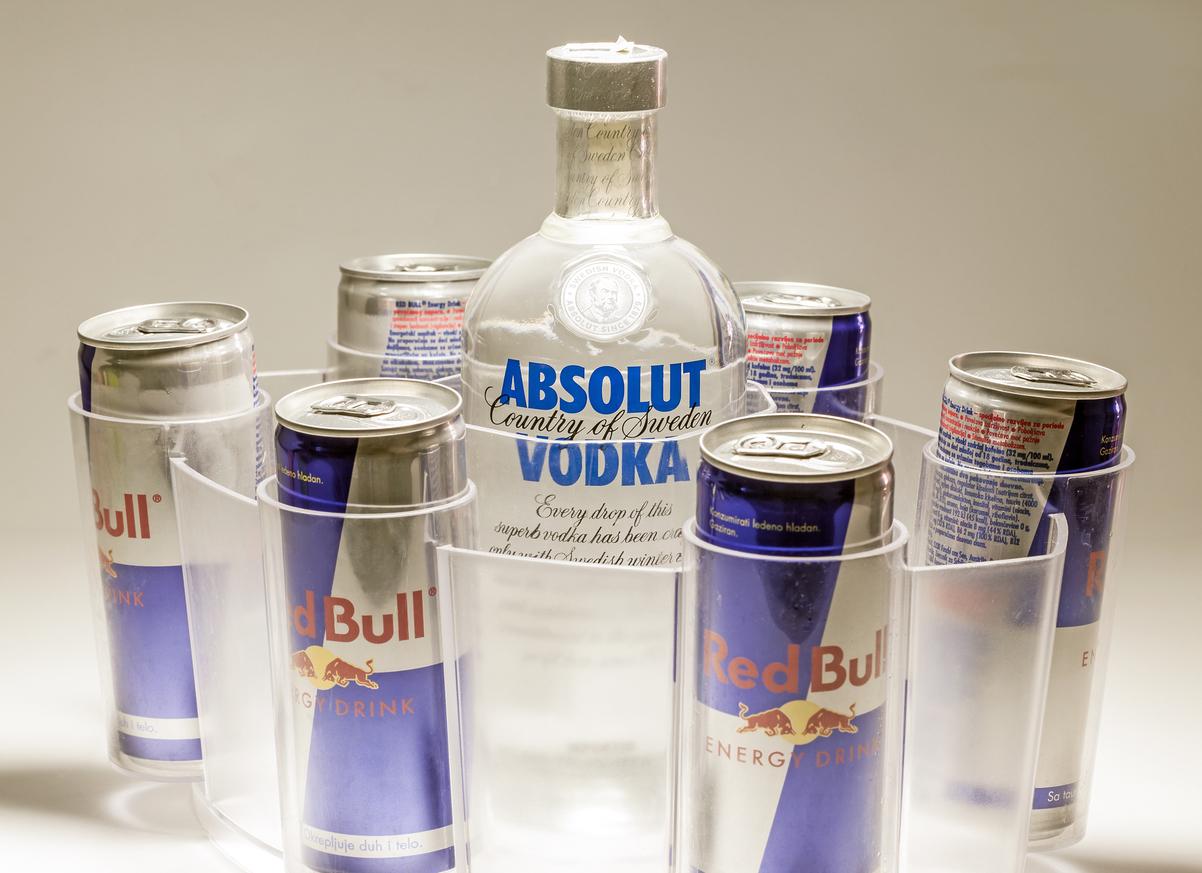
The taurine contained in energy drinks can promote cardiovascular risks by making atherosclerotic plaques unstable.

- Although taurine reduced the size of atherosclerotic plaques in mice, it also made them more likely to crack, thereby increasing cardiovascular risk.
- Indeed, plates treated with taurine had less collagen and smooth muscle cells, two essential elements to maintain their strength.
- Likewise, taurine increases the production of enzymes responsible for the breakdown of collagen in artery walls. These enzymes act like little wreckers, weakening the structure of plaques and increasing their chances of rupturing.
Taurine, an amino acid widely present in energy drinks and food supplements, is sometimes touted for its benefits for the body. For example, it would limit weight gain and anxiety, while improving endurance and muscular strength. But does that mean that it is beneficial for the heart? A new study, published in the Journal of Exploratory Research in Pharmacologysuggests that taurine could actually increase cardiovascular risks by making atherosclerotic plaques unstable.
The effects of taurine on plaques in the arteries
Atherosclerosis, characterized by the accumulation of fatty deposits in the arteries, is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. When these plaques rupture, they trigger heart attacks or strokes. According to researchers from several institutes in Nanjing (China), although taurine reduces the size of these plaques in mice, it also makes them more likely to crack, thus increasing cardiovascular risk.
To reach this conclusion, scientists analyzed blood samples from 145 people, including healthy individuals and patients with coronary heart disease. Surprisingly, taurine levels were higher in heart attack patients than in healthy ones. It was this observation that prompted researchers to explore the effects of taurine on mice genetically modified to develop atherosclerosis.
After administering taurine to the rodents for four days, the researchers noted a reduction in the size of the plaques in the arteries, but also a reduction in their stability, and therefore a greater risk of rupture. Indeed, plates treated with taurine had less collagen and smooth muscle cells, two essential elements to maintain their strength. “To give a picture, it’s a bit like taurine reducing the size of a snowpack on a mountain, but making that snowpack more fragile and more likely to trigger an avalanche.”can we read in a press release.

Taurine not recommended in case of cardiovascular history
The study also found that taurine increased the production of certain enzymes responsible for breaking down collagen in blood vessel walls. These enzymes act like little wreckers, weakening the structure of plaques and increasing their propensity to rupture. Although previous studies had suggested that taurine could prevent atherosclerosis by lowering “bad” cholesterol levelsthis new research therefore indicates that its short-term impact could be inversely risky, particularly in individuals who already have cardiovascular problems. Other studies here and there had reached more or less the same conclusion.
The Nanjing researchers do not necessarily recommend completely eliminating taurine from your diet, because it is naturally present in the body and has important functions there. However, they call for increased vigilance on the part of health professionals and consumers.