It was long believed that heart problems were the prerogative of men in their sixties who were too good-natured. It is not so. Women are even less and less protected. “The heart of women is more innervated than that of men. It is therefore richer in stress hormone and estrogen receptors.explains Pre Claire Mounier-Vehier, cardiologist and vascular doctor at the University Hospital of Lille. Thus, a hormonal upheaval and stress (acute or chronic) will have more repercussions on their heart. Thinner, female arteries are also more prone to spasms, which can promote the formation of microlesions that go unnoticed for years, but which weaken the heart. In women, atrial fibrillation, the most common heart rhythm disorder, also leads to a 20 to 30% higher risk of cerebrovascular accident (CVA) than in men, and its consequences are also generally greater. severe.
In video: 5 foods that your heart does not like
A greater risk of heart failure
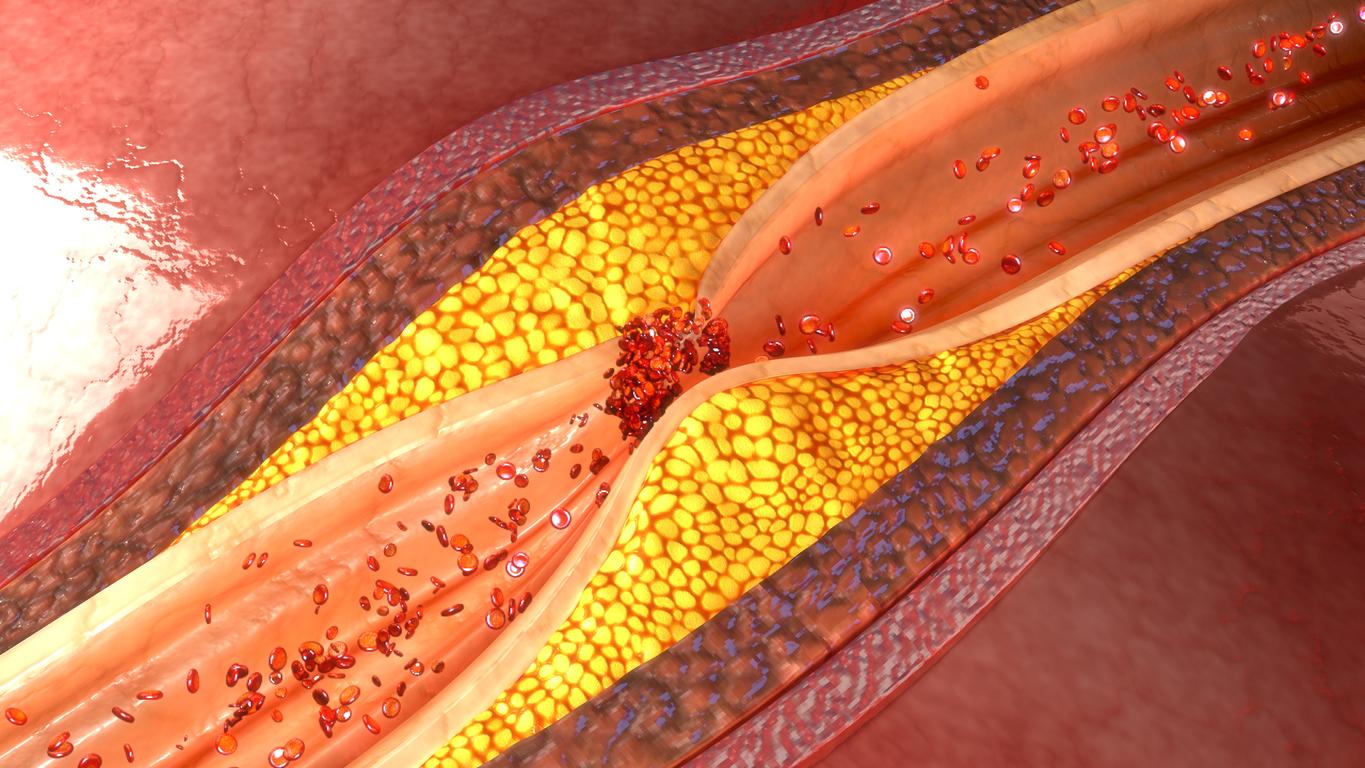
Schematically, the process is always the same: an arteriole or an artery is partly obstructed by a clot (thrombus) or an atheroma plaque (atherosclerosis), blood circulation is hindered, the heart is less well vascularized, it suffers . If the heart can no longer do its pumping job properly to eject blood to the rest of the body, we speak of heart failure. It can settle in quietly and manifest itself after a few years by fatigue, palpitations and shortness of breath during efforts at first, then gradually in daily life and even at rest. Heart failure can be the cause of a heart attack, but it is also its main sequel.
A progression of the infarction in women
If a zone of the heart ceases to be irrigated by one of the coronary arteries which supply it with oxygen, it is the infarction, brutal and sudden, which leads to necrosis (death) of part of the heart muscle. It is then necessary to immediately telephone 15 or 112, for support by the emergency services as soon as possible and for the interventional cardiologists to repair/unclog the coronary artery involved in the infarction. In the vast majority of cases, in order to keep the artery (or arteries) dilated and to revascularize it, one or more stents, tiny tubes that will keep the artery open to restore blood circulation, will be implanted. Sometimes, a bypass will be privileged: it is then a question of implanting a vein or an artery (taken from the patient) between the aorta and a coronary artery to restore blood flow by “bypassing” the narrowing.
More and more strokes in people under 50
When the person suffers from heart rhythm disorders, a clot can form in the heart chambers and migrate into a cerebral artery, this is called an ischemic stroke. This accident, which affects more and more women under 50, causes within minutes the death of millions of neurons and the rapid loss of certain faculties such as speech and mobility. Again, you have to react as quickly as possible by calling 15 or 112, because every minute counts. At the hospital, an MRI or CT scan will confirm the diagnosis. If there is still brain tissue to be saved, the patient may benefit from a mechanical thrombectomy after injection of a thrombolytic drug into a vein (intravenous thrombolysis). “Under X-ray control, I will use the femoral vein to introduce several nested catheters, mount them in the aorta, then in the carotid and so on until the thrombus”,explains Dr. Fabrice Bing, interventional neuroradiologist. In contact with the clot, we can do a simple aspiration or even deploy a stent in the artery: this is treatment by thrombectomy. Like a fish hook, this stent will hook the thrombus and allow it to come down and then come out. “At the same time as the stent is removed, a suction pump is connected to the catheter to ensure that the entire thrombus comes back.”
Our Experts:
- Pre Claire Mounier-Vehier, cardiologist and vascular doctor at Lille University Hospital
- Dr Fabrice Bing, interventional neuroradiologist
Read also :
- Hypertension: Symptoms and Treatments
- Menopause: the 15 good gestures to take care of your heart
- 9 heart-healthy foods
- What sport to practice to maintain your heart?