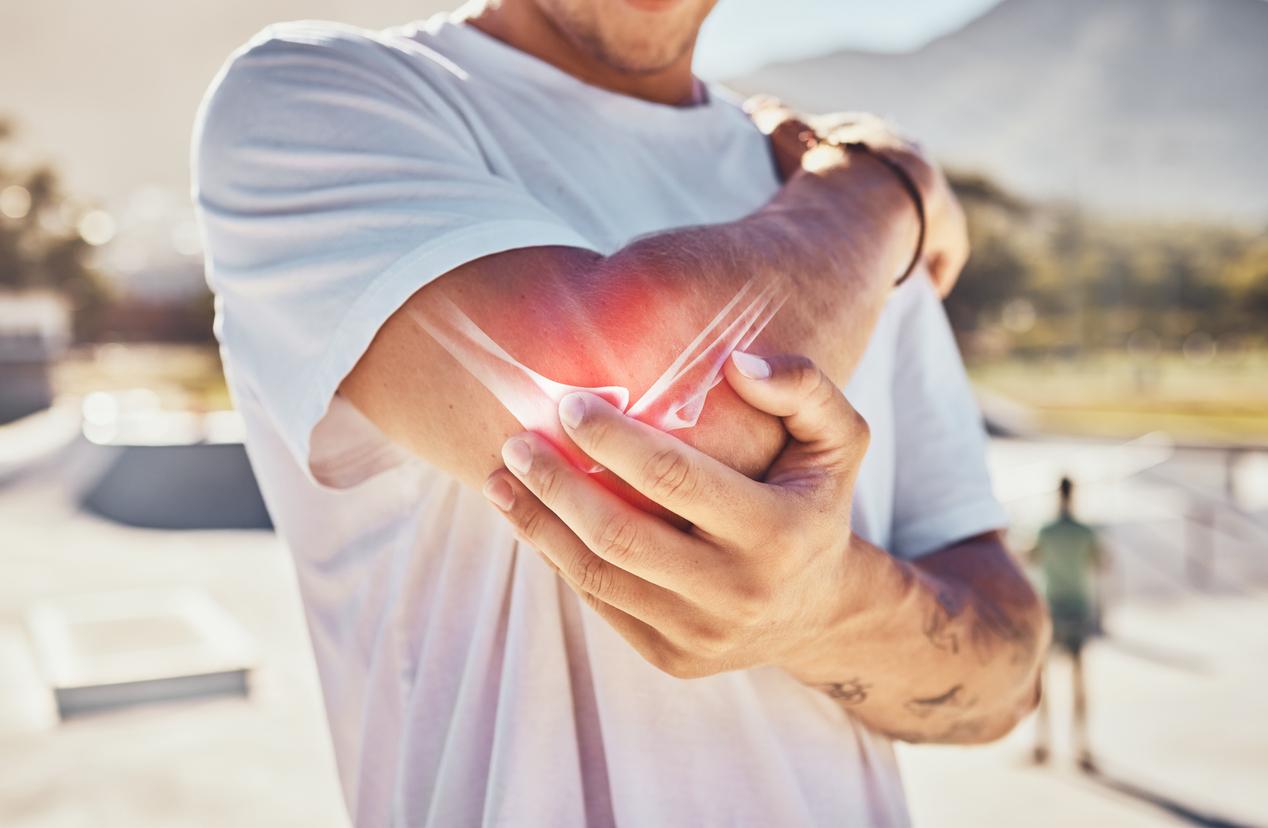
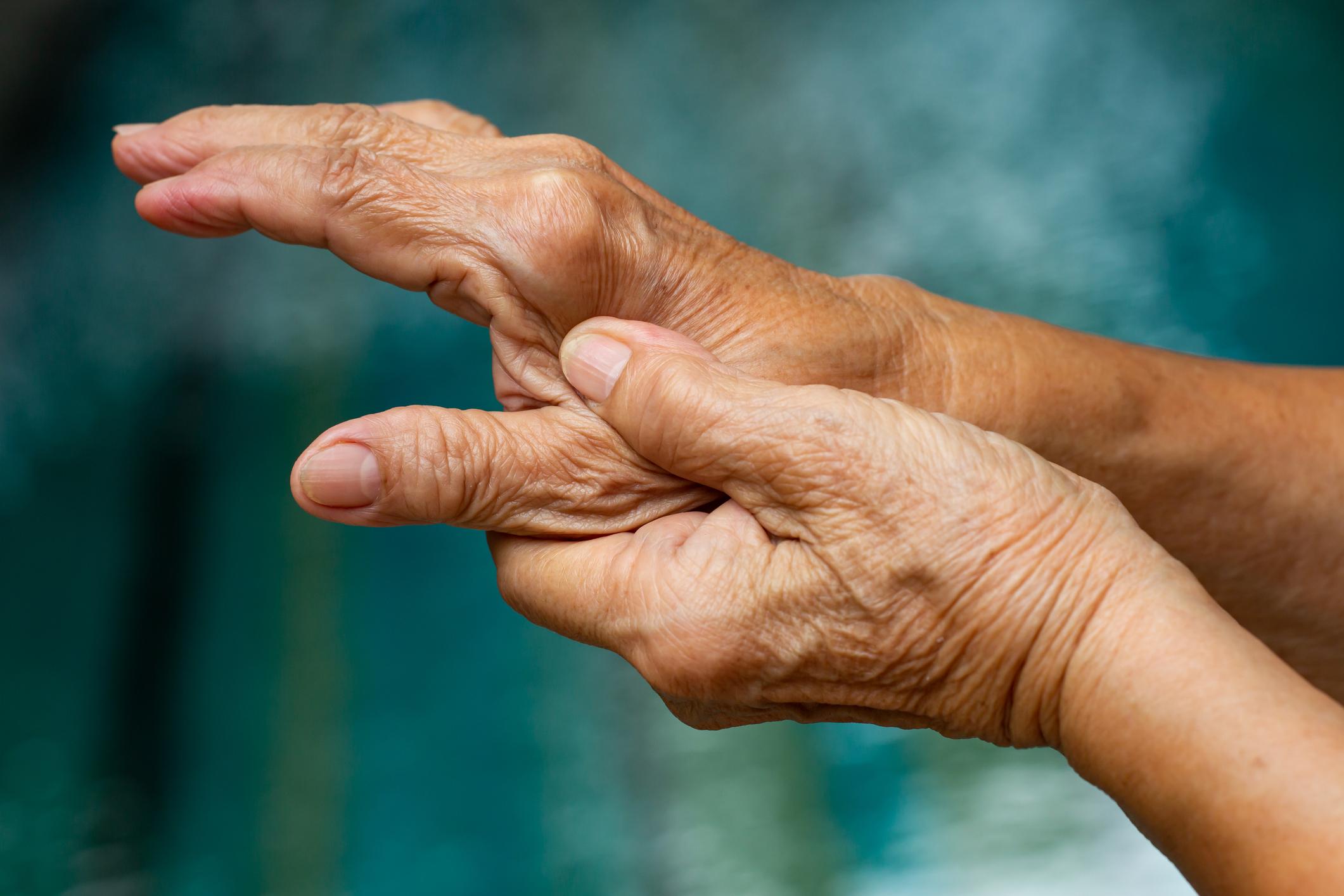
Various studies indicate that in the case of osteoarthritis, patients with knee or hip surgery often have serious complications and persistent pain.
According to a new study, total knee replacement surgery is associated with a higher number of serious adverse events than non-surgical treatment. To reach these conclusions, the researchers assembled a cohort of 100 patients with moderate to severe osteoarthritis of the knee. 10% of these operated patients having received a knee prosthesis were confronted with a complication, such as a bacterial infection in the joint or a phlebitis which could be complicated by a pulmonary embolism.
Another try further concludes that the proportion of people with long-term pain varied from around 7% to 23% after hip replacement surgery and from 10% to 34% after knee replacement surgery. Corollary results indicate that significant pain was also reported in 9% of patients after hip replacement surgery and in approximately 20% of patients after knee replacement surgery.
Combination of healthy eating and regular exercise
Before the operation, remember that it is possible to reduce the symptoms of osteoarthritis simply by adopting a healthy diet and lifestyle. Conducted by the University of Surrey, England, and published in the journal Rheumatology, a study has examined in 68 previous works the link between diet and self-management of osteoarthritis pain. Its conclusive results encourage people suffering from the disease to reduce their calorie intake, exercise regularly and consume essential fatty acids to reduce joint pain.
“It is the combination of a healthy diet and regular exercise that decreases the pain of osteoarthritis and keeps the joints healthy “, explains Ali Mobasheri, professor of musculoskeletal physiology at the University of Surrey. . “Lifestyle should also be taken into account when trying to reduce the pain of osteoarthritis. Patients cannot expect miracles from dietary interventions if they are overweight, drink or smoke a lot. Evidence shows that smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have a negative effect on the body’s energy metabolism and inflammatory markers in the liver that can promote inflammation and disease in the body, “the specialist continues.
Inflammatory flare-ups
A chronic joint disease, osteoarthritis affects cartilage, the tissue that covers the ends of bones in a joint. Some elements are risk factors such as age, being overweight, carrying heavy loads repeatedly, but in some cases the disease is hereditary. At times, the cartilage breaks down rapidly, causing what are known as arthritis attacks, or flare-ups, which are very painful. The rest of the time, many pains, associated with stiffness, poison the lives of people suffering from osteoarthritis, despite the consumption of painkillers.
Affecting nearly 10 million people in France, mostly women over 60, osteoarthritis and its management represent a real public health issue. It is estimated that by 2050, 130 million people will suffer from osteoarthritis, which will represent a considerable burden on the health services of different countries. This prospect is all the more worrying given that currently, no treatment can cure the causes of osteoarthritis.

.