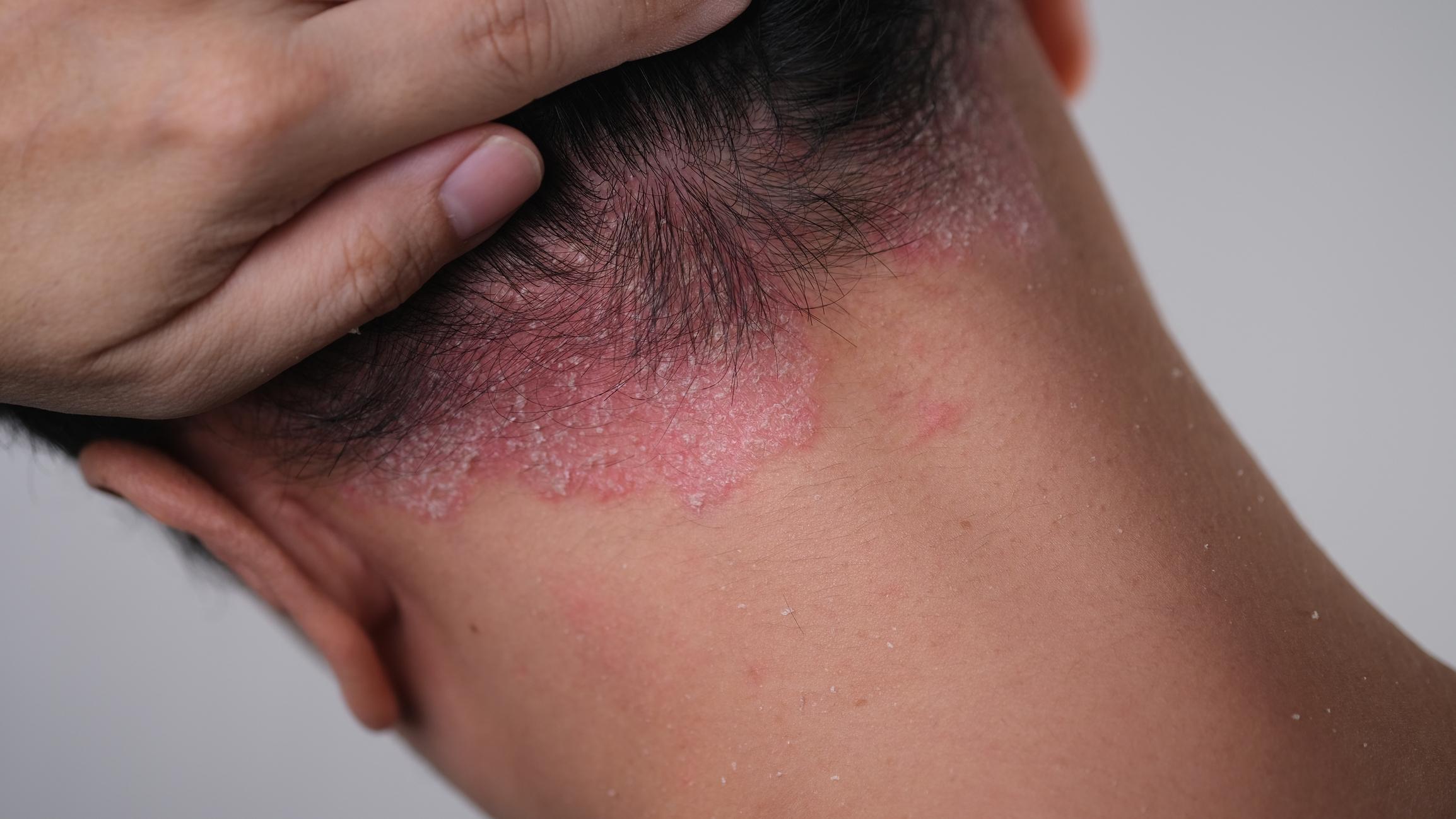
Lupus affects more than 20,000 people in France. This disease is said to be rare but remains relatively frequent.
Unlike the wolf who baptized it, lupus is not endangered in France. Quite the contrary. This rare disease affects several thousand French people. But it remains misdiagnosed, with a major impact on the quality of life. On the occasion of the World Day dedicated to him on May 10, Why actor returns to this pathology in four questions.
What’s this ? Lupus is an autoimmune disease with many faces. The body produces autoantibodies which cause an inflammatory reaction. As a result, the symptoms manifest themselves on several levels. In 80% of cases, patients present with skin damage. The “wolf mask” is the most famous sign.
But in 8 out of 10 cases, patients also suffer from joint symptoms, which are particularly marked during the period of an attack. Lupus is far from stopping there. It also causes kidney or eye damage, thrombosis, hair loss … It is this protean character that gives its name to systemic lupus erythematosus.
Who is affected? The vast majority of patients are female (85%) and adult. It is, most often, between 15 and 45 years that the first symptoms appear. But in 5 to 10% of cases, lupus can appear during childhood. Health Insurance estimates that a total of 20,000 to 40,000 people suffer from this disease.
Patients must wait 2 to 5 years before obtaining a diagnosis adapted to their condition. And in 6 out of 10 cases, they do not have the appropriate treatment.
How do you spot it? The diagnosis of lupus can be made by several health professionals: internist, rheumatologist, ophthalmologist or dermatologist. They rely for this on several examinations, starting with a blood test. It helps identify autoantibodies specific to the disease. The damage must also be localized on imaging.
Can we treat it? There is currently no cure for lupus. On the other hand, several classes of drugs make it possible to control its evolution. Certain so-called “basic” treatments control inflammation – synthetic antimalarials, for example. Others can be used as an adjunct, during inflammatory outbreaks. This is the case with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids.
Multidisciplinary follow-up is strongly recommended. It allows, in fact, to monitor local attacks of lupus. The kidneys and cardiovascular system, in particular, are at high risk in these people.

.