How do omega-3s and vitamin D improve cognitive functions? Via serotonin, answer researchers in a journal.

Taking omega-3s and vitamin D improves cognitive functions, and behavior in certain brain disorders, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder (manic depression), attention disorders with or without hyperactivity ( ADHD) … But how? American researchers answer this question, in a review published in the FASEB Journal.
Serotonin
For them, the missing link is serotonin, a substance that transmits nerve impulses between neurons. This neurotransmitter is already known to play a role in pathologies such as depression. But also autism, ADHD, schizophrenia and bipolarity, pathologies in which patients have low levels of serotonin in their brain.
Serotonin is synthesized in the brain from tryptophan. It is one of the amino acids that go into the composition of proteins. It is also an amino acid said to be essential because it can only be provided through food. And this conversion of tryptophan to serotonin is activated by vitamin D, which is a hormone.
The action of omega-3s
Researchers have also elucidated the mechanisms of action of omega-3s. Thus, a type of omega-3, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), increases the release of serotonin by reducing certain inflammatory processes. Another omega-3, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), makes serotonin receptors more accessible to this neurotransmitter by increasing the fluidity of cell membranes.
“In this review, we explain how serotonin is a critical modulator of executive function, impulse control, the filter of sensory stimuli in the brain, and pro-social behavior,” says Dr. Rhonda Patrick, of the Children’s Hospital Oakland Research Institute. “We link the production and function of serotonin to vitamin D and omega-3s. This suggests a path these important micronutrients can take to help brain function and affect our behaviors, ”he adds.
Deficiencies
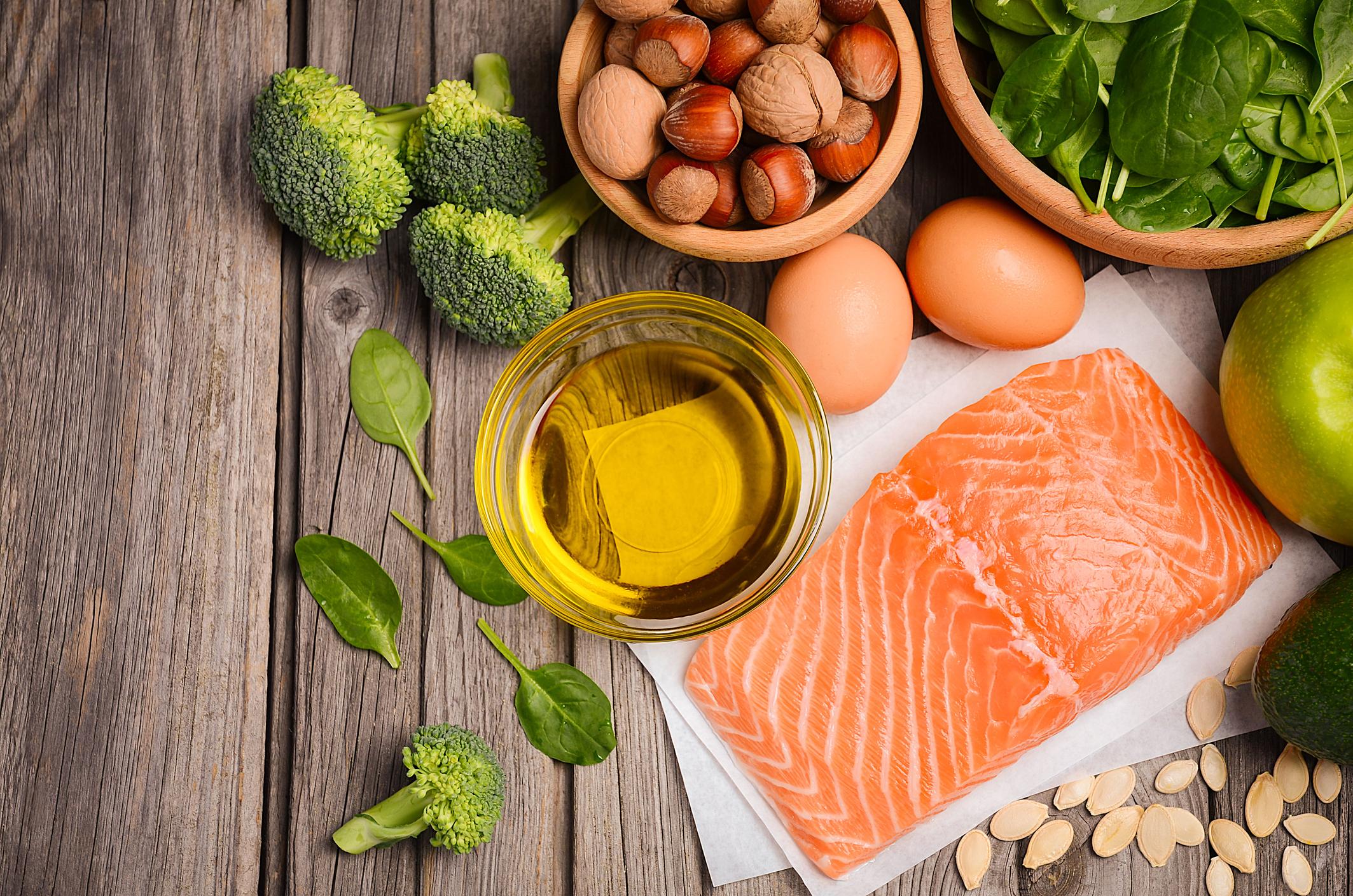
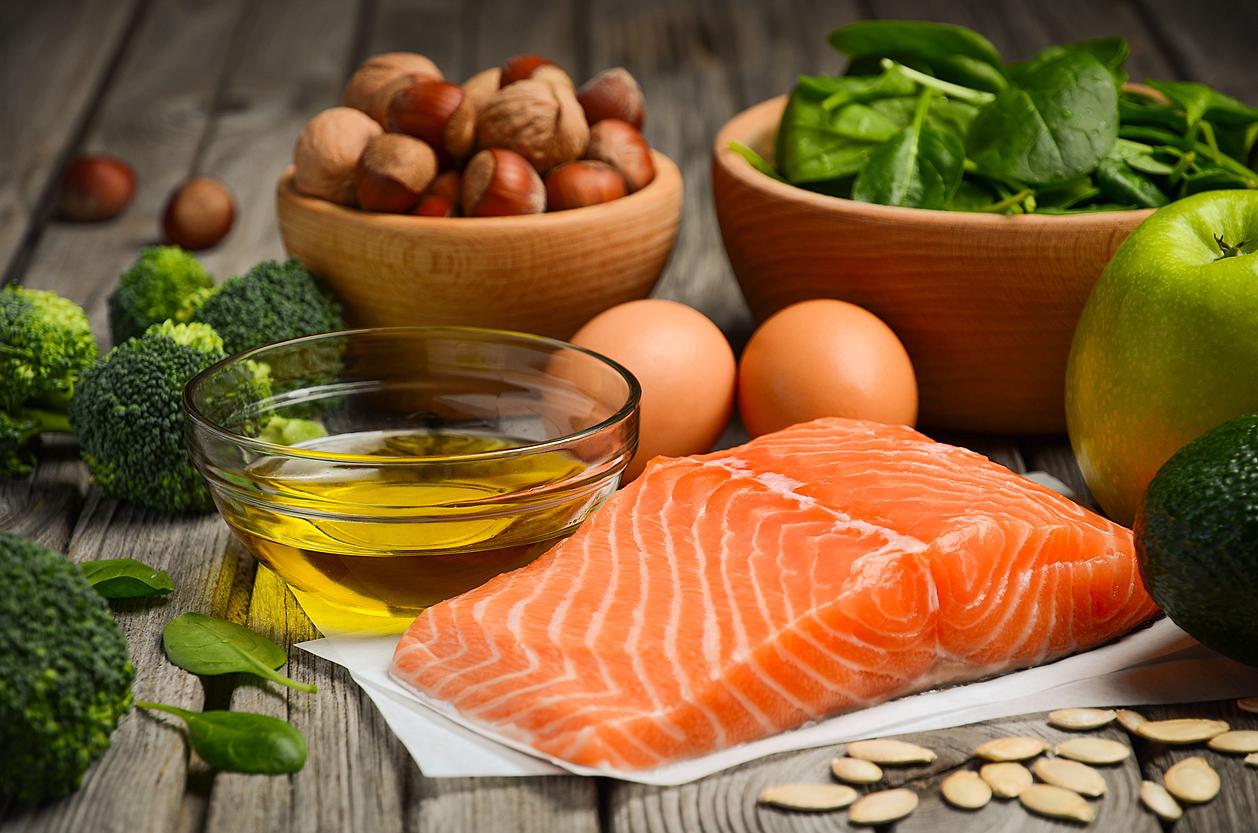
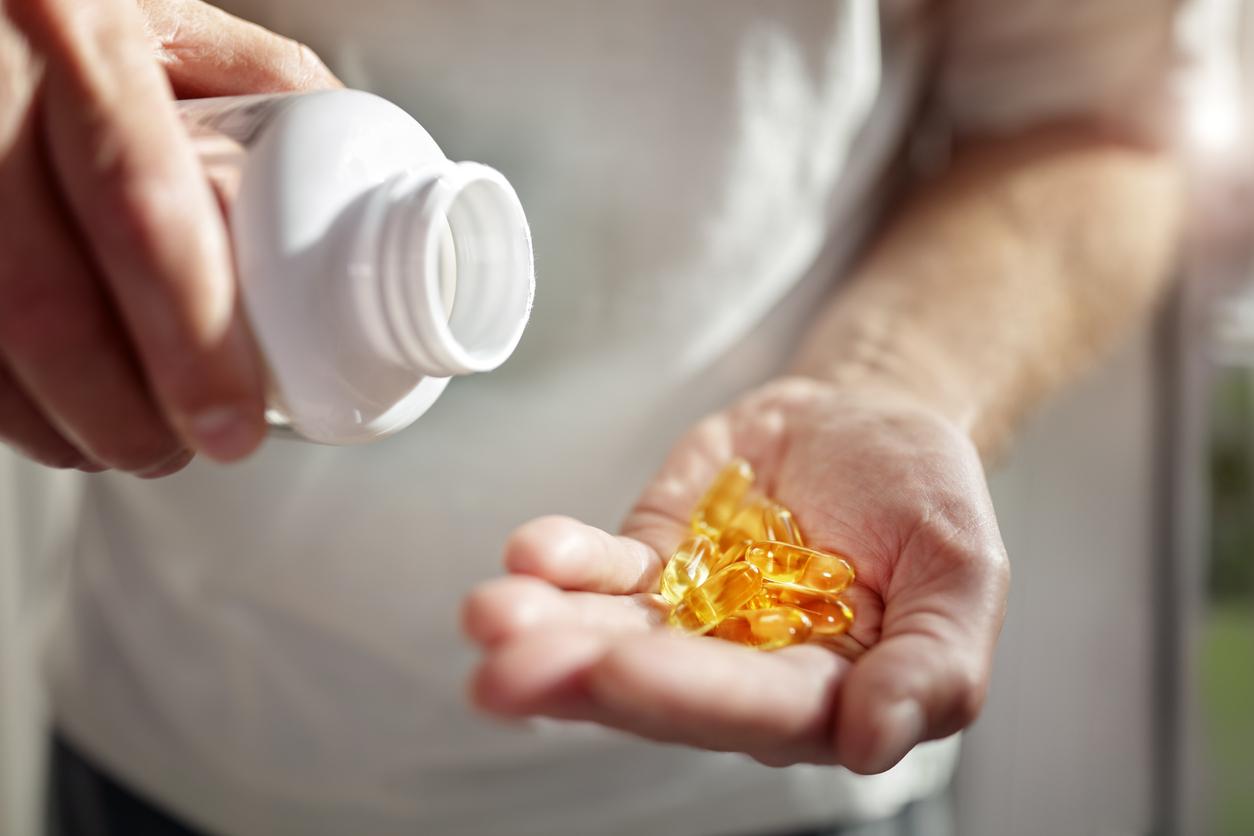
The researcher points out that in the United States, there are deficiencies in vitamin D and omega-3. In France, 80% of adults have vitamin D insufficiency (rate less than 30 nanograms per milliliter), 42.5% a moderate to severe deficit (less than 20 ng / ml) and 4.8% a severe deficit (less than at 10 ng / ml). Exposure to the sun is necessary for the body to produce vitamin D. This production can be supplemented by consuming egg yolks and fatty fish, the latter also being a source of omega-3.
.