A plug of earwax
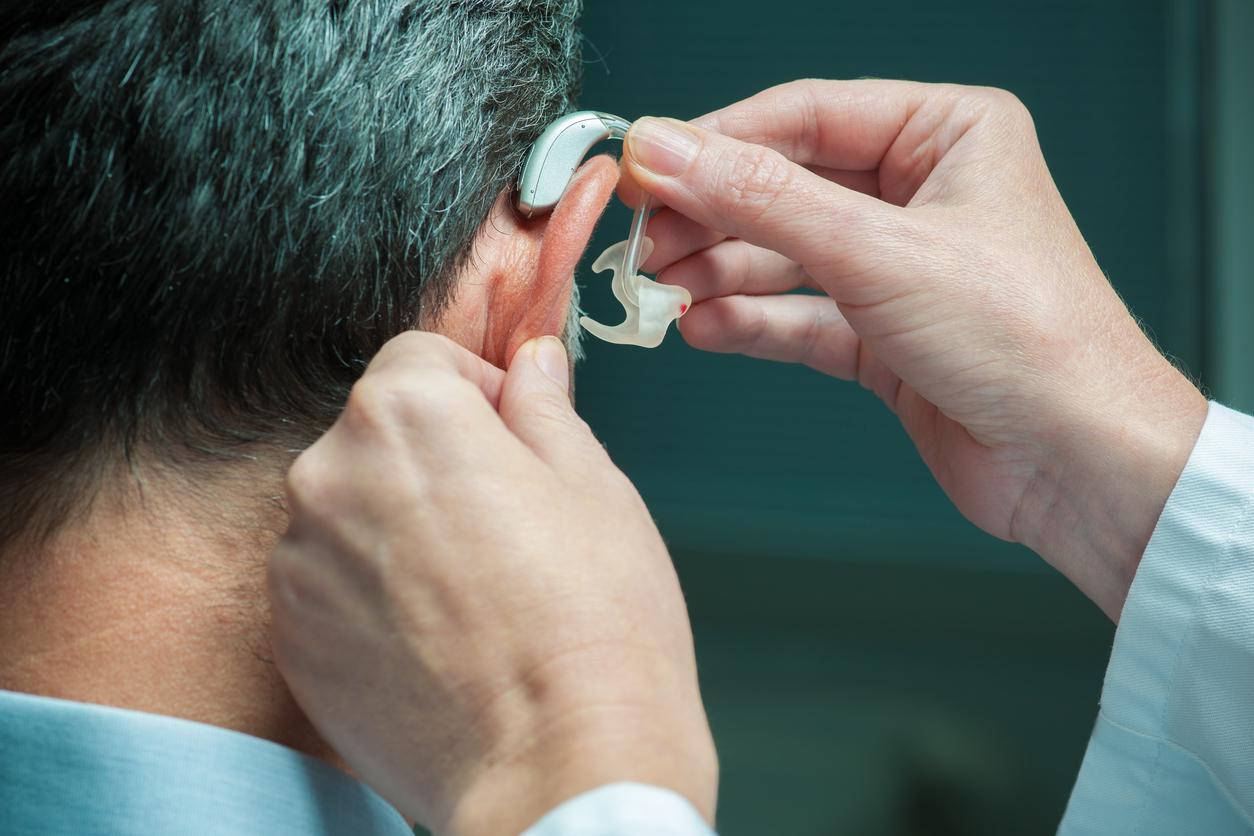
Certainly not very inviting, cerumen (or ear wax) is useful for protecting the eardrum. But its accumulation, in adults as in children, can obstruct the external auditory canal. A decrease in hearing acuity, even deafness, buzzing or tinnitus often put the chip … to the ear!
What to do ? First, have their eardrum examined by a general practitioner. Then extract the stopper (alone or at your doctor’s) with lukewarm water, using a syringe or a pear (first, soften it with an auditory spray or a little Cérulyse then massage the back of the ear). Do not insist if it is painful. If this does not improve, consult an ENT doctor, who will aspirate the plug.
Otitis
Common in children, these infections and inflammations can also affect adults. They are manifested by a ear pain, fever, purulent discharge. In children, learning difficulties or language delay should alert to the possibility of chronic otitis.
What to do ? If it is a acute otitis(often following a cold), take paracetamol to decrease pain. If necessary, the doctor can prescribe an antibiotic for 8-10 days. When ear infections are too frequent, the removal of the adenoids is sometimes considered. In the event of chronic otitis (serous), the doctor may recommend the installation of trans-tympanic ventilators (or yoyos) for 12 to 18 months.
Eczema of the duct
Unwanted scratching, heavy earwax plugs or the wearing of earplugs can generate eczema of the external auditory canal and cause persistent, very unpleasant itching. Swimmers are more often affected by this condition (involved, frequent baths and insufficient ear drying).
What to do ? Consult an ENT doctor to perform an aspiration-evacuation of earwax. A treatment based on local corticosteroids (in the form of drops) will also be set up for ten days, possibly renewed if the problem persists.
An allergy to earring metal
This skin reaction is most often due to the nickel present in the metal of the fancy earrings. Eczema can form where the skin comes in contact with this alloy. Swelling of the earlobe, redness, itching, or even discharge of pus are possible signs.
What to do ? Quite simply, stop wearing jewelry containing this metal for a few days, if not permanently. Gold, silver or allergy-guaranteed earrings are not affected. It is also possible to apply colorless varnish on the stem of the jewel, as protection at the level of the contact areas. If the problem persists, the doctor may prescribe topical corticosteroids.
Psoriasis
This chronic skin disease may also extend to the ears, rarely inside the duct, but rather around, and up to the scalp.
It is manifested by the formation of red (then white) patches that itch intensely.
What to do ? Apply a corticosteroid-based cream (topical corticosteroids) to the irritated area. A dermatologist can perform an aspiration of the dead cells which will help soothe the red patches. If psoriasis affects other parts of the body on a recurring basis, you really need to see a doctor. A basic treatment skin disease will make things better.
Read also :
He develops an infection for a cotton swab in his ear
How to properly protect the ears