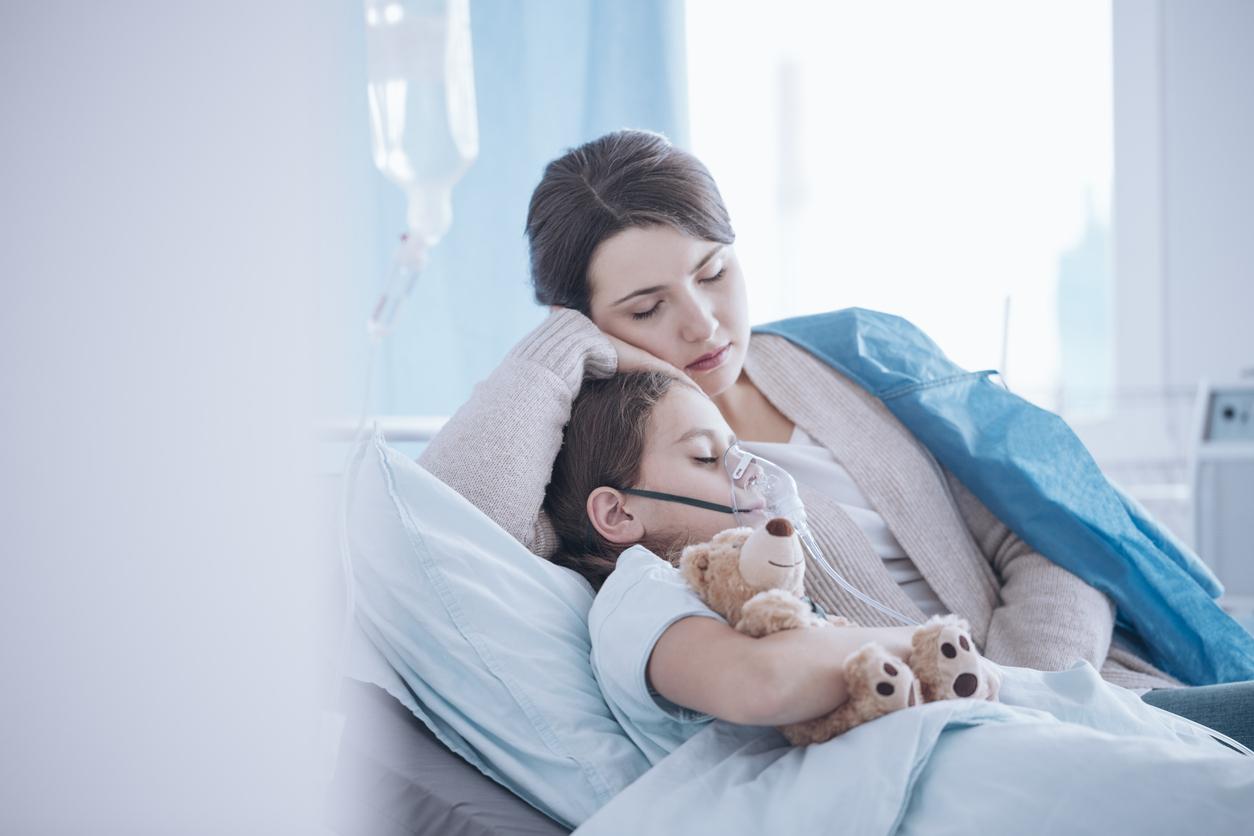
Pneumonia is an acute respiratory infection that affects the lungs. The alveoli fill with pus and fluid, making it painful to breathe and restricting oxygen uptake. According to information from World Health Organization, this infection is caused by a number of infectious agents, bacteria, viruses or fungi.
While classical pneumonia is treated with a simple administration of antibiotics, community-acquired pneumonia is still common and when it results in hospitalization in intensive care, mortality can reach 30%, according to the document “Acute severe community pneumonia”, posted online by the department of anesthesia-resuscitation-Smur of the Lariboisière Hospital.
A weakened immune system is believed to be the main cause of an increased risk of contracting pneumonia. “The diagnostic strategy and the criteria of severity allowing referral to an intensive care unit are fairly well established and the major concern of clinicians remains the identification of the etiological agent and the rapid initiation of an appropriate antibiotic treatment. “, explains the department. In Europe, the incidence of pneumonia is low, ranging from 4.7 to 11.6 per 1,000 inhabitants per year, of which 10% will be hospitalized.