perspire
It is normal to sweat a lot in heat, sports, crowds or nervousness. Yet many people find it annoying. They are afraid of smelling bad or having a wet T-shirt all day long.
In addition, there is a group of people who sweat more than others. Read here what you can do to reduce sweating or prevent perspiration.
lose moisture
By perspiring, the body loses moisture through millions of sweat glands. This moisture ends up on the skin and there it evaporates. In this way, the body ensures an ideal body temperature during heat or great exertion.
Even when it is cold, the skin has a barometer function; then the pores close, keeping the warm ‘inside’. Perspiration and perspiration are therefore just part of it.
Cause
Why one sweats more than the other is not always clear. Various causes are: predisposition, great physical exertion, stress, anxiety, poor condition, fever (for example with the flu), an overactive thyroid gland, a low blood sugar level, the menopause or an abnormality of the nerves involved in sweat regulation.
Good hygiene
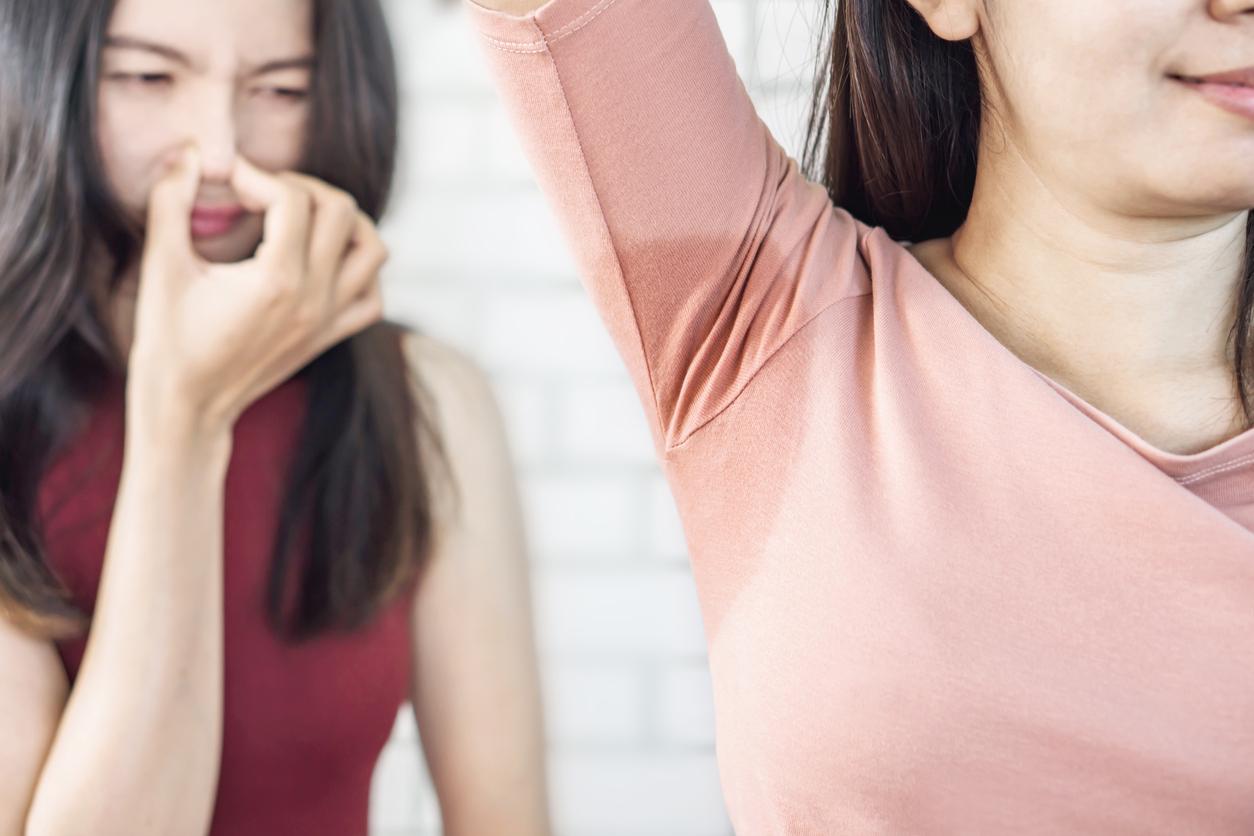
Perspiration is naturally odorless, but can become unpleasant if it comes into contact with bacteria, such as those found on the skin or in clothing. That is why good hygiene is of great importance if you want to prevent perspiration odors.
If you wash yourself daily and wear clean clothes, there is nothing to worry about. Moreover, by shaving armpit hair, bacteria cannot settle in the hair, so that less odor is possible.
Deodorant
The vast majority of deodorants have little or no effect on the production of sweat. So people continue to produce sweat, only those substances influence the smell. A deodorant does not last all day. There are some who continue to work for more than fourteen hours. Long enough to feel ‘armpit fresh’ from early in the morning until late at night.
antiperspirant
Products with zinc paste or aluminum chloride do ensure that less sweat is produced. These products are called antiperspirants. The ingredients in antiperspirants constrict the sweat glands, which slows down the production of sweat.
Antiperspirant Tips
-
Do you suffer from perspiration odors in a blouse or shirt? Just ‘spraying’ with deodorant is pointless if your clothing is already soiled. Only on clean skin has a deodorant effect.
-
Depilate your armpits if you want to be armpit fresh. Armpit hair is a hotbed of and for bacteria. On clean, smooth skin, these – and therefore also perspiration odors – have less chance.
-
Use a deodorant without alcohol after hair removal. Otherwise your skin is on fire.
-
A roller lasts longer than a spray. But you can possibly share a spray with your partner.
Hyperhidrosis
Sweating is one of the main ways the body loses heat. However, people with hyperhidrosis sweat much more than is necessary to keep their body temperature constant. Continuous sweating, especially of the armpits, palms or soles, is the result. The symptoms start at a teenage age and often last for decades.
In some people, hyperhidrosis is present from birth. Sometimes sweating is exacerbated by physical exertion, mental concentration, nervousness or a warm temperature. But even without these stimuli, there is often a constant annoying sweat production. Hyperhidrosis is when more than 100 grams of fluid is produced in one armpit over a five-minute period.
It is estimated that one percent of the population has hyperhidrosis. There are different treatments; from very simple to very heavy, with surgical interventions. Which treatment one follows depends on where the hyperhidrosis has developed and how big the problem is. It is therefore best to consult a dermatologist in case of hyperhidrosis.
Therapy
From a medical point of view, there are no objections to trying to prevent or reduce sweating. There are several ways to treat excessive sweating:
-
Iontophoresis is a treatment that uses a water bath to pass a light electrical current through the skin’s surface. It’s not entirely clear how and why iontophoresis works, but it’s thought that the electrical current and minerals in the water create a microscopic thickening of the skin’s outer layer, reducing the secretion of sweat to the surface.
Iontophoresis is mainly used for excessive sweating of hands and feet and when used properly it can sometimes lead to good treatment results. The treatment is repeated every day for five to ten days, until sweat production is reduced to an acceptable level. Thereafter, a maintenance treatment schedule should be maintained ranging from once a week to once every four weeks.
-
Botulinum toxin – or Botox for short – treatments ensure that sweating can be stopped for a longer period of time. By injecting a small amount of Botox, the signals from the sweat nerves are stopped. The effect lasts for a few months and then has to be repeated again.
Research has shown that treating armpits, hands, feet and face with Botox is safe and effective. In a clinical study of 322 patients with severe forearm hyperhidrosis, 81 percent of patients experienced a decrease in sweat production of more than 50 percent. Half of the patients found a decrease in sweating that lasted for almost seven months.
Follow-up injections are needed to suppress sweating. These booster injections are required at intervals ranging from a few months to a maximum of sixteen months. Many people experience the injections in the palm as very painful. Sometimes the treatment is therefore carried out after a nerve anesthetic or general anaesthetic.
Sources):