Between 2,000 and 3,500 m altitude, people have a lower risk of suffering from a stroke and of dying from it.

- Stroke is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide.
- It is usually caused by a blood clot, which then blocks one of the arteries supplying the brain.
- More than 160 million people in the world live at an altitude of more than 2,500 m.
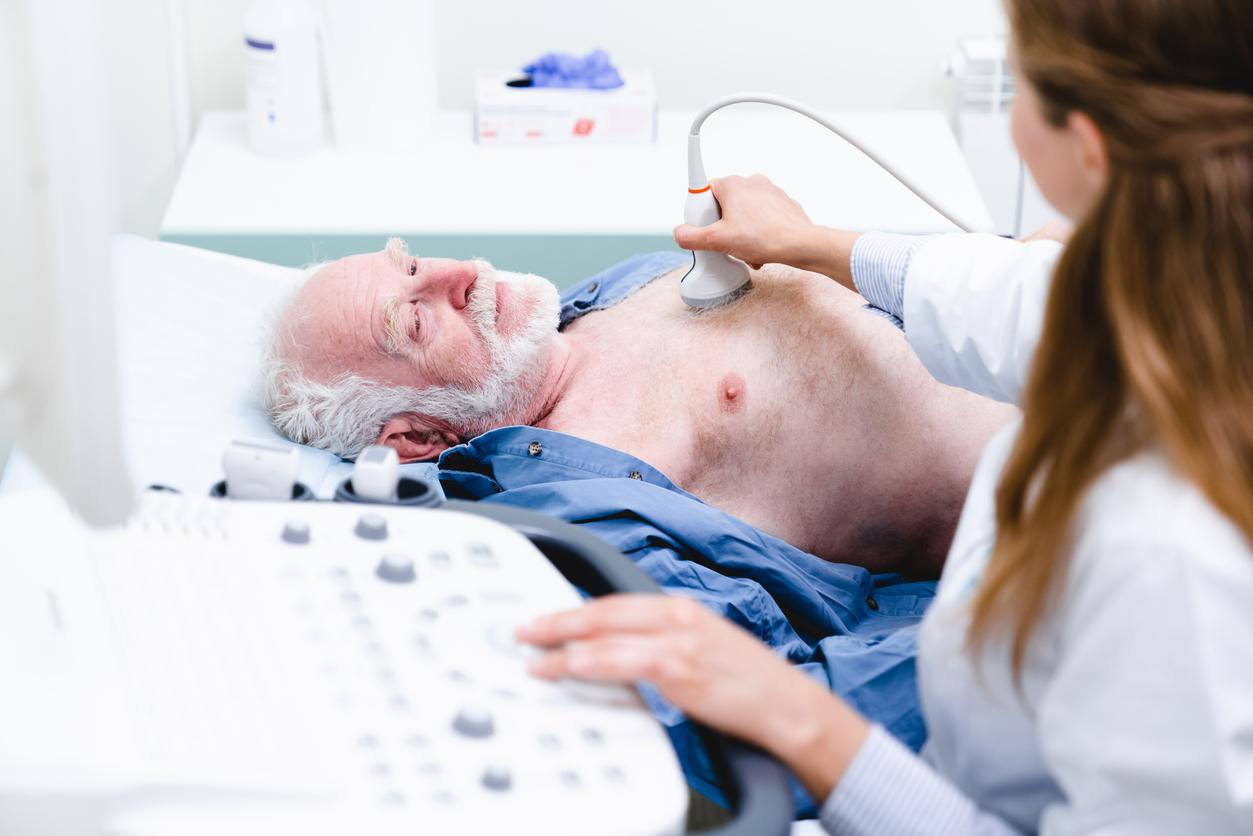
What are the health effects of living at altitude? The lower concentration of oxygen in the air has consequences for the organism. It has long been accepted that this phenomenon increases the production of red blood cells to improve oxygenation. A research team wanted to go further: they conducted a study in high altitude villages in Ecuador to understand if this lifestyle could reduce the risk of stroke. Their results are published in Frontiers in Physiology.
A lack of information on the effects of altitude
“The main motivation for our work was to raise awareness of a problem that is very little exploredexplains Esteban Ortiz-Prado of the Universidad de las Americas in Ecuador, and lead author of the study. More than 160 million people live above 2,500 meters and there is very little information regarding epidemiological differences in stroke at altitude.” With his team, he dissected the medical records of nearly 100,000 people who had had a stroke. They lived at four different altitude levels: low altitude (less than 1,500 m), moderate altitude (between 1 500 to 2,000 m), high altitude (between 2,500 and 3,000 m) and very high altitude (between 3,500 and 5,500 m) They found that people living at high altitudes, from 2,500 m , were older at the time of their stroke, compared to those living lower down, and people who lived at higher altitudes were less likely to be hospitalized or die from stroke. is greater between 2,000 and 3,500 meters, but attenuates above 3,500 meters.
What are the causes of this protective effect?
Several hypotheses have been put forward by researchers to explain this phenomenon. Living at altitude forces the body to adapt to the lower presence of oxygen. This could improve blood clotting, and reduce the risk of stroke, but also make it easier to make new blood vessels and improve recovery after the accident. These people may have a more developed vascular network in the brain: this helps them to better use the oxygen they consume, and thus this would protect them from certain consequences of stroke. These are multiple: mobility disorders, paralysis, difficulty speaking, etc.

.