While drug treatments remain essential when suffering from rheumatoid arthritis, an anti-inflammatory diet is increasingly becoming an effective complementary strategy for alleviating symptoms.
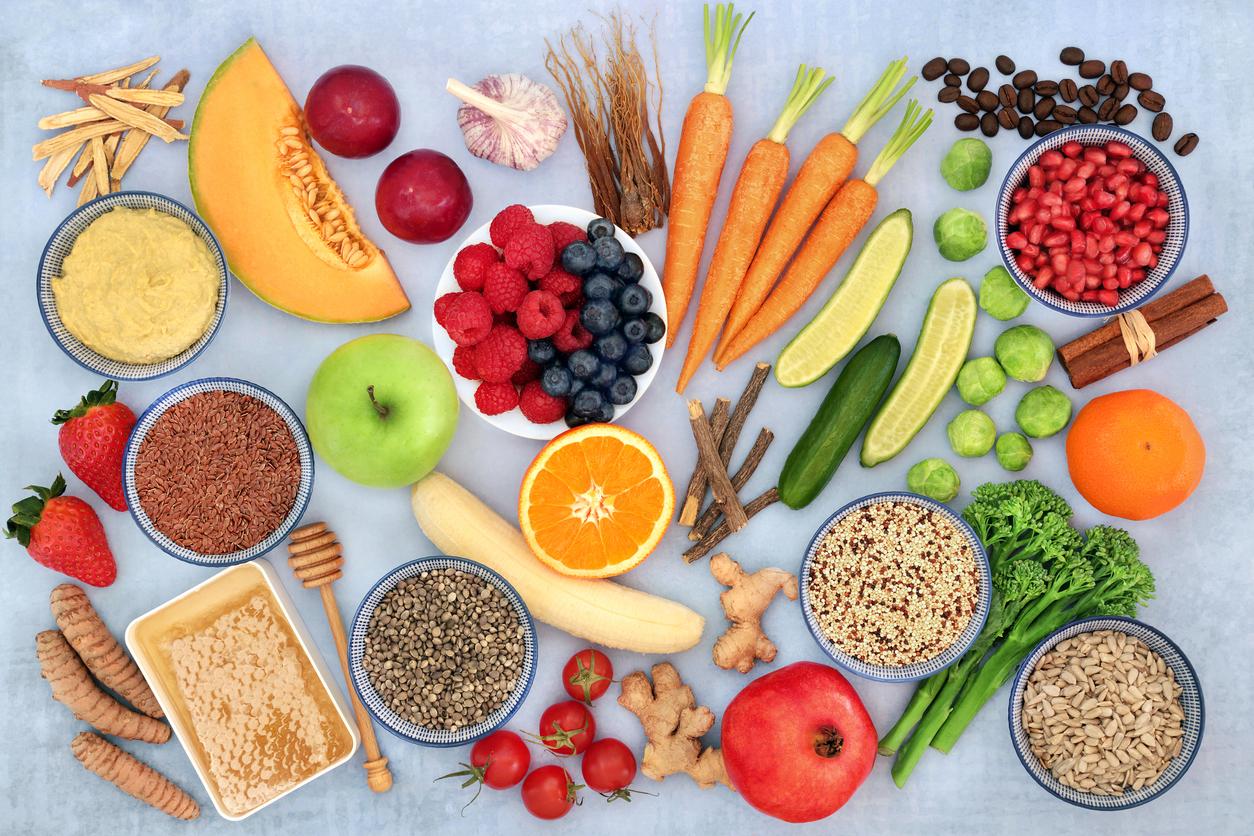

- Since rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory disease, a suitable diet can greatly improve the quality of life of patients.
- By focusing on foods rich in omega-3s, antioxidants and fiber, and limiting inflammatory foods (refined sugars, saturated fats, processed foods), it is possible to reduce joint pain and improve mobility.
- However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for personalized support.
Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by chronic inflammation of the joints. This inflammation causes pain, stiffness, and the progressive destruction of cartilage. Reducing inflammation through diet can help alleviate these symptoms.
Anti-inflammatory diet reduces joint pain and stiffness
Chronic inflammation is at the heart of rheumatoid arthritis, and certain foods can exacerbate this inflammatory response. Conversely, eating a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce inflammation. Recent studies have shown that omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and flaxseed, as well as antioxidants in fruits and vegetables, can have a soothing effect on joint inflammation. Additionally, foods like turmeric and ginger, known for their natural anti-inflammatory properties, may be beneficial additions to the diet of rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Recent research has shown that patients who follow an anti-inflammatory diet report significant reductions in joint pain and stiffness. For example, a Mediterranean diet, rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, fish, and healthy oils like olive oil, has been linked to lower inflammatory markers in the blood. At the same time, avoiding pro-inflammatory foods like refined sugars, saturated fats, and ultra-processed foods is crucial to minimizing inflammatory flare-ups.
Joint-friendly foods
To fight inflammation, favor the following foods:
• Omega-3 : Present in oily fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), flax seeds and nuts, they have powerful anti-inflammatory properties.
• Colorful fruits and vegetables : Rich in antioxidants, they help fight free radicals responsible for inflammation.
• Spices : Turmeric, ginger, cinnamon… these spices have recognized anti-inflammatory properties.
• Legumes : Lentils, chickpeas, beans… They are rich in fiber and vegetable proteins, and promote good intestinal health, linked to inflammation.
• Fermented foods : Yogurts, kefir, sauerkraut… They contain probiotics which contribute to the balance of the intestinal flora, essential for a good immune response.

Foods to limit
• Red meats and whole dairy products : Rich in saturated fatty acids, they can promote inflammation.
• Processed foods : Sodas, snacks, and prepared foods are often high in sugar, salt, and additives, which can worsen inflammation.
• Refined vegetable oils : Sunflower, corn or soybean oil should be avoided as they can promote inflammation.
In conclusion, diet plays an important role in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. By adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, combined with appropriate medical treatment and regular physical activity, it is possible to significantly improve your daily life.