What we eat impacts our health and that of the planet, but can we reconcile the two? Yes, answer many scientists who have studied the subject.

- The researchers found that the dietary habits associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease also led to lower greenhouse gas emissions and used less nitrogen fertilizer, cropland and water.
- Other studies also show that vegetarian and vegan diets help reduce cholesterol, risk of diabetes, chronic diseases.
- For the planet, the animal protein with the lowest environmental impact is eggs.
The number of obese people is exploding worldwide with its share of complications: type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, cancers, etc. And in the meantime, the planet is suffocating. A study by Nature Food published in March 2021 shows that global food production is responsible for more than a third of our greenhouse gas emissions that cause climate change. So yes, our diet will always have an impact on our Earth, but this impact can be much less than today. Moreover, and this is good news, it is possible to reduce our footprint by eating better!
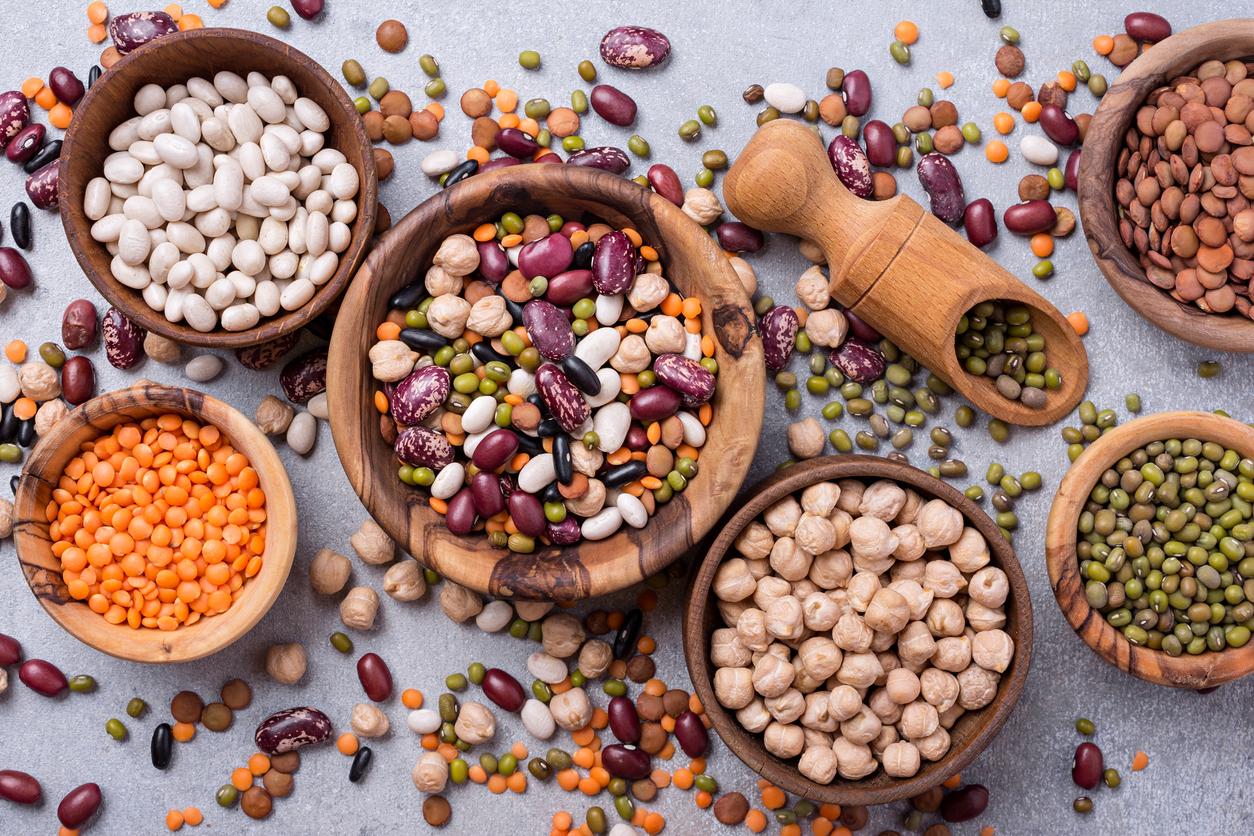
Eat more plants for our health and that of the Earth
Most studies assessing the effects of dietary intake on the environment have concluded the same thing : the more animal foods were replaced by plant foods, the lower the environmental impact of the diet. And that’s a good thing, because these foods “are also better for our health”, recall in a statement researchers from the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy in the United States.In a study on dietary intake, environmental impact and incidence of cardiovascular disease, they explain, The researchers found that the dietary habits associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease also led to lower greenhouse gas emissions and used less nitrogen fertilizer, cropland and water.”
“Vegetarian diets are associated with the greatest reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and land and water use, but you don’t have to give up all meat, fish and poultry to make a difference.they continue. Simply replacing ruminant meat (cow, sheep and goat) with other animal proteins (fish, poultry, pork, skimmed milk and yogurt and eggs) has been shown to reduce environmental impact, butthey concede, not as much as following a plant-based vegetarian or vegan diet.”
What are the benefits of a vegetarian diet for humans?
A plethora of studies show the health benefits of vegetarian and vegan diets for human health. In particular, they help reduce cholesterol, the risk of diabetes, chronic diseases, etc. A recent study shows that in just a few weeks, a vegan diet can also improve cardiovascular health. And, while this cliché still exists, athletes have nothing to fear from such a diet, because it has been proven that plant-based proteins are as effective as meat for building muscle.
On the other hand, be careful not to fall into the trap of ultra-processed foods under the pretext that they are produced from plants, because they too can increase cardiovascular risks.
And what about the planet? The animal proteins that have the most harmful impact on our Earth are beef (99.48 kg of greenhouse gas emissions/kg), lamb (39.72 kg of greenhouse gas emissions/kg), followed by pork (12.31 kg of greenhouse gas emissions/kg) and poultry (9.87 kg of greenhouse gas emissions/kg), dairy products, and seafood. Eggs, the ultimate anti-crisis product that, contrary to popular belief, do not raise cholesterol, are also the animal proteins that consume the least carbon (4.67 kg of greenhouse gas emissions/kg), land and water than the others. In comparison, rice results in a release of 4.45 kg of greenhouse gas emissions/kg, tomatoes 2.09 kg and potatoes only 0.46 kg.