Mumps is a contagious viral infection that spreads through contact with infected saliva.
Mumps is a contagious viral infection caused by the paramyxovirus. This virus spreads through contact with infected saliva. When a mumps patient sneezes or coughs, saliva droplets are sprayed into the surrounding air. If others come into contact with these droplets, the virus can spread.
After exposure to the mumps virus, an incubation period (‘incubation period’) of 14 to 24 days generally follows. At this time, there is no sign of the disease yet.
During that period, the virus begins to spread in the cells of the upper respiratory tract and of the lymph nodes to multiply, thereby increasing the virus content in the bloodstream. The first symptoms of mumps are shivering, headache and a general feeling of discomfort. After 12 to 24 hours, swelling of the salivary glands follows. These glands usually become sensitive to touch and painful when chewing and swallowing. You can also develop a fever, up to 40 ◦C.
Mumps can lead to complications such as deafness, meningitis or nerve damage. In boys and men, painful swelling of the testicles can also occur as a side effect of mumps.
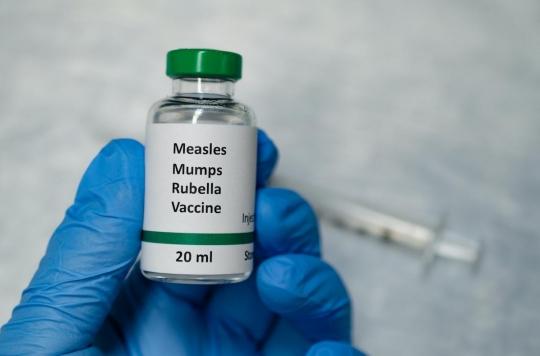
An effective vaccine against mumps is available. Since 1987, children in the Netherlands at the age of 14 months receive the so-called. MMR Injection, against Mumps, Measles and Rubella. The MMR vaccine should not be given to pregnant women.







-1582216824.jpg)