Four crisis exit phases are envisaged by the National Academy of Medicine. For now, we find ourselves in the second, the duration of which is… indefinite.

- Phase 2, known as “deconfinement”, could lead to a rollback in the event of a worsening of the health situation
- Phase 3 is the one everyone is waiting for … but it depends on the arrival of a vaccine or adaptations linked to social or economic necessities
With the Covid-19 pandemic, uncertainty has gripped France. When will we get out of the crisis? How to achieve it? What steps should we go through? In an attempt to provide some answers – despite the lack of data currently available – the National Academy of Medicine has drawn up a pre-report on the phases of the epidemic. She identifies four.
Phase 1: Slow the Spread
The first was to curb the spread of the new coronavirus: it took place from March 17 to May 11, since it resulted in the confinement of the entire French population. “It was the only strategy applicable once the epidemic had reached a level incompatible with its cessation by simple confinement of patients detected as affected”, can we read in the document. According to the Academy, four criteria were essential to get out of this first phase.
These were the sustained reduction in the number of cases for at least two weeks, to be able to test all people with symptoms, but also to be able to carry out active surveillance of all confirmed cases and their contacts. The final criterion: public hospitals had to be able to safely treat all patients requiring hospitalization without resorting to crisis care standards.
Phase 2: Partial deconfinement
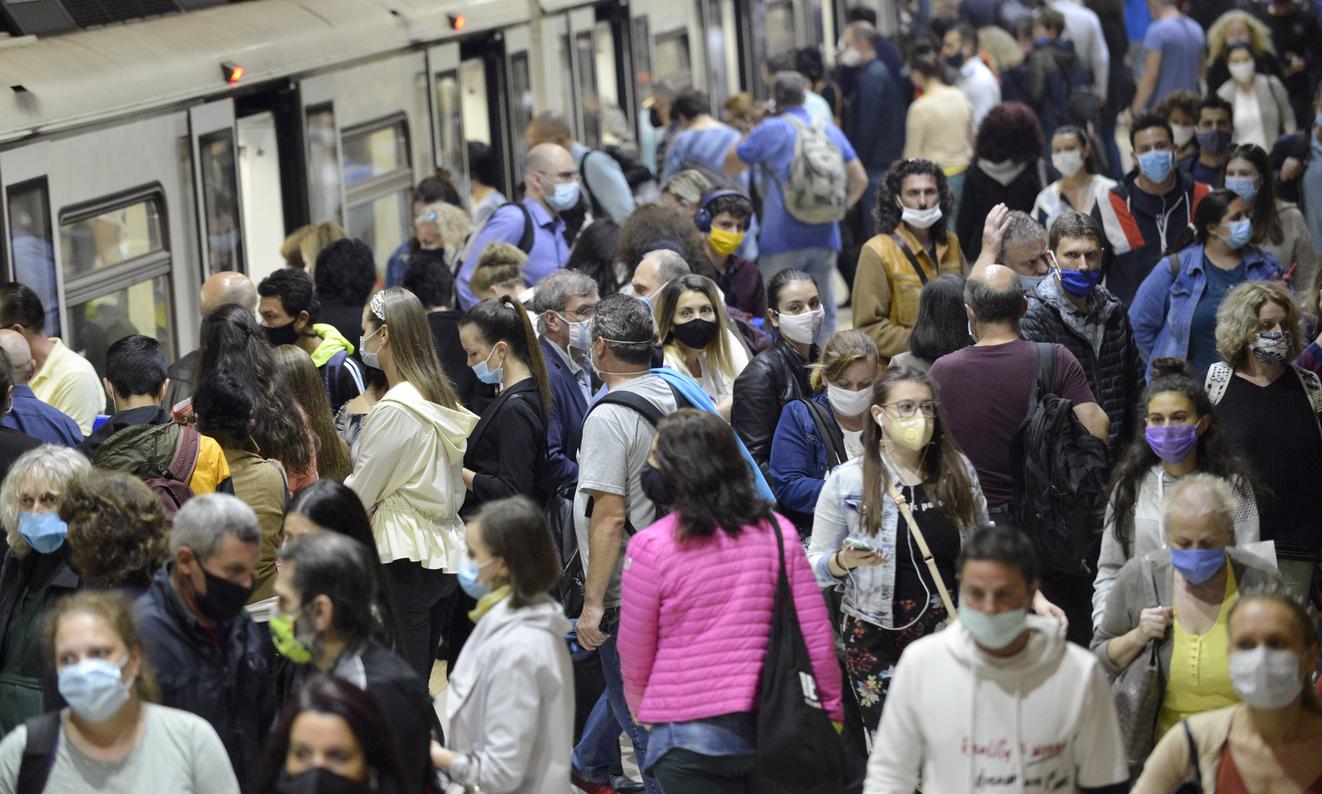
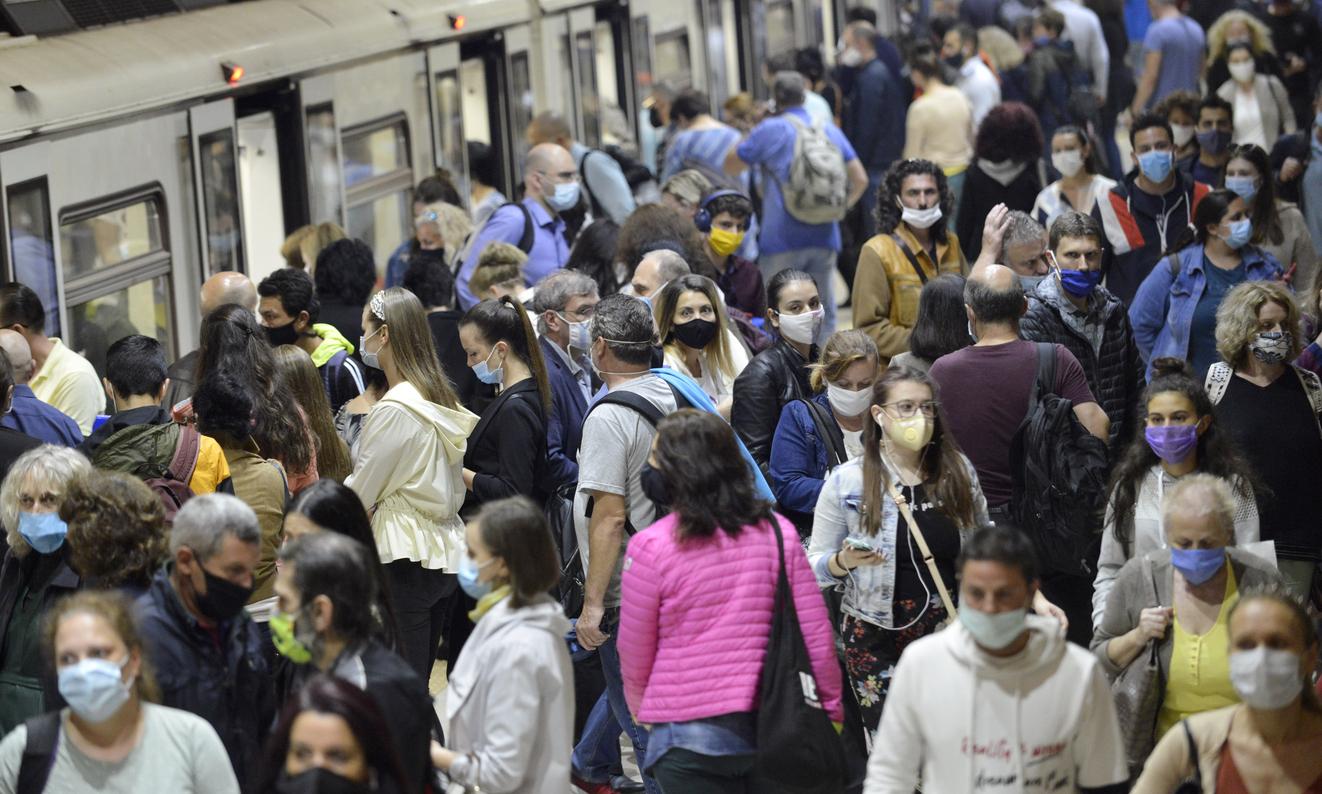
We are currently in the second phase presented by the Academy: the partial deconfinement of the country. “This step consists in part of a return to the situation that preceded the viral expansion requiring containment. However, certain measures of distancing and limiting gatherings will still be in place to prevent the resumption of transmission”, she explains. Maintaining the closure of restaurants and bars, wearing a mask is compulsory on public transport, a ban on traveling more than 100 kilometers from your home unless there are compelling reasons… Everything is in place so that we don’t have to walk. back.
Because, as the Academy points out, a return to the first phase could prove essential depending on the evolution of the situation. This is what would happen if there was a sustained increase in new cases for five days or if hospitals were no longer able to safely treat all the patients who needed to be hospitalized. In parallel, the second phase envisaged by the Academy should be accompanied by the acceleration of the development of therapeutics and a coordinated mobilization of the scientific community.
Phase 3: Remove the constraints via a vaccine or, failing that, a voluntary acquisition strategy
If the second phase is successful, several scenarios are considered. To understand them, you have to project yourself into the two types of third phase imagined by the institution. Indeed, if this step would result in the lifting of the measures put in place during the partial deconfinement, the means to achieve this could vary. The third phase could either consist of the implementation of vaccine protection to remove the constraints, or, in the absence of a vaccine, the development of voluntary and selective acquisition of group immunity.
To get out of the second phase and reach this last scenario, the appearance of a vaccine would have to appear too distant while the social and economic situation of the country worsens. “Unless we consider that the epidemic will end on its own without a significant new wave, Phases III.A and III.B would, if they lead to positive results, end Phase II, the duration of which is currently undetermined”says the Academy.
Phase 4: Follow-up and preparation for a new pandemic
Finally, according to the institution, the fourth phase would consist of dealing with the aftermath of the Covid-19 epidemic and preparing for a new pandemic. For this, several recommendations, including investment in research, the development of infrastructures already in place, the training of the necessary manpower in public health and the establishment of a rapid and clear process of alert. Objective: to ensure that the exceptional situation we are going through never happens again.
.