Illness with many faces
Lupus: Fans of the television series House probably know this rare disease by name. Creator David Shore even received an award from the organization Lupus LA for raising awareness of this condition. Yet knowledge about the disease often does not go beyond the name.
Lupus falls under the rheumatic diseases and is often abbreviated as LE. The disease has been known to physicians since 1828.
What is lupus?
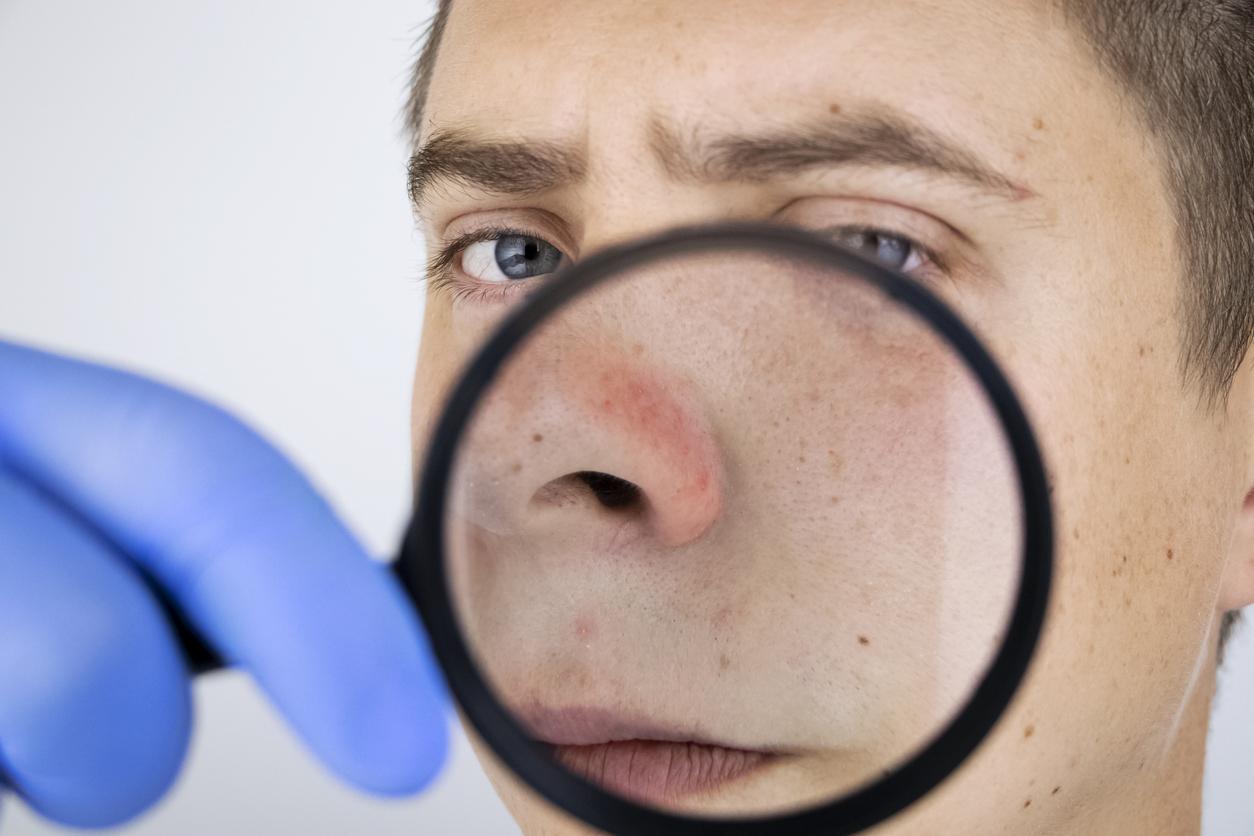
Lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease of unknown cause. The immune system turns against the body, causing inflammation. In LE, these inflammations are usually in the skin and joints, but also in organs such as the kidneys, nervous system, heart, lungs and blood vessels. Characteristic of LE is a butterfly-shaped, red skin abnormality in the face.
There are several forms of lupus erythematosus:
- Cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) – only the skin is affected
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) – all kinds of organs can be affected
- Drug induced lupus erythematosus (DILE) – caused by the use of certain drugs
In CLE, a distinction is made between three variants: acute CLE, subacute CLE and chronic CLE. This form is also sometimes called discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE). Lupus erythematodes disseminatus is also still used for SLE.
Lupus is the Latin word for wolf and erythematosus means redness. This name was given to the disease because the characteristic rash on the face was thought to resemble a wolf bite.
Women higher risk
About 1 in 4000 people in the Netherlands suffers from lupus. The autoimmune disease occurs mainly in women and usually starts between the ages of 20 and 40. Asian and black people are more likely to get the condition than white-skinned people.
DILE is equally common in men and women. Most people who get this condition are between the ages of 50 and 70. The medications that can cause this form of lupus are more commonly used in this age group.
Cause unknown
The exact cause of lupus is unknown, but there are strong indications that heredity, hormones, severe stress and infections play an important role. For example, female hormones promote lupus, while male hormones provide protection. Sunlight also seems to influence the development of lupus. There is insufficient evidence of heredity, but the disease seems to occur more often in some families.
With DILE – as mentioned earlier – the cause of the complaints lies with certain medication, such as statins (cholesterol-lowering drugs) and biologicals (biological rheumatism inhibitors).
Disease with many symptoms
The disease LE causes many different complaints: the whole body can be involved. In CLE it is mainly the skin abnormalities that come to the fore, while in SLE the complaints are more general. You can think of fatigue, lack of energy, fever and weight loss. Also, the internal organs sometimes play up. Common symptoms are:
- joint inflammation (arthritis)
- joint pain (arthralgia)
- skin abnormalities
- heart problems (chest pain, shortness of breath, fever, palpitations)
- kidney inflammation (you often don’t notice it yourself)
- lung abnormalities (pneumonia, inflammation of the lung, pulmonary embolism)
- neurological complaints
- abnormality in the blood
- hypersensitivity to sunlight
- sores (aphthous ulcers) in the mouth, throat and nose
- thrombosis
- abrasive and dry feeling in the eyes
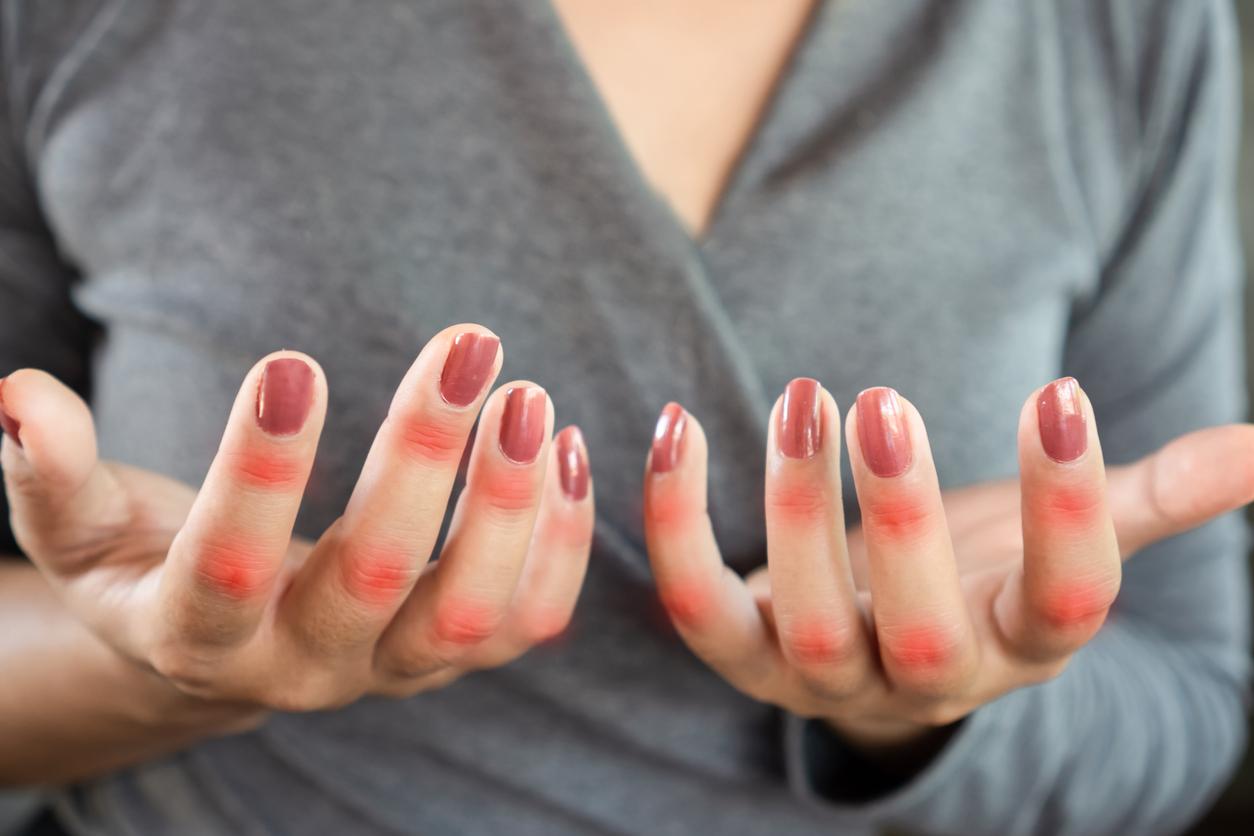
- Raynoud’s phenomenon (dead fingers or toes)
Making the diagnosis
Since the symptoms of LE can vary greatly, there are also various investigations to make the diagnosis. If a doctor suspects lupus, a physical exam, blood and urine tests, and sometimes a biopsy will often be done. In some cases, more additional research is needed. You can think of a heart film or X-ray of the lungs.
The diagnosis usually uses a list of criteria developed by the American Association of Rheumatologists (ACR) to compare lupus patients in scientific research. To know for sure that someone has lupus, four of the criteria below must be met. If there are fewer than four, the disease is called SLE-like.
- butterfly shaped skin rash on your face
- disc-shaped skin lesions (thickened red patches)
- hypersensitivity to sunlight
- mouth or nose sores
- arthritis in two or more joints
- inflammation of the pericardium (pericarditis) or the lining of the lungs (pleurisy)
- renal abnormality
- disorders of the nervous system (epilepsy or psychosis)
- abnormalities in the blood
- presence of certain antibodies in the blood
- an increased level of ANA in the blood (antinuclear antibodies, also called ANF)
Therapy
Cutaneous and systemic lupus are chronic and therefore do not go away. The illnesses can calm down, but sometimes flare up again. The course differs from patient to patient. Skin lesions can become malignant over time, so longer existing spots must be closely monitored. Lupus caused by medication is usually mild and goes away as soon as you stop taking the medication.
Treatment of PE is usually done by a rheumatologist, but sometimes other specialists such as a dermatologist, neurologist or nephrologist (kidney specialist) are also involved. The goal is not to cure the disease, but to reduce the symptoms. For this purpose, among other things, use is made of:
- painkillers
- anti-inflammatories
- antimalarials
- corticosteroids (anti-inflammatory and constrict blood vessels)
- cytotoxic agents (suppress immune system)
- methotrexate and cyclosporine (suppress immune system)
- antibiotics
- blood pressure lowering drugs
- blood thinners
- anti-seizure drugs
Some patients also try alternative treatments such as acupuncture, homeopathy, herbal therapy, alternative diets and massage. Most of these treatments have not been shown to actually give results, but it sometimes pays to try because it can relieve your complaints. Always consult with your specialist.
Can You Prevent Lupus?
Since the cause of the condition is unknown, you cannot prevent the disease. However, it is important to avoid direct sunlight with skin disorders. Inflamed or painful joints often benefit from exercise. A healthy lifestyle is generally very important. Get plenty of rest, don’t smoke and avoid excessive alcohol consumption. Try to avoid contact with infectious diseases.
A special diet is not necessary, especially ensure a healthy and varied diet. In the case of kidney disease or high blood pressure, salt intake must sometimes be limited or extra attention must be paid to protein intake. Some people with LE have a flare-up of skin symptoms after eating alfalfa. It is unclear what causes this, but it is advisable to avoid alfalfa in LE.
It is also sometimes wise to take extra vitamin D, especially if you are not allowed to go out in the sun. Always discuss this with your doctor first.
Lupus and Pregnancy
Lupus usually does not have to stand in the way of a desire to have children. Women with lupus are normally fertile and the pregnancy usually goes without complications. Discuss your wish to have children in time with your doctor. Certain medications can adversely affect fertility or the unborn child. The same goes for some antibodies in the flood. It is therefore important that you do not become pregnant until the disease has been inactive for at least six months.
If the disease is active, there is an increased risk that the disease will flare up further during pregnancy. And that also increases the risk of miscarriage, a child born too early or too small and various pregnancy problems such as preeclampsia. It is therefore important that you are guided by a rheumatologist and gynaecologist. They can also prescribe medication that is not harmful to the baby.