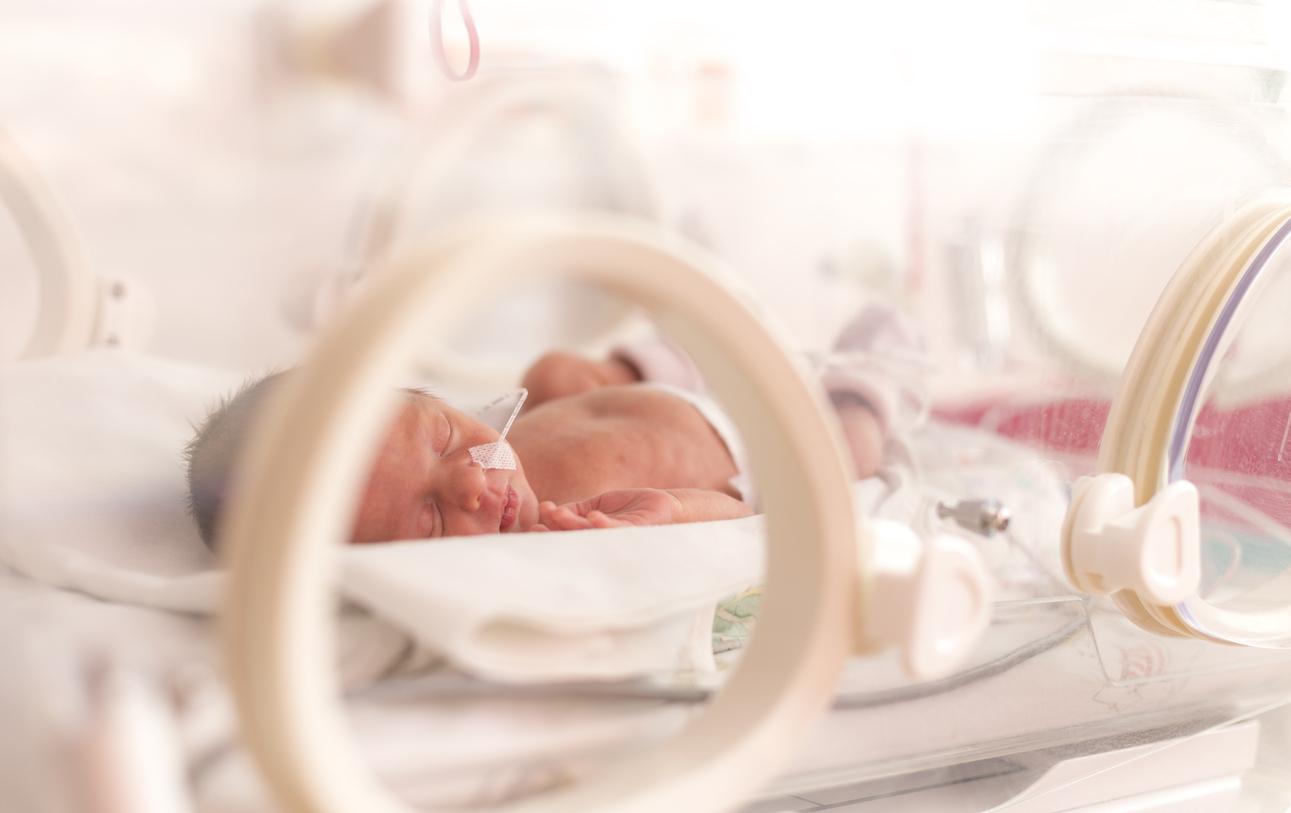
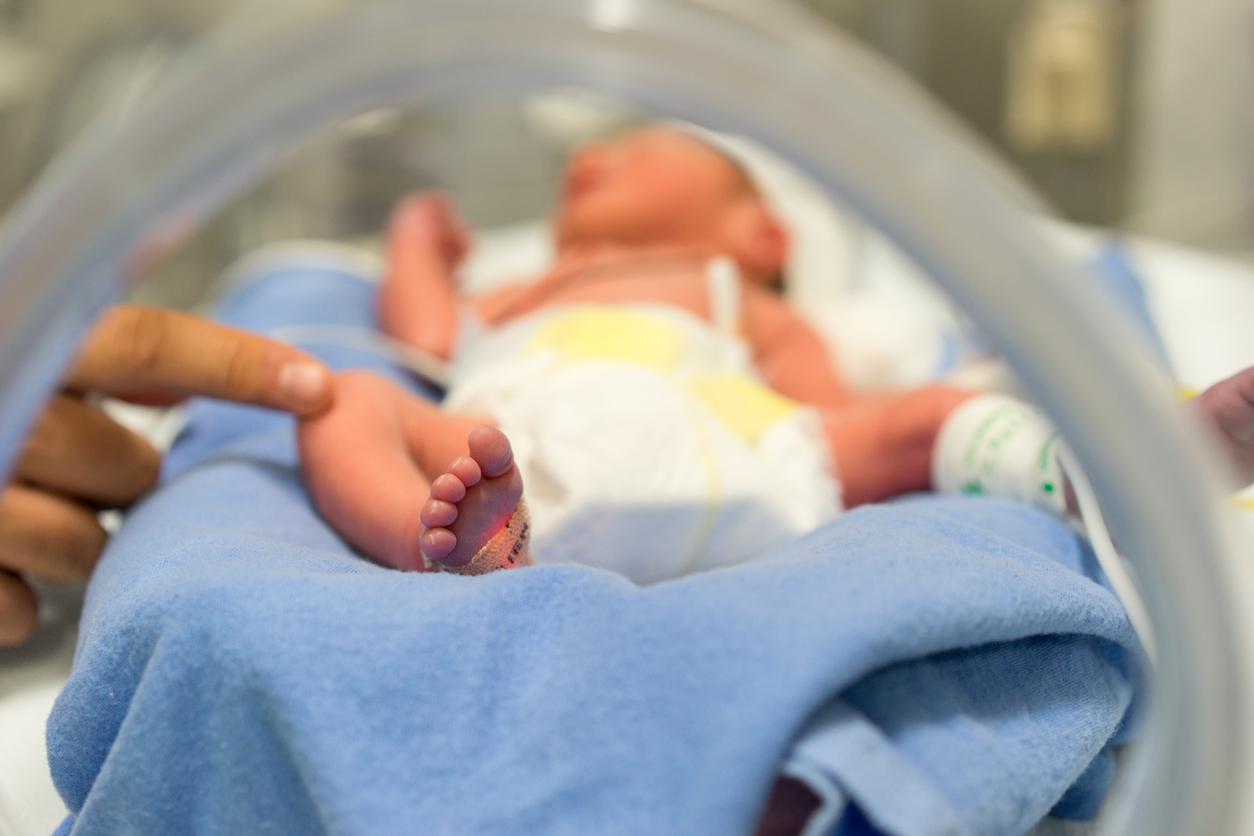
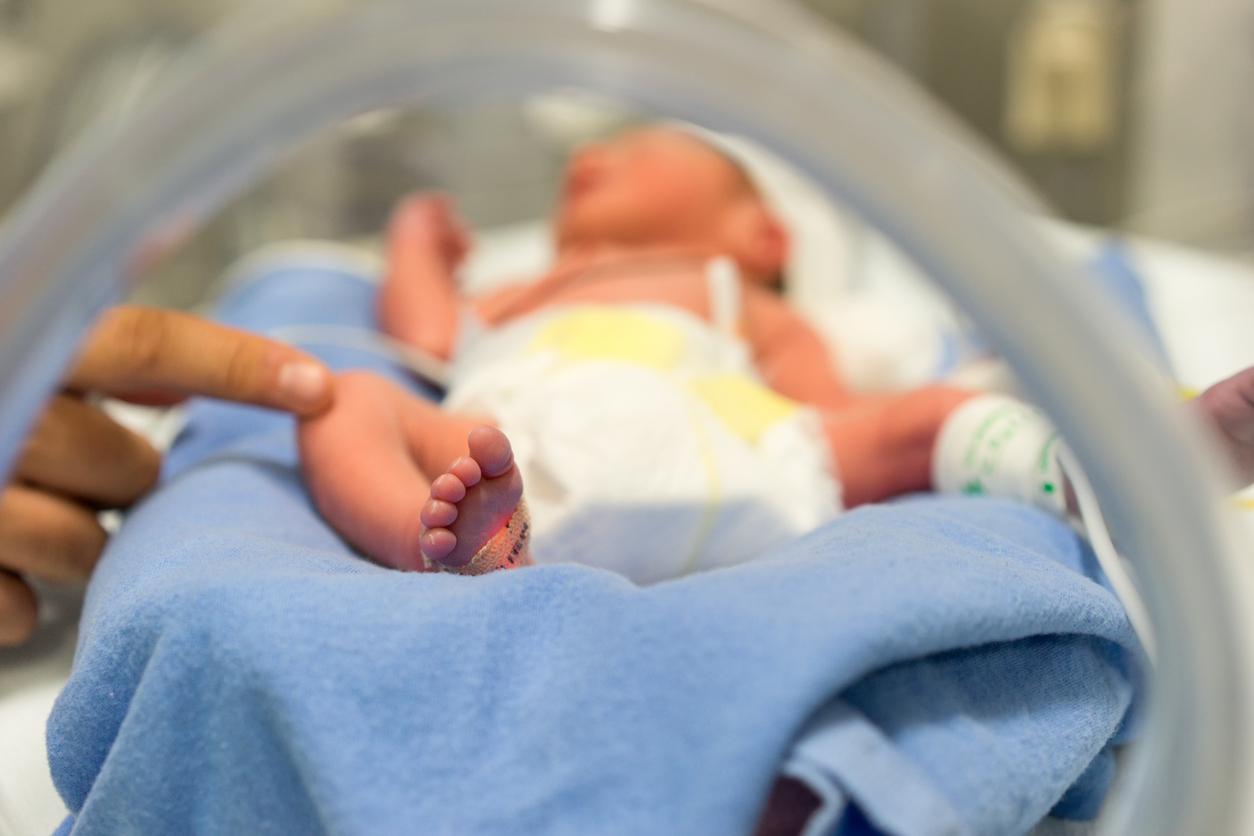
Titouan is very premature. Born almost 4 months too early, he suffered a cerebral hemorrhage and requires heavy assistance. Her parents requested that the care be stopped.
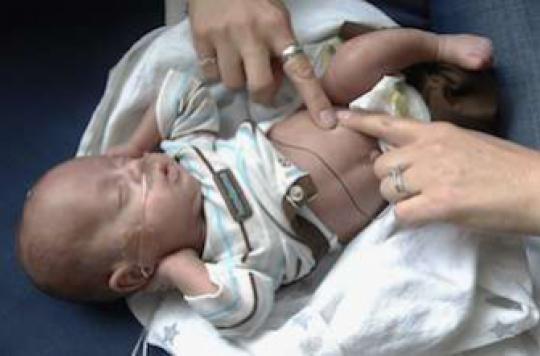
He weighs just 900 grams and had a brain hemorrhage soon after birth. Little Titouan, born last August 31 at the Saintes hospital (Charente-Maritime), is very premature. Since his birth, he has been on artificial respirator and infusion and will certainly suffer from the after-effects of his bleeding. Titouan’s mother, Mélanie, has asked doctors to stop treatment, which she describes as “therapeutic relentlessness. But the doubt remains on the importance of the after-effects which the infant will undergo.
What is extreme prematurity?
A very premature baby, like little Titouan, is an infant born well before the term of pregnancy, between 22 and 32 weeks of gestation. In France, 10,000 births correspond to this definition each year, ie one in five premature babies. These events are less and less rare: in 2003, the National Institute of Health and Medical Research (Inserm) observed an increase in the rate of very prematurity, which stands at 10-18%.
What are its causes ?
Premature birth occurs spontaneously in 60% of cases. This is what happened when Titouan was born. Most often, it starts around the fifth or sixth month of pregnancy, sometimes due to an infectious environment or a premature rupture of the water bag. Several factors promote premature labor. They can be due to the fetus (multiple pregnancy, malformations, growth retardation), to the mother (infection, diabetes, etc.), but also to the placenta. The lifestyle, especially smoking, or the age of the mother also promote early onset of labor.
In 40% of cases, doctors induce premature labor when the vital prognosis of the mother or the child is threatened.
What impact on the newborn?
When birth occurs prematurely, the fetus is not fully developed. In very premature babies, it is even more true: the risk of sequelae is four times greater than in children born at term. Most often, their lungs are still immature, and infants need respiratory support. Very premature babies may also present with immaturity of digestive function, cardio-respiratory rhythm, liver, kidneys and central nervous system.
In France, of the 10,000 very premature babies born each year, 800 to 1,000 have a motor impairment. Neurological sequelae are also frequent: 2% of children born before term suffer from visual impairment, 1% from hearing disorders. At 5 years old, 12% of them are also intellectually retarded.
It is precisely these risks of sequelae that motivate Titouan’s parents to demand that the treatment be stopped. The caregivers, on the other hand, want to give the child a chance and have followed the procedure. To resolve the situation, the Saintes hospital appealed to the ethics committee of the Clamart hospital (Hauts-de-Seine), whose decision should be known today.
.