Associations are asking to extend access to the vaccine against monkeypox (or “Monkeypox”).
- Monkeypox usually heals on its own and symptoms last 2 to 4 weeks.
- Severe cases occur more frequently in children and are related to the extent of exposure to the virus, the patient’s medical condition and the nature of the complications.
- Lately, the fatality rate is around 3-6% of cases.
Faced with the increase in cases of monkeypox, LGBTQI + associations are asking to extend access to the vaccine to men having homosexual relations.
“We must be able to offer a pre-exposure vaccination, before coming into contact with the virus”, explains Franck Barbier, course and program manager at Aides, to France News. “There is an explosion of cases, a lack of information, a lack of prevention, a lack of doses”, adds Marc-Antoine Bartoli, coordinator of Act-up Paris. The High Authority for Health (HAS) has been seized to render an opinion on this file. For the moment, it only recommends the vaccination of contact cases.
577 cases in France
As of July 5, 2022, 577 cases have been identified in France: 387 in Ile-de-France, 52 in Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, 37 in Occitanie, 30 in New Aquitaine, 23 in Hauts-de-France, 21 in Provence -Alpes-Côte d’Azur, 8 in Normandy, 6 in Grand Est, 5 in Brittany, 4 in Pays-de-la-Loire, 3 in Bourgogne-Franche-Comté and 1 in Centre-Val de Loire.
Monkey pox (also called “simian orthopox virus” Where “monkeypox”) is a viral zoonosis (virus transmitted to humans by animals) whose symptoms are less severe than those observed in the past in subjects with smallpox. “The incubation period of the virus generally varies from 6 to 13 days, but can range from 5 to 21 days”, explains the WHO.
Two periods
The infection is split into two periods:
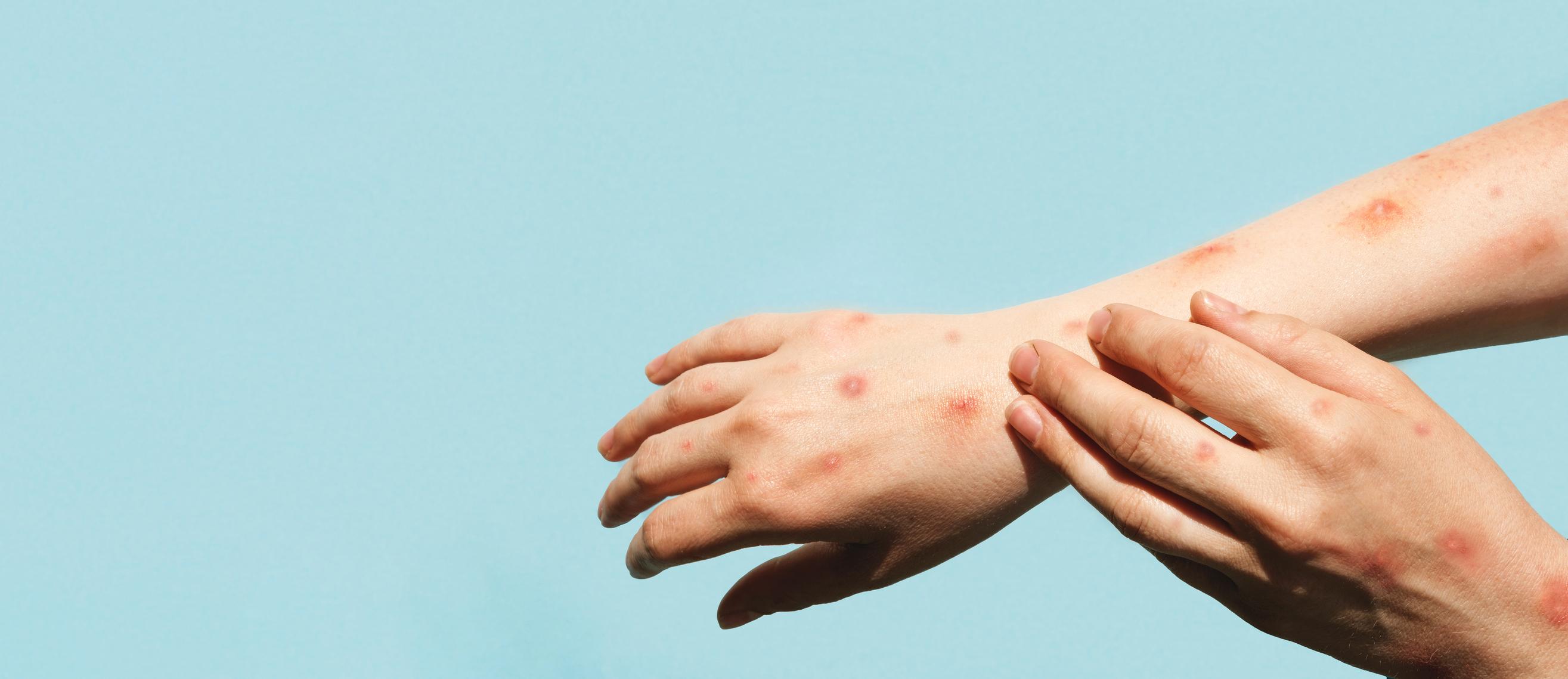
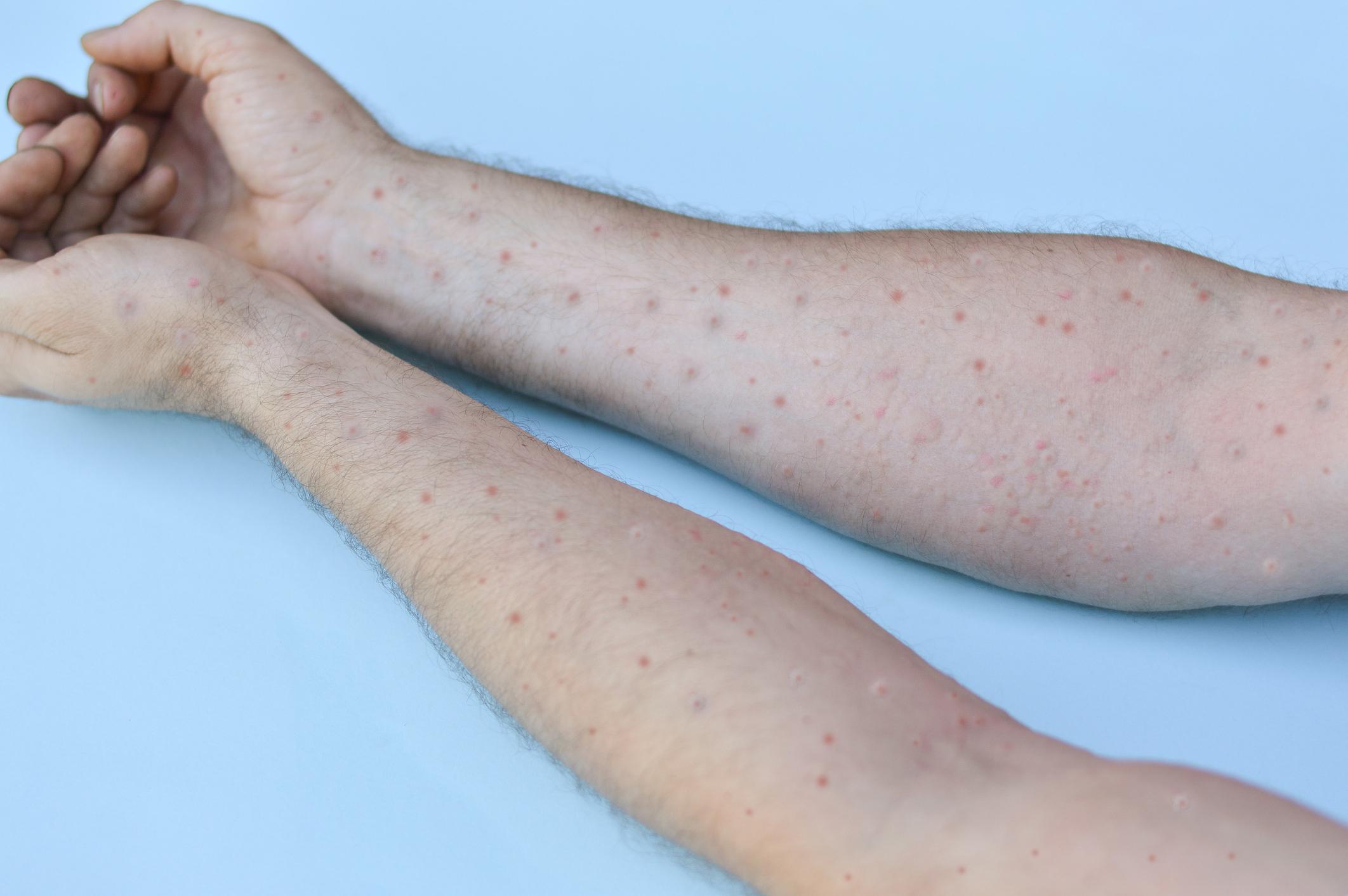
– the invasive period (which lasts from 0 to 5 days) characterized by the appearance of fever, intense headaches, lymphadenopathy (swollen lymph nodes), back pain, myalgia (muscle pain) and marked asthenia (lack of energy). Lymphadenopathy is a feature of monkeypox that distinguishes it from other diseases that may initially show similarities (chickenpox, measles, smallpox).
– The rash, which usually begins within 1 to 3 days of the onset of fever. It usually focuses more on the face and extremities than on the trunk. “It affects the face (in 95% of cases), the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet (in 75% of cases). The oral mucous membranes (in 70% of cases), the genitals (30%) and the conjunctivae (20%) as well as the cornea are also marked”, says the WHO.