With global warming, France must, in particular, rethink its heatwave alert thresholds. This is a recommendation from experts on the eve of COP21.

Less than a week before COP21, the major climate conference to be held in Paris, more and more work studying the impact of climate change on health is being published.
The last Weekly Epidemiological Bulletin (BEH) of the Institut de Veille Sanitaire (InVS) thus offers a reflection on climate-related developments specific to France. They are particularly interested in the temperature changes recorded in recent years.
The authors then warn about the health risks associated with this global warming, and suggest rethinking public policies and the organization of society, in order to better support these transformations.
By 2050
Since 1880, the average temperature has already increased by 0.85 ° C globally. According to InVS researchers, this is also the case in France. This temperature rise should continue in the coming years and above all, accelerate.
Several predictions for metropolitan France thus speak of a temperature increase of between 0.6 and 1.3 degrees between 2021-2050, compared to the period 1976-2005. This could result in an increase in marked episodes of heatwave or extreme cold.
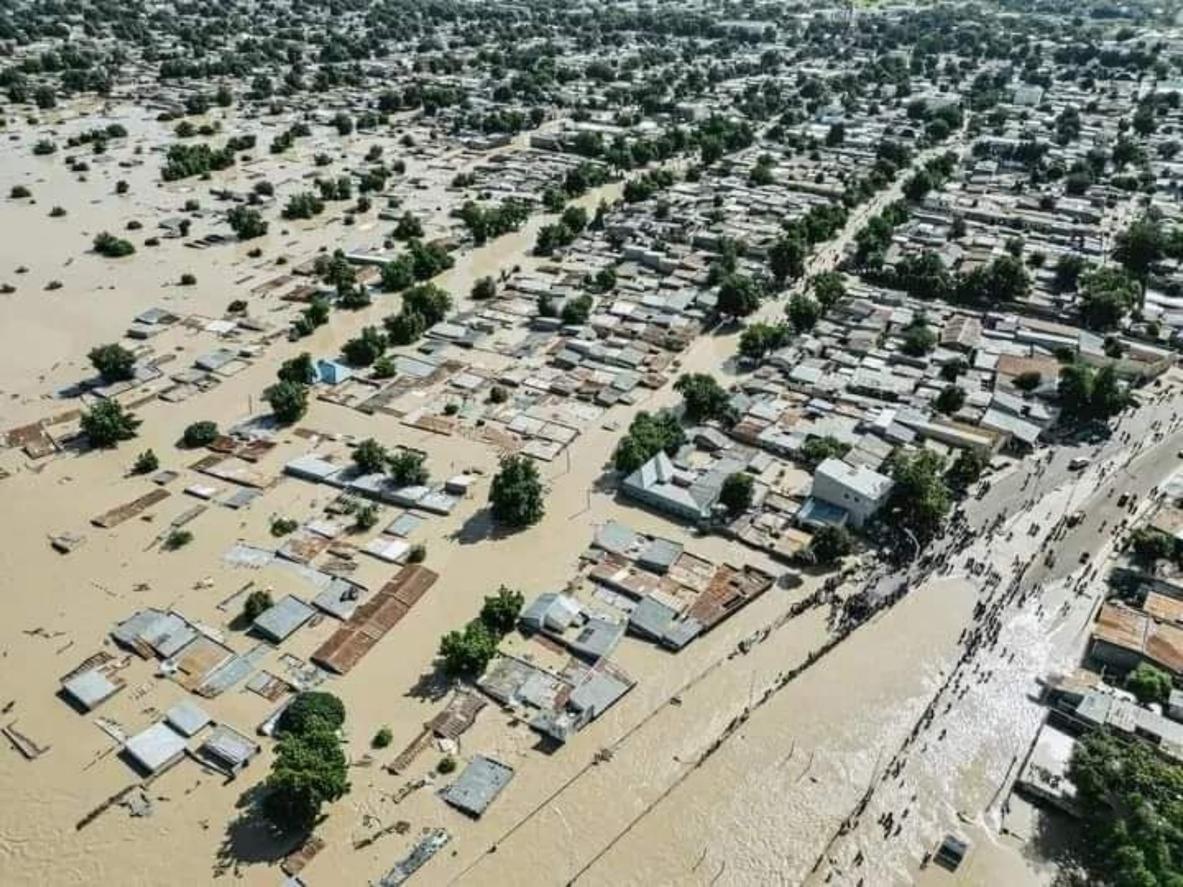
In general, other extreme phenomena are to be expected, such as, for example, abundant precipitation in summer, or forest fires spreading to regions so far spared such as the Pays de la Loire, France. horizon 2050.
Prevent health impact
By describing these potential climatic variations in France, the researchers hope to push the authorities into a broader reflection on the adaptation of society to global warming.
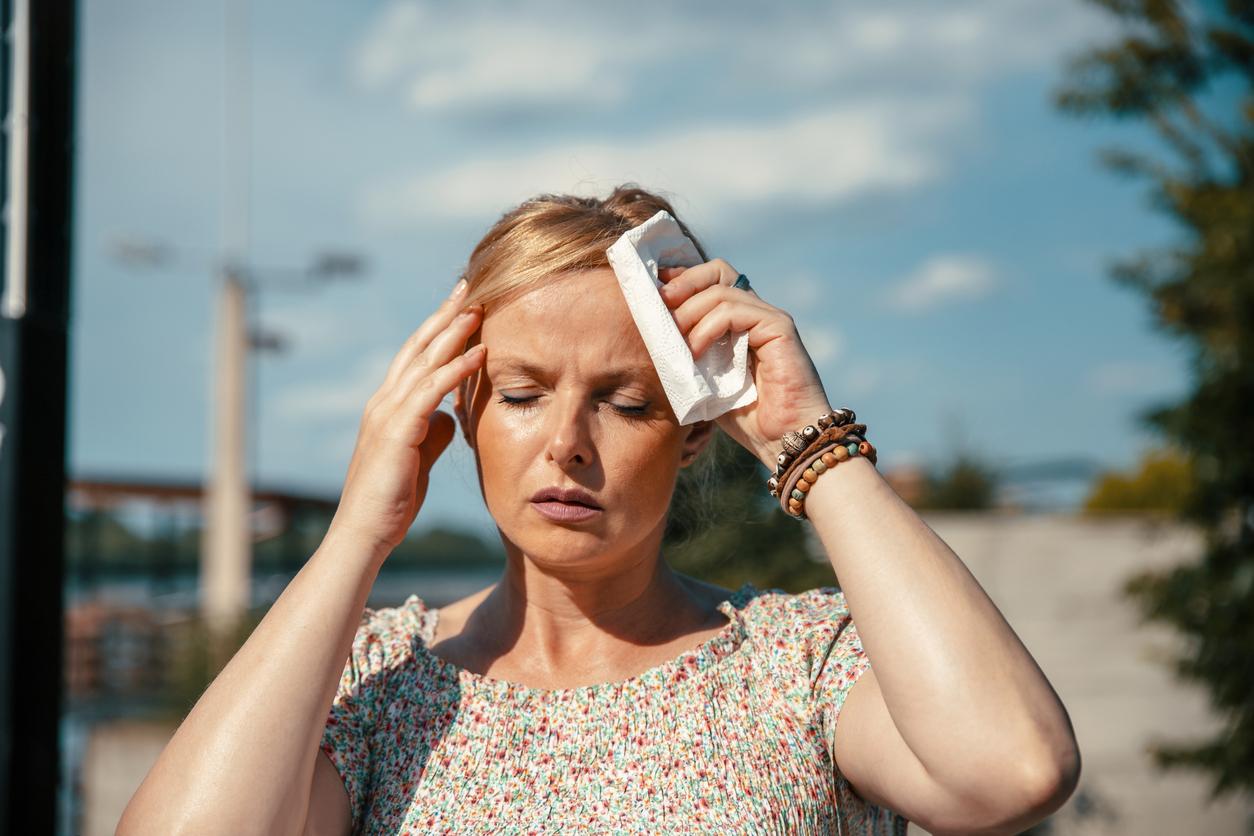
Extreme temperatures greatly increase the risk of mortality. The 2003 heatwave, which was particularly violent, caused nearly 15,000 deaths, for example. In addition, heat peaks are often associated with major pollution peaks, causing many respiratory diseases and allergies. Almost a quarter of the French population thus suffers from allergic pathologies.
To prevent such scenarios from happening again, even though the temperature will continue to rise, several solutions can be found in France. At present, only emergency measures are in place to fight against global warming, as with the National Heatwave Plan.
Experts believe that this is not enough, and that France must adapt in depth. For example, it must rethink its heat wave alert thresholds defined since 1973, which will soon no longer be relevant, while the average summer temperature increases every year. It must review its prevention plans so that the French permanently integrate what must be done to protect themselves in the event of high heat.
Social reorganization
Beyond its concrete measures, it is the very organization of French cities, habitats, and society that must be redefined. This supposes to think carefully upstream, in order to avoid that these new models do not increase any more inequalities between the citizens.
For this, the researchers stress that the simplest solutions are perhaps the best: buildings designed to limit energy consumption and the development of green spaces clean up the environment and constitute islands of freshness in urban areas, to set up quickly.
There is an urgent need to act, and the researchers hope that COP1 will lead to an agreement limiting the increase in temperatures to 2 ° C compared to the pre-industrial period. We talk a lot about the impact of climate change on a global scale, but France must on its own scale review its management system for extreme weather phenomena, to keep its population in good health.
.