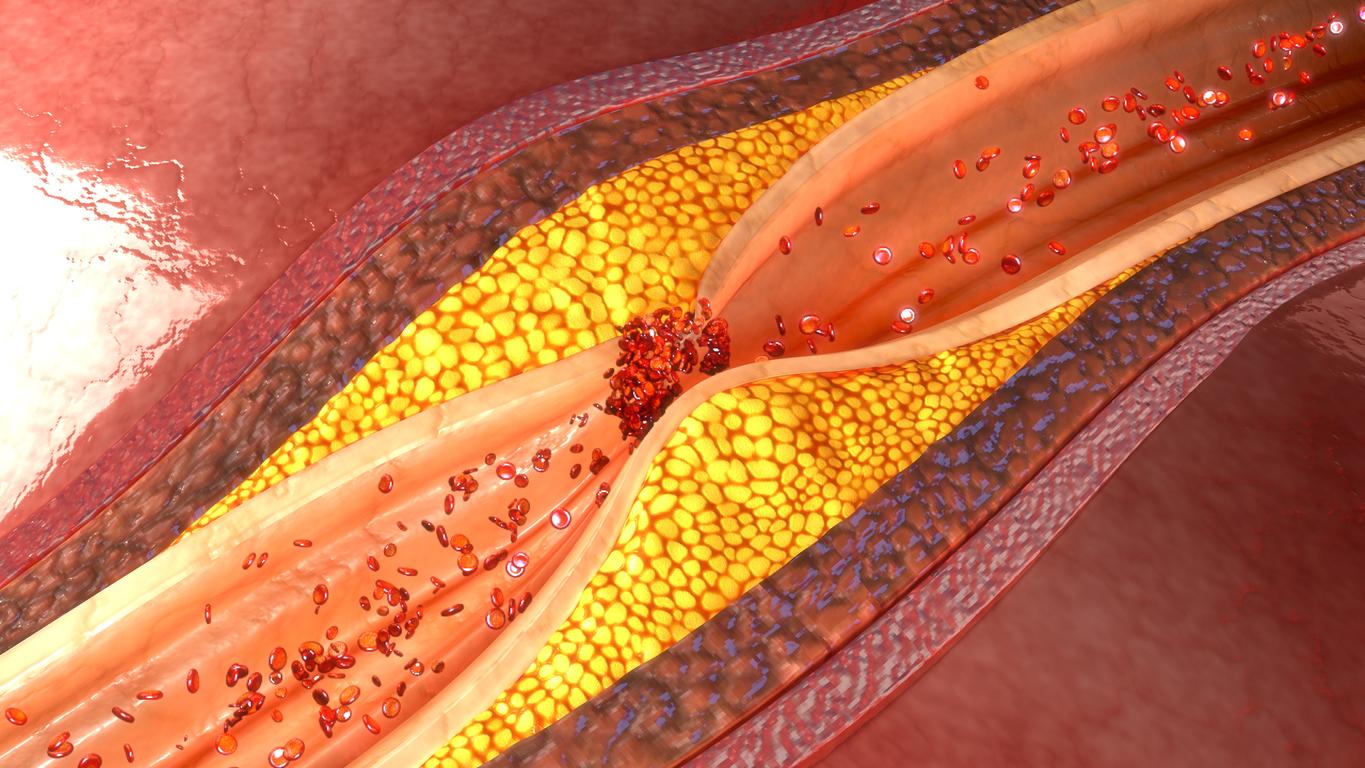
To reduce the risk of cardiovascular illnesses, it would be essential not to lack vitamin D. The minimum content to limit heart problems would be 15 nanograms per milliliter of blood.
Researchers at the Intermountain Heart Institute in Salt Lake City (Utah) followed 230,000 patients for 3 years, focusing particularly on serious cardiovascular accidents (heart attacks, coronary heart disease, kidney failure, etc.) and premature death.
The conclusions of this new study revealed that there is a specific level of vitamin D at which the risk of cardiovascular events increases markedly.
This is because people with a vitamin D content of less than 15 nanograms per milliliter of blood have the highest cardiovascular risk. They had a 35% increased risk compared to those with higher vitamin D levels.
“Although vitamin D levels above 30 ng / ml have long been considered normal, more recent research indicates that levels above 15 ng / ml are sufficient,” says Dr. Brent Muhlestein, co-director of research cardiovascular at the Intermountain Heart Institute in Salt Lake City, Utah.
If the findings of this study are encouraging, researchers will conduct a clinical trial to determine if vitamin D supplements can help them reduce their cardiovascular risk in the long term.
Fill up on vitamin D
This new study also reminds us that vitamin D would prevent heart disease. However, a recent study by the National Institute of Health and Medical Research (Inserm) reveals that more than half of French people (58%) lack vitamin D, with a concentration of less than 20 nanograms per ml of blood and 15% are even deficient (less than 10ng / ml). In order not to be insufficient, you should at least have a blood concentration of vitamin D between 30 and 45 ng / ml of blood.
Vitamin D is found in oily fish, egg yolks and organ meats, but it is mainly produced by our body when our skin is exposed to the sun. “An exposure to the sun, the practice of a physical activity and the maintenance of a stable and” normal “weight would make it possible to fill up with this nutrient essential for health”, according to the researchers of Inserm. But, be careful, vitamin D supplementation should absolutely not be done without medical advice.
Read also:
Vitamin D: what do we risk if we are deficient?
Multiple sclerosis: vitamin D deficiency doubles the risk
Vitamin D: 5 signs that you may be lacking