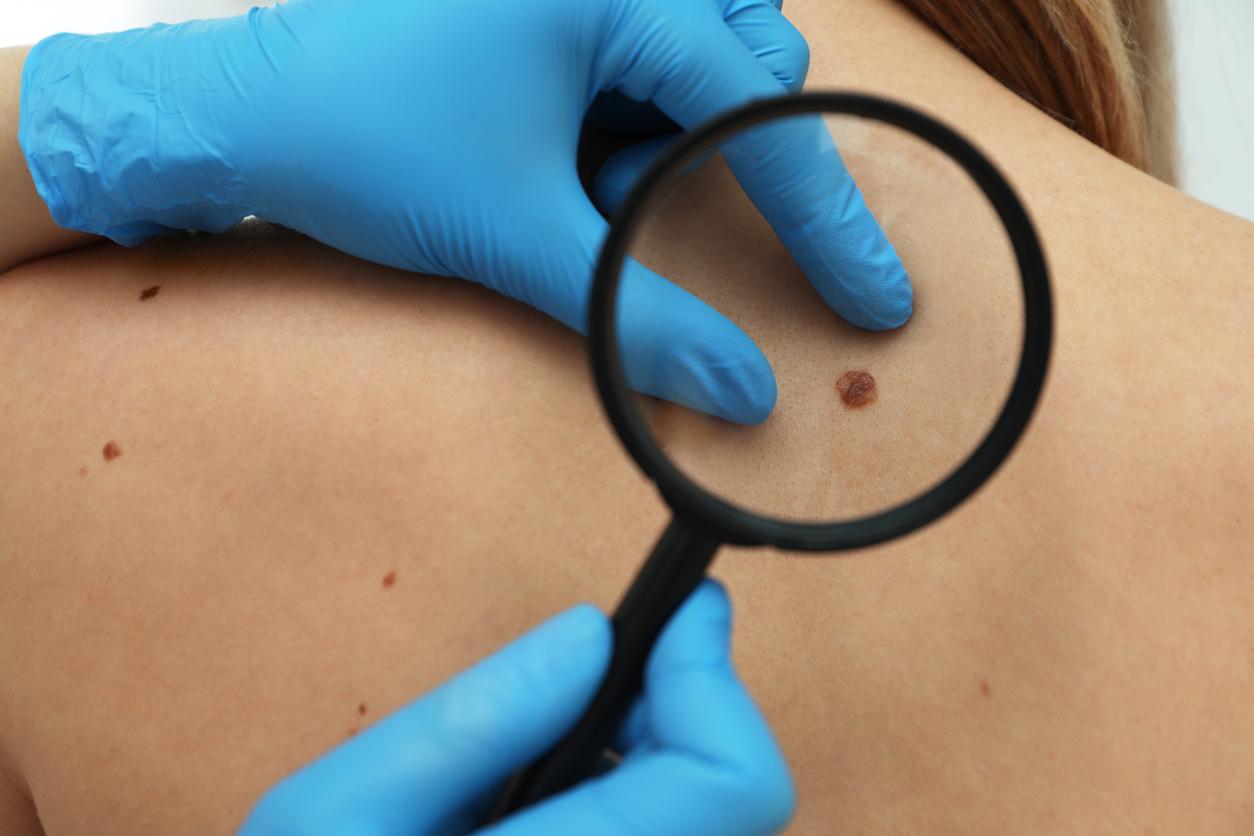
The skin cancer screening week, which was to be held from May 11 to 15, has been suspended due to the current health crisis. Why doctor insisted on talking about the three forms of skin cancer, driven by the conviction that information can save lives.

Each year, 80,000 new cases of skin cancer are diagnosed in France. Although unknown to the general public, there are three types of skin cancer, all of which have different survival statistics.
Cutaneous melanoma
Melanoma is probably the best known of all. With 15,404 new cases estimated in 2017 in metropolitan France and 1,783 deaths (1,036 men and 747 women)it represents 10% of skin cancers and affects more women (53%) than men (47%).
Ihe incidence and mortality from melanoma increased significantly between 1980 and 2012, in particular due to overexposure to UV radiation from tanning centers and the sun. Eighty percent of melanomas develop from healthy skin and 20% of cases from a pre-existing mole. According to the league against cancerthis pathology represents the leading cause of death for women aged 25 to 29.
Cutaneous melanoma is the most aggressive of skin cancers and can spread to other organs quickly (metastases). The survival of the patient depends the stage of his disease at the time of diagnosis: according to the American epidemiological surveillance program SEERthe 5-year relative survival is 98% at the localized stage, 62% with locoregional extension and 15% at the metastatic stage.
Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for 70% of skin cancer cases and is among the most treatable cancers, in particular because it grows slowly, locally, without spreading to other organs.. It is generally located on areas exposed to the sun and in 80% of cases on the face and neck, which makes it quickly detectable.
It mainly affects people over 50 and is, unlike melanoma, more common in men than in women. The advanced forms can be worrying, but the vital prognosis is rarely engaged. However, basal cell carcinoma can grow in width and depth, disfigure the patient and cause the loss of an eye, nose or ear.
The goal of treatment is to remove the tumor and surrounding healthy tissue to limit the risk of recurrence. Surgery may be an option, as may radiation therapy and destruction with nitrogen (cryotherapy) or electrical pulses (electrodesiccation). Chemotherapy may be considered, but is rarely necessary.
Squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma develops from cells located on the surface of the epidermis. Its evolution presents more risks than basal cell carcinoma, in particular because it has the capacity to form metastases, that is to say to spread to the rest of the body, including the level of the oral and genital mucous membranes. Ihe dangerousness of this type of cancer would be 2 to 5% when it affects the skin, but 20% when it affects a mucous membrane.
It usually appears on healthy skin, often following prolonged or even chronic exposure to UV rays. It manifests itself in the form of red or brown crusts, more or less thick, sometimes difficult to perceive. If in doubt, it is strongly recommended to consult a doctor, because diagnosed early, squamous cell carcinoma has a cure rate of 90%.
.