While French cities are crumbling under waste due to the mobilization of garbage collectors, some experts fear a resurgence of leptospirosis.

- In mainland France, leptospirosis, which lasts 4 to 14 days, affects approximately 600 people each year.
- It is caused by pathogenic bacteria, which are maintained quite easily in the external environment (fresh water, muddy soils).
- This disease, which requires hospitalization, can range from an influenza-like illness to a multivisceral attack with a hemorrhagic syndrome.
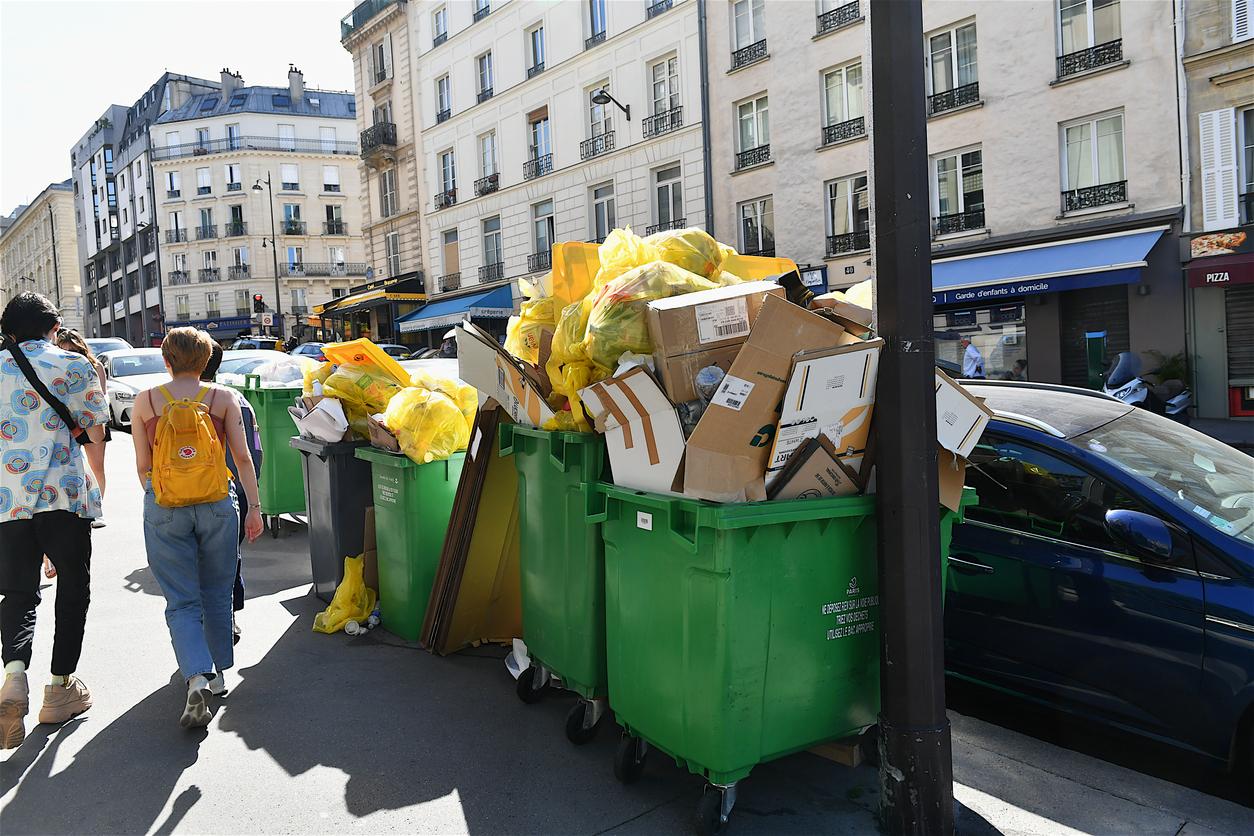
For more than a week, garbage collectors have been on strike and protesting against the pension reform. In Paris, they confirmed that their mobilization would at least continue until March 20. In several cities in France, garbage cans are piling up on the sidewalks. An accumulation of waste that attracts rats carrying certain pathologies, including leptospirosis.
Leptospirosis, an occupational disease and a leisure zoonosis
It is a zoonosis “very widespread in the world, particularly in tropical environments and whose incidence in France has increased in recent years”according the ministry of health. In France, the number of cases has increased from 300 to 600 per year since 2014. “The seasonality of the disease is very marked, with an upsurge during the rainy season in tropical regions or during the summer-autumn period in temperate countries (swimming in fresh water)”, precise the Pasteur Institute. The people most at risk of developing leptospirosis are farmers, veterinarians, garbage collectors or even sewer workers, but also those practicing water sports (swimming, canoeing, kayaking, fishing, hunting, canyoning, etc.).
Rats “excrete the bacteria in the urine”
This condition is caused by pathogenic bacteria, of which the most common serogroup in France is Leptospira icterohaemorrhagiae. The latter develop in warm and humid environments (fresh water, muddy soils) where they can survive for several months. “Its main reservoirs are rodents, in particular rats, which excrete the bacterium in the urine and thus soil their environment and occasionally dogs, livestock (pigs)”, says the Ministry of Health. In humans, the bacteria enters through part of the injured skin or mucous membranes. As with many diseases, transmission is direct through simple contact with an infected animal or through a bite. It can also be indirect during swimming activities in fresh water.
Leptospirosis: what are the symptoms?
In general, leptospirosis lasts from 4 to 14 days. This disease is manifested by fever, chills, tachycardia, splenomegaly (an abnormal increase in the volume of the spleen), muscle pain, joint pain, headache, skin rash or meningeal syndrome . “It can, however, progress to renal, hepatic, meningeal or pulmonary damage. In 20% of cases, it is complicated by a hemorrhagic syndrome. (…) Serious forms combine acute renal failure, neurological damage (convulsions, coma) and more or less severe hemorrhages (pulmonary, digestive). Late ocular complications (uveitis, keratitis) may occur”, details the Institut Pasteur.
How to treat leptospirosis?
Hospitalization is necessary for severe forms of the disease. The treatment is based on medical resuscitation and the administration of antibiotics (amoxicillin, cephalosporin and cyclins) to reduce the risk of complications, symptoms and shorten its evolution. “A monovalent human vaccine is offered in France only to highly exposed workers (sewer workers, garbage collectors). Individual protection (gloves, glasses, boots) is recommended during risky activities. A multivalent vaccine for dogs is very widely used In France”, can we read on the website of the Institut Pasteur.