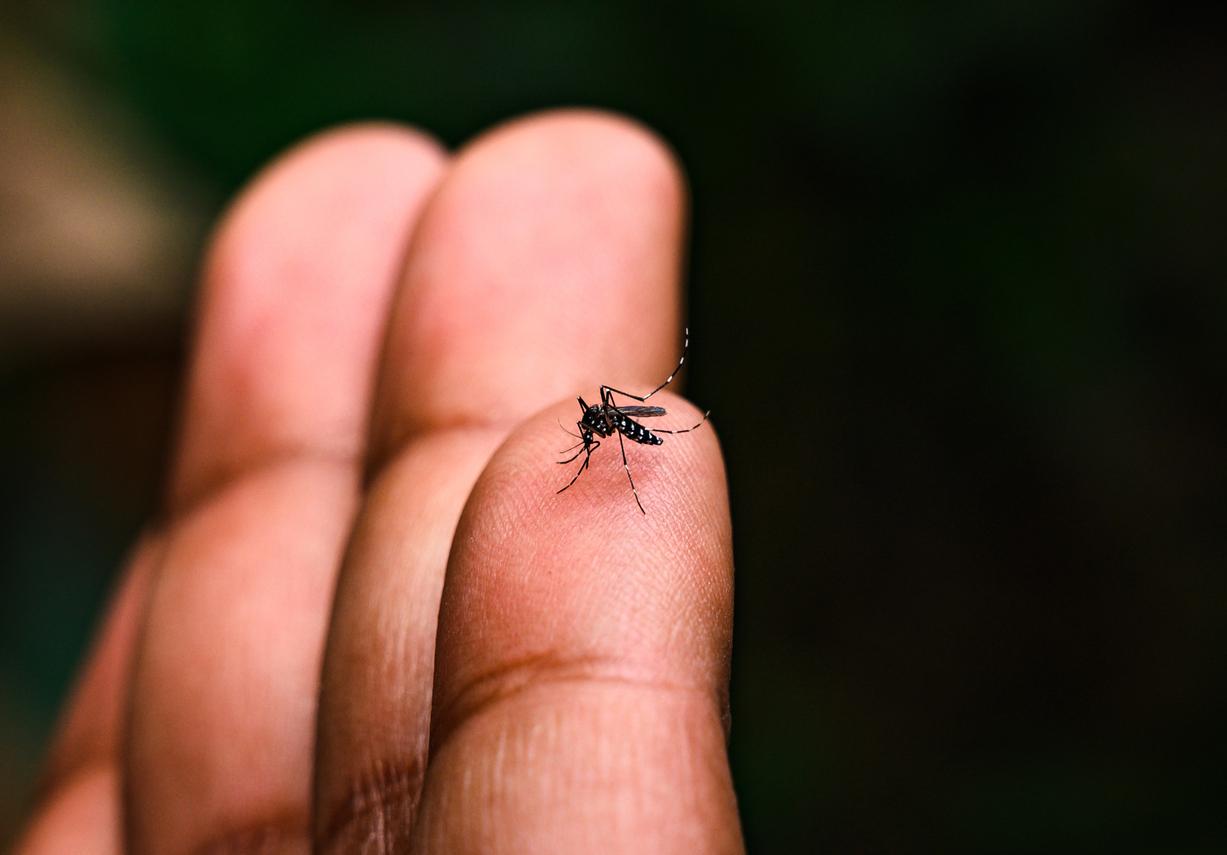
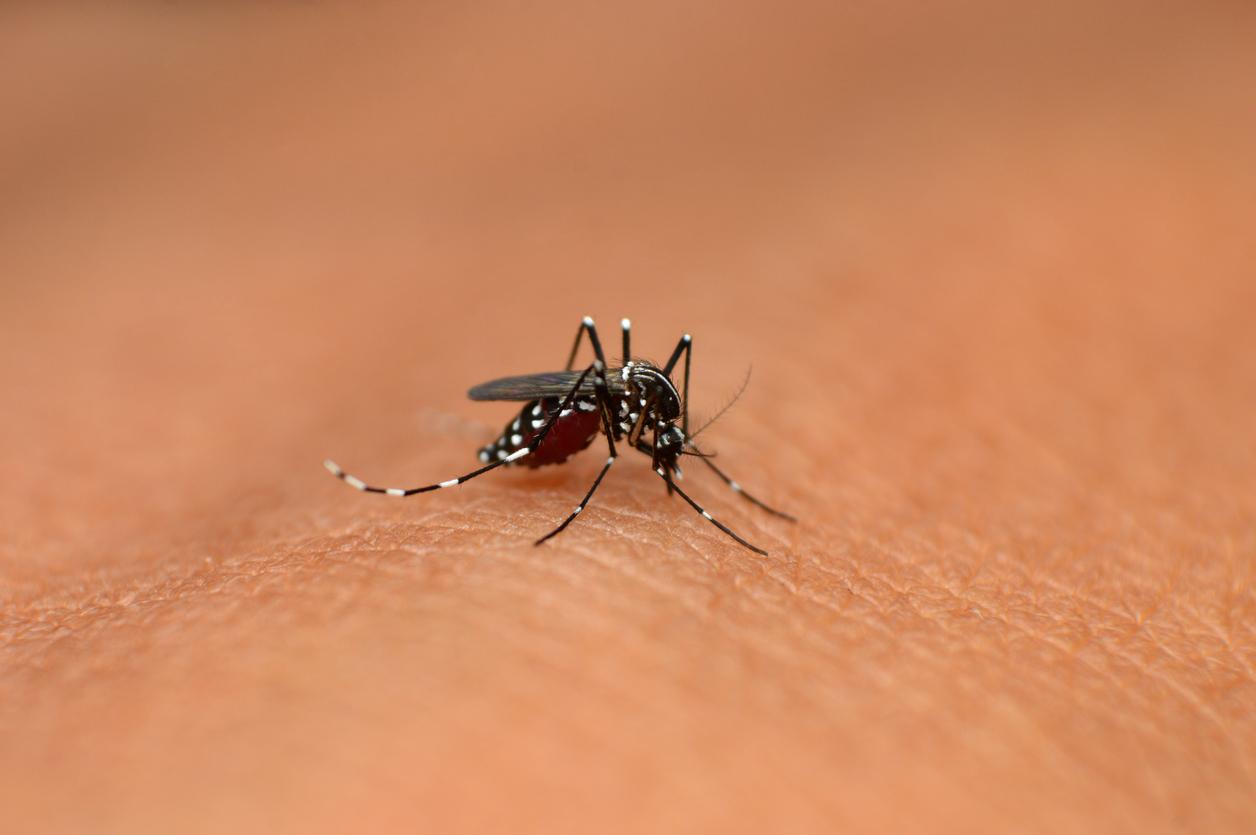
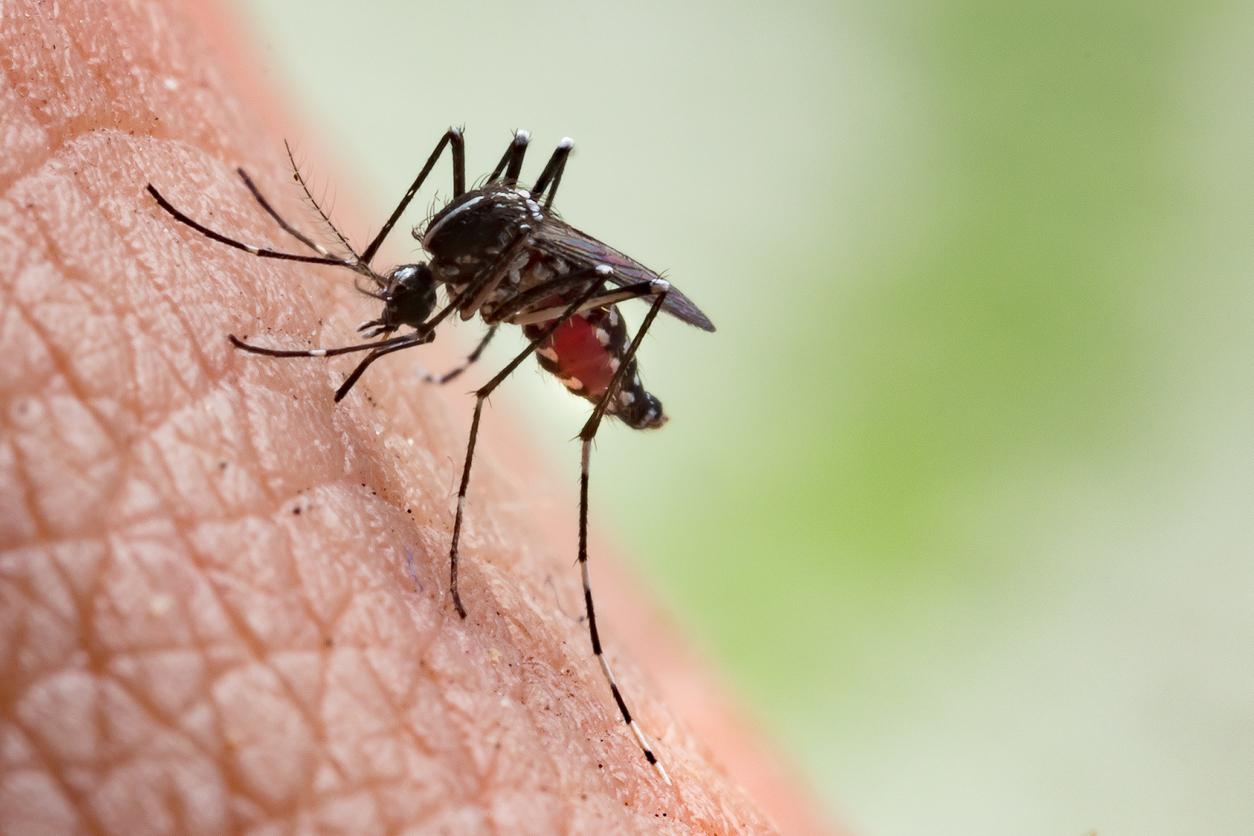
Chikungunya is a virus transmitted by a mosquito called Aedes albopictus by scientists, but more commonly known as the “tiger mosquito”, due to its contrasting black and white coloration. The disease is transmitted from man to man: the mosquito picks up the virus when it bites a sick person and then transmits it to all the healthy people it bites.
According to the Regional Health Authority (ARS) of Guadeloupe and Saint Martin, cases suggestive of chikungunya have been recorded on the Franco-Dutch island of Saint-Martin. The Health Agency (via the Health Watch division) and the National Institute for Health Watch immediately deployed a reinforced surveillance system.
After a silent incubation of 4 to 7 days on average (but which can go up to 12 days), a high fever suddenly appears accompanied by sometimes intense pain in the joints. They mainly affect the extremities (wrists, ankles and phalanges). Other signs may also occur: myalgia (pain in the muscles), headaches or skin pruritus, especially in the arch of the foot. Bleeding gums are also possible, especially in children.
The acute phase of Chikungunya infection lasts an average of 5 to 10 days: during this time the person is still contagious and will transmit the virus to the mosquitoes that bite them, which maintains the chain of transmission. Acute symptoms usually subside within 5 to 10 days. Nevertheless, joint relapses with or without fever may occur intermittently.
Chikungunya was previously unknown on the island of Saint-Martin. These first cases were transmitted by the Aedes Aegypti mosquito, which also transmits dengue fever. The ARS therefore carried out mobile spraying of insecticide and called on the population to dry up the breeding grounds of stagnant water which allow mosquitoes to reproduce.
It is also recommended to:
– wear covering and loose clothing impregnated with fabric insecticide
– apply mosquito repellents (repellents) to uncovered skin
– sleep under a mosquito net impregnated with fabric insecticide
– also use insecticides inside homes (electric diffusers) and outside (coils)
– connect the air conditioning because mosquitoes hate the coolness.