Onychomycosis is a common condition of fingernails and toenails caused by fungi.
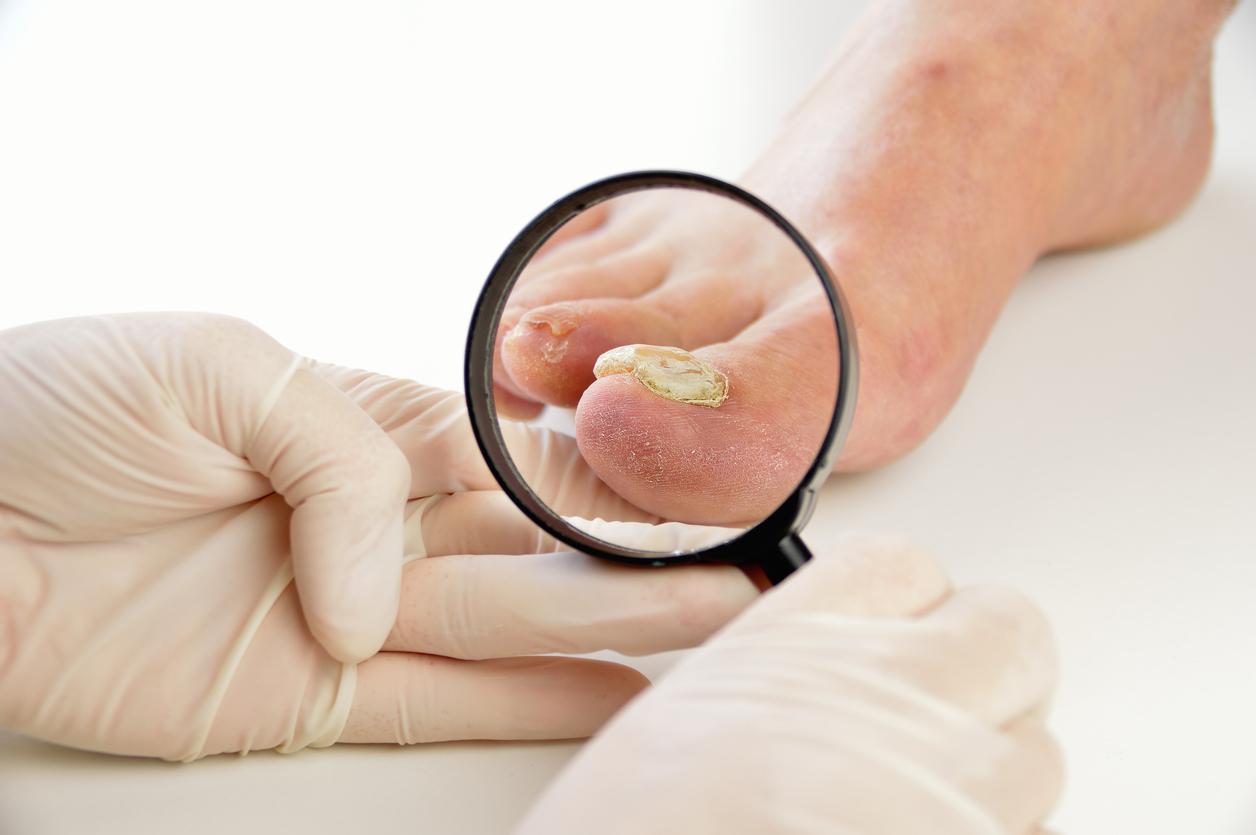
- Infection of the nails with fungi is called onychomycosis.
- This infection affects both children and adults. Although older people may suffer more.
- Treated in time, the infection heals well.
“Onychomycosis”, the medical term for a fungal nail infection, is a condition that can affect adults and children, but becomes more common in older people. The fungi responsible for this infection mainly target the toenails, causing symptoms such as thickening of the nail, its yellowish color, and its fragility. In some cases, a yellow streak may be observed on the nail, resulting from fungus buildup. The diagnosis of onychomycosis is usually made by microscopic examination or fungal culture, allowing the type of fungus to be identified.
Risk factors and symptoms of onychomycosis
Several factors can increase the likelihood of contracting the infection. Advanced age, the presence of tinea pedis (fungal infection of the foot, commonly called athlete’s foot), repeated nail trauma, and a weakened immune system are all conditions predisposing to this nail infection.
Typical symptoms include thickening, yellowing and brittle nails, sometimes associated with color changes. It is essential to diagnose and treat any concomitant skin fungal infections to prevent recurrence of onychomycosis.
Treatment options
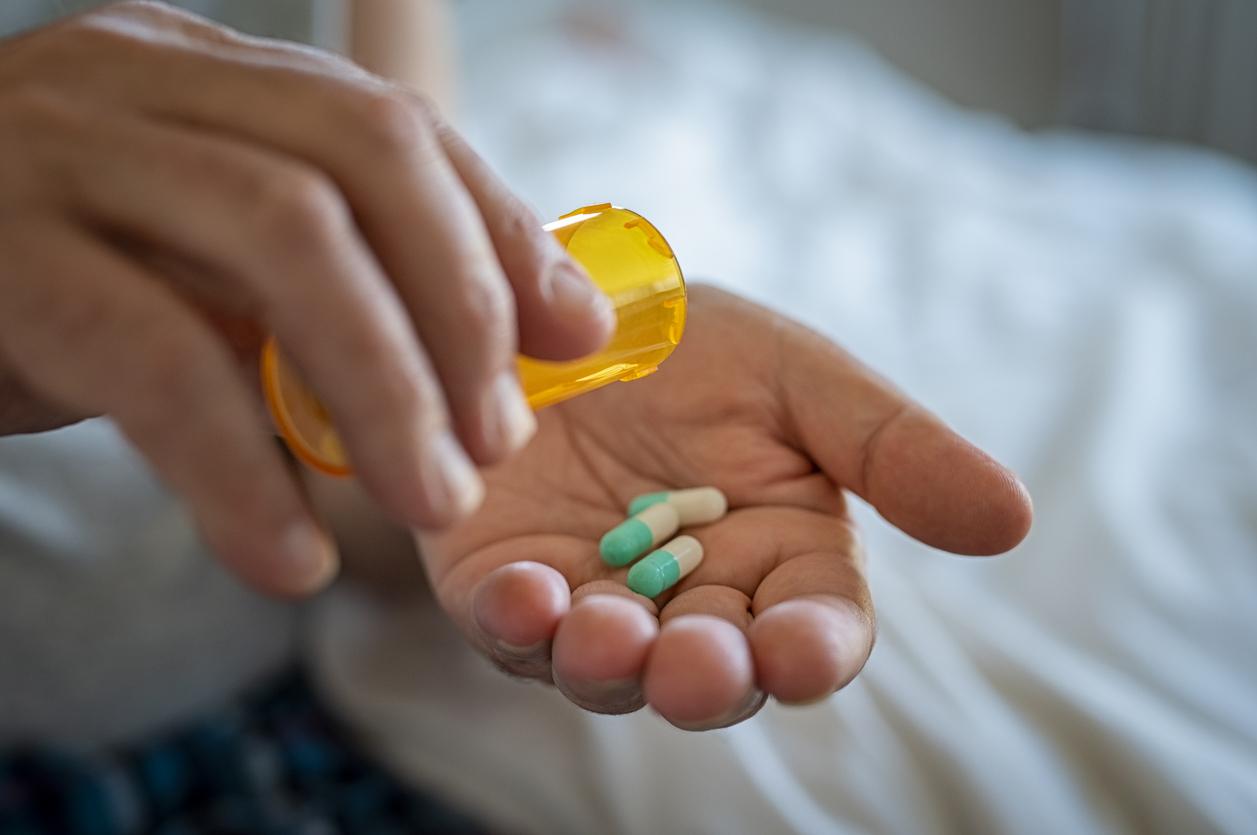
Faced with onychomycosis, there are a variety of therapeutic options. From topical treatment to orally administered antifungals, the choice of treatment will depend on the type of fungal infection and the patient’s preferences. Topical medications, in the form of liquids applied directly to the nails, are generally safer, although requiring prolonged application for optimal results. Conversely, oral antifungals are more effective, but can cause side effects. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected nail parts. A combined approach of topical and oral treatments may be recommended to maximize treatment effectiveness.