France lacks ambition in its strategy to fight hepatitis B and C, which claims 4,000 victims each year. In a report produced under the aegis of the French Agency for Research on AIDS and Hepatitis (ANRS) and the French Association for the Study of the Liver (AFEF), a group of experts insists on the imperative to increase mobilization against viral hepatitis. A work that requires stepping up vaccination and screening by means of rapid tests.
“It is important that measures allowing a strengthening of prevention, screening and care of infected people are quickly implemented”, argues the report.
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. When the latter is due to a virus, hepatitis is said to be viral. These two hepatitis affect people in a precarious situation more, says Inserm. Only 49% and 56% of people infected with hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus know they are sick. An effort must therefore be made to screen the most vulnerable populations. Starting with injecting drug users who use or share used syringes, vectors of infection. The following are also concerned: migrants from regions such as Africa, homosexual populations and those from certain overseas regions.
Generalize rapid screening
For these populations at greater risk, the use of rapid screening tools such as the TROD (rapid diagnostic orientation test) should be developed, according to the report. They allow results to be obtained in just 30 minutes compared to several days with conventional tests. This “promote[ait] the screening of populations who do not frequent conventional medical structures “.
The report also proposes to extend screening to men aged 18 to 60 and to “pregnant women at the first prenatal consultation”.
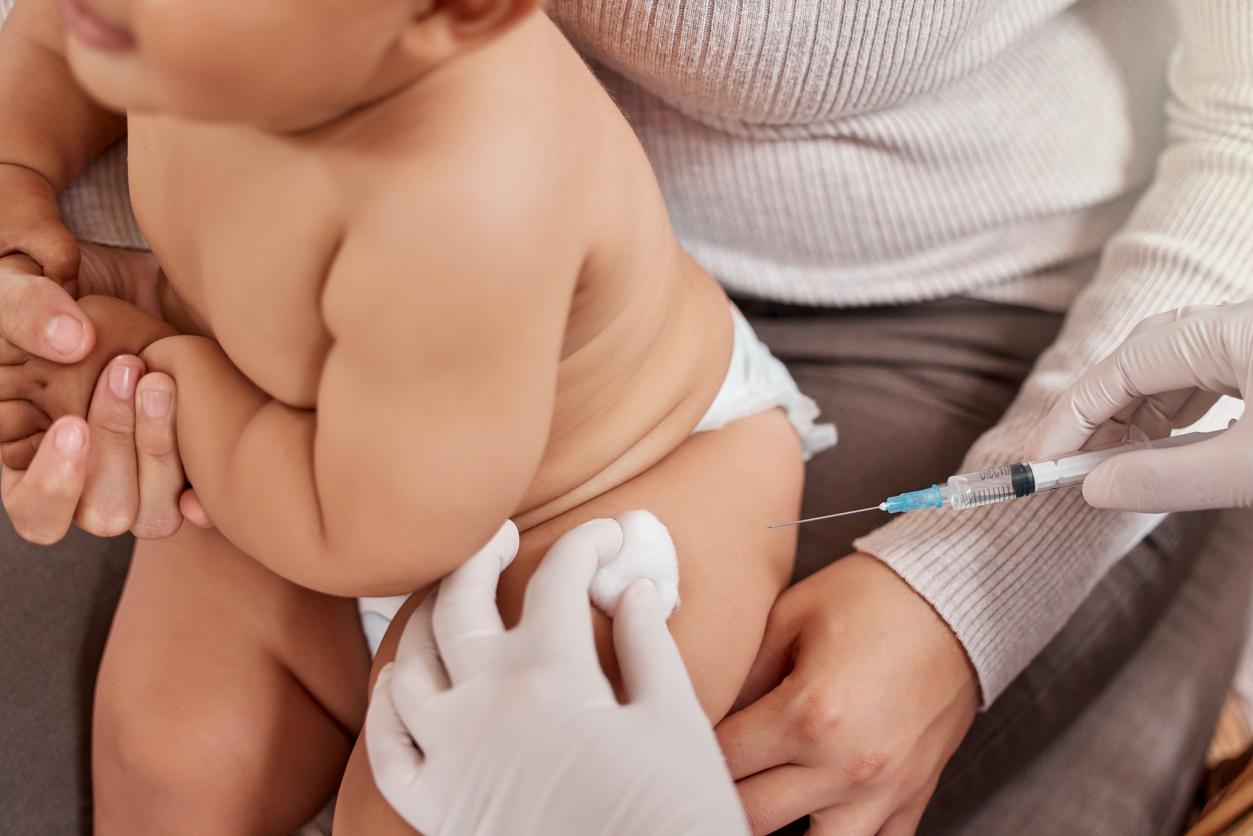
Increase vaccination
Another important area of intervention is hepatitis B vaccination. The vaccination coverage rate must be improved for people at risk (drug users, nursing staff, migrants, etc.)
There is no vaccine against hepatitis C. The challenge is therefore to develop “cost-effectiveness” studies on new treatments against hepatitis. While research has made great strides in recent years in developing more effective drugs with fewer side effects, the costs of these new treatments remain prohibitive.
For hepatitis C, a Sofosbuvir tablet is billed for 1,000 dollars (approximately 729 euros) in the United States, which amounts to 84,000 dollars (approximately 60,000 euros) for 12 weeks of treatment …
Do you find that you are sufficiently informed about hepatitis? Have your say on our forum!