Faced with the COVID-19 pandemic, containment measures were the first to be adopted by the majority of countries. Yet a study finds that the strategy of testing and self-isolating the sick may be more effective in combating emerging epidemics.

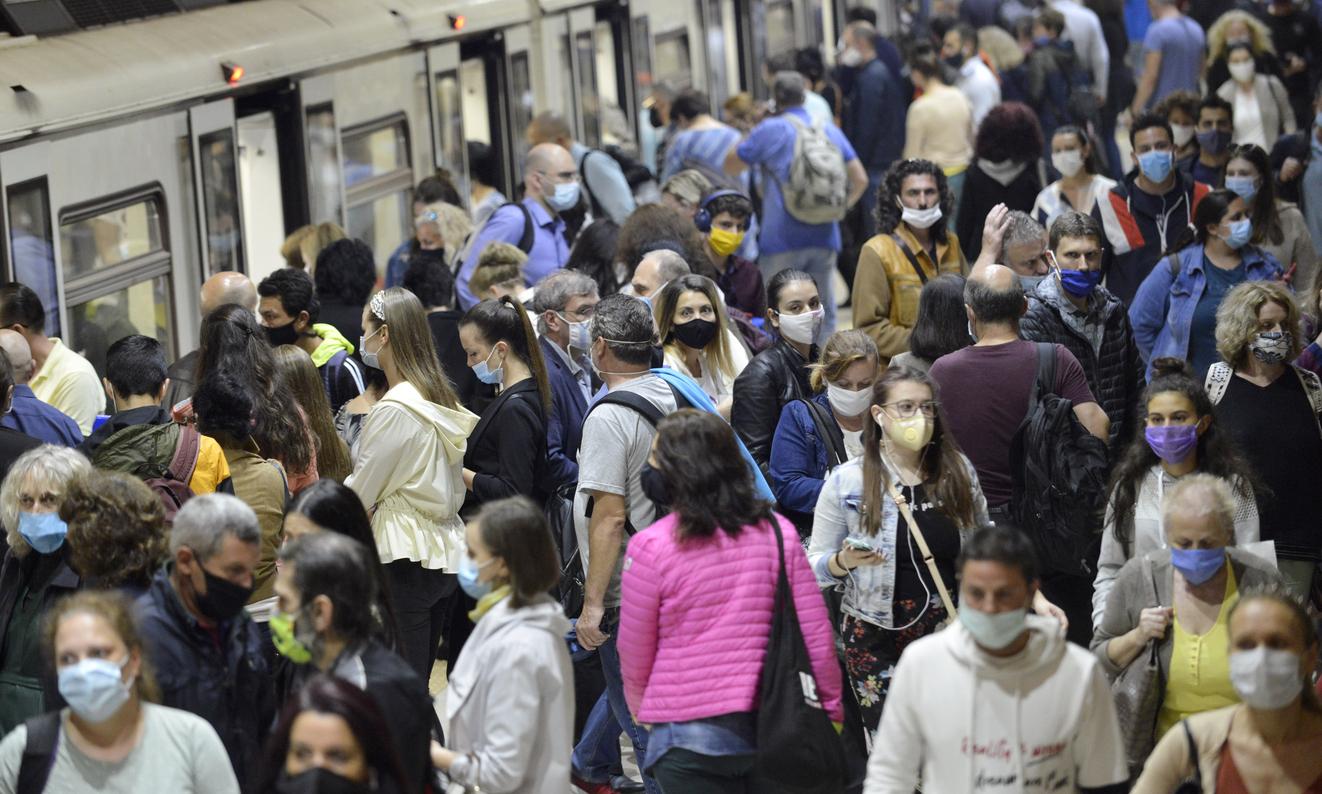
- In an attempt to control the Covid-19 epidemic, most countries have chosen to confine populations.
- This strategy is challenged by a study showing the benefits of measures based on testing and isolating infected people.
- These testing and self-isolation measures appear more effective in controlling a pandemic.
During the Covid-19 epidemic, most countries, including France, chose to confine populations by stopping part of economic activity, favoring teleworking and closing schools. However, According to a study published in Scientific Reports by researchers at the University of Wyominga random testing strategy would outperform such a physical distancing strategy in mitigating the effects of a pandemic.
The harmful effects of containment measures
According to the researchers, the containment measures had a negative impact on the economy, which resulted in a decrease in production and consumption and led to a reduction in employment, loss of income and various effects. negative effects on physical and mental health due to the reduction of social interactions.
In addition, containment measures have caused delays in medical care unrelated to COVID-19. These economic and health impacts have been greater in countries where containment measures have been the strictest.
The Benefits of the Test and Isolate Strategy
The strategy of testing and self-isolating patients who have tested positive helps reduce the spread of the virus by quickly identifying infected people and isolating them to prevent them from spreading the disease. This strategy also makes it possible to reduce the economic and social impact of containment measures, while guaranteeing a better health response.
Indeed, people who test positive are quickly placed in quarantine to prevent them from infecting other people. People who have been in contact with the sick can also be tested to prevent them from spreading the virus in turn. This strategy thus makes it possible to limit the spread of the virus in a more targeted and less costly way than general containment measures.
An epidemiological and economic model to compare the different strategies
To reach these conclusions, the researchers used epidemiological and economic data to measure the impacts of different public health policies. In particular, they modeled the spread of the epidemic in a simulated population, as well as the economic effects of the containment measures and the test and self-isolation strategy.
The results show that containment measures generate higher economic costs than the test and self-isolation strategy. Targeted testing and self-isolation measures, on the other hand, are more effective in containing the epidemic and have only a limited economic impact.