Celiac disease often complicates digestion, leading to symptoms like constipation. Adopting appropriate eating habits and daily practices can help you relieve these discomforts. Here are the latest recommendations to better manage this condition on a daily basis.

- Constipation in celiac patients can be effectively managed by a gluten-free diet rich in fiber, good hydration and regular physical activity.
- Fiber supplements and probiotics may also provide additional relief.
- Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice tailored to your condition.
Celiac disease, an autoimmune condition triggered by the ingestion of gluten, affects approximately 1% of the world’s population. While gluten intolerance is usually associated with symptoms like diarrhea and abdominal pain, constipation is also a common problem among sufferers. This constipation can be a source of discomfort and significantly affect quality of life. This article explores practical strategies and recent recommendations for effectively managing constipation related to celiac disease.
Celiac disease causes an abnormal immune response when gluten is consumed, damaging the lining of the small intestine. This disrupts nutrient absorption and can lead to various digestive symptoms, including constipation. A 2022 study published in the Journal of Gastroenterology found that nearly 20% of celiac patients report frequent episodes of constipation, often linked to nutritional deficiencies and chronic intestinal inflammation.
Adopt a gluten-free diet rich in fiber
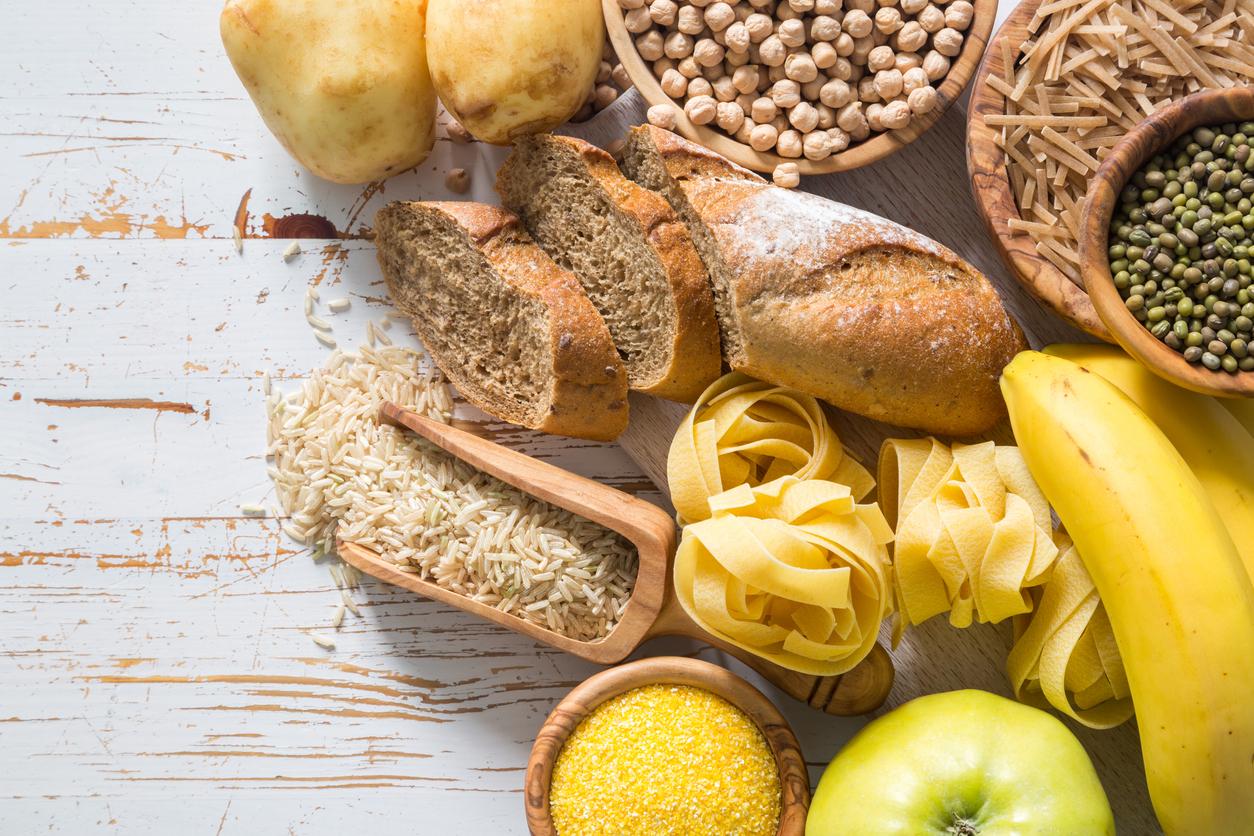
A gluten-free diet is essential for anyone with celiac disease. However, many gluten-free products lack fiber, which can make constipation worse. To remedy this, include foods that are naturally gluten-free and high in fiber into your diet. Fruits, vegetables, legumes, and gluten-free whole grains like quinoa and buckwheat are excellent sources of fiber. Fiber increases the volume of stools and promotes their passage through the intestinal tract.
Adequate hydration
Water plays a crucial role in digestion. Insufficient hydration can make stools hard and difficult to pass. It is recommended to drink at least 1.5 to 2 liters of water per day. In addition to water, herbal teas and broths can also help maintain proper hydration. A 2023 study in Nutrition Reviews confirmed that increasing fluid intake significantly improves constipation symptoms in patients with celiac disease.
Regular physical activity
Physical exercise stimulates intestinal transit. Activities like walking, jogging, yoga and swimming can help reduce constipation. Try to devote at least 30 minutes a day to moderate physical activity. Exercise also improves muscle tone in the abdomen, which can make it easier to pass stools.
Supplements and probiotics
For some people, dietary adjustments and exercise aren’t always enough. Fiber supplements, such as psyllium, may be beneficial. Additionally, probiotics can help balance intestinal flora and improve digestion. Specific strains of probiotic bacteria, such as Bifidobacterium lactis, have shown positive effects on constipation in recent studies. It is important to speak with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement.
By adopting these strategies, people with celiac disease can improve their intestinal comfort and quality of life. Proactive management of constipation is essential to prevent complications and live more peacefully with celiac disease.
Current innovations and research
Research on celiac disease and the management of its symptoms is constantly evolving. Researchers are exploring new therapies, such as specific digestive enzymes that break down gluten, and personalized nutritional approaches based on the gut microbiome. These advances could offer promising new solutions for people suffering from constipation due to celiac disease.