The Covid-19 pandemic has increased the use of disinfectants, but scientists warn that some can be dangerous.
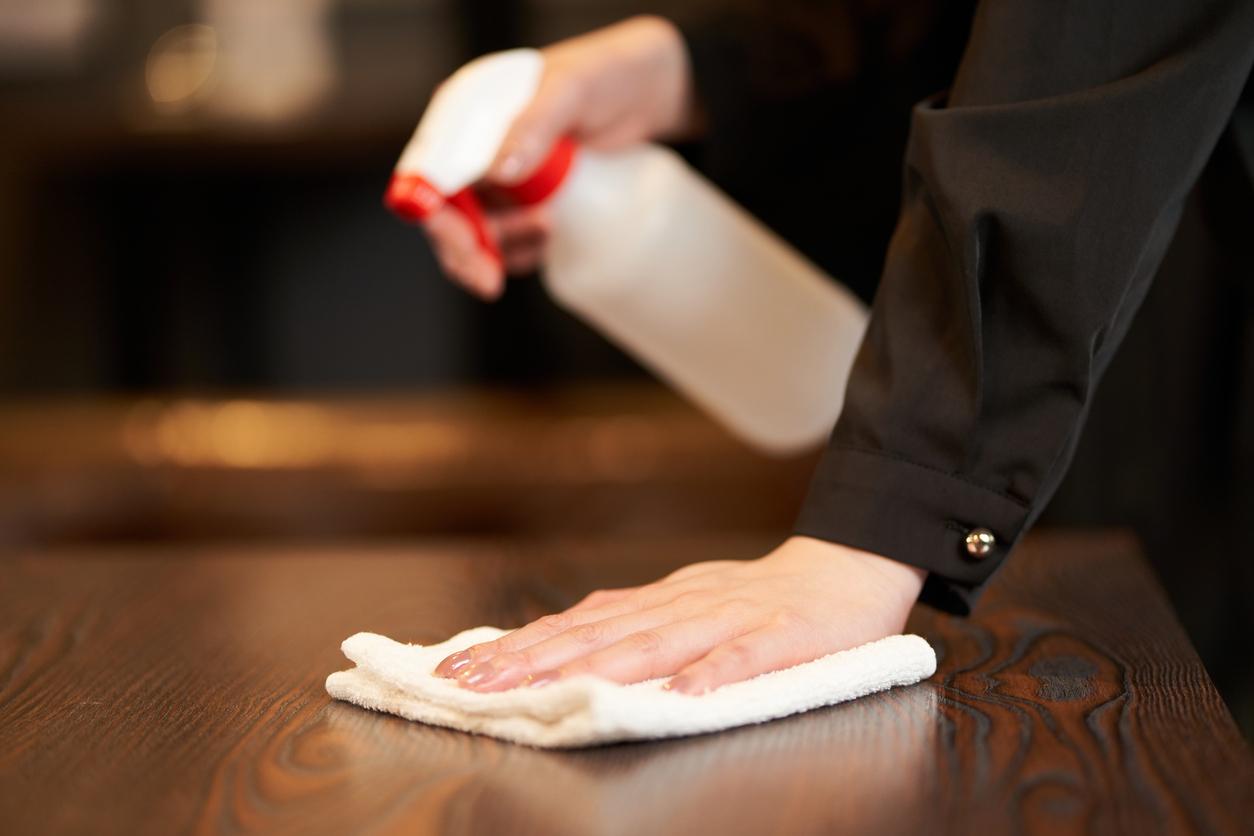

- The Covid-19 pandemic has contributed to the increase in the use of disinfectant products.
- However, some, such as quaternary ammonium compounds, can be dangerous to health.
- A group of scientists calls for limiting their use and favoring water and soap.
The Covid-19 pandemic has changed our habits. Some have returned over time but others persist, such as the use of disinfectants. According to more than 20 American scientists, the use of anti-microbial chemicals has increased dramatically. However, these can have effects on health and the environment, and increase the resistance of bacteria to antibiotics. In the review Environmental Science & Technologythey call for limiting the use of these solutions.
Disinfectants: what are quaternary ammonium compounds?
Researchers are targeting quaternary ammonium compounds, also called quats (QACs). The best known is benzalkonium chloride, but the others have names ending in formulas like “ammonium chloride“. They are used for their antiseptic properties in household products but also in certain toothpastes or hygiene products. However, several studies have shown that they can be dangerous for health. “Studies have found associations between CAQs and asthma, dermatitis and inflammation, note the authors. Studies on laboratory animals also raise concerns about potential links to infertility, birth defects, etc..” In addition, they recall that it has been proven, since the 1950s, that these chemical compounds contribute to resistance to antimicrobials, a phenomenon considered a threat to global health according to theWorld Health Organization. Products can make bacteria resistant to CAQs and more potent antibiotics.
Quaternary ammonium compounds: inappropriate or even harmful use
In their recent work, the twenty or so scientists explain how these products are increasingly marketed. “Disinfecting wipes containing QACs are often used on children’s school desks, hospital examination tables, and in homes where they remain on these surfaces and in the airsays Courtney Carignan, co-author and professor at Michigan State University. Our review of the scientific literature suggests that disinfection with these chemicals in many cases is unnecessary or even harmful..” As a replacement for these substances, she recommends carrying out regular cleaning with soap and water, when disinfection is necessary, it is better to use more “safe” products.
Why is it important to limit the use of these chemicals?
“It’s ironic that the chemicals we deploy in vain for one health crisis actually fuel another.“, believes Erica Hartmann, co-author and professor at Northwestern University. “Antimicrobial resistance was already contributing to millions of deaths a year before the pandemic. Overzealous disinfection, especially with products containing QACs, threatens to worsen the situation.” On the other hand, we should not fear a greater spread of Covid-19, on the contrary, Carol Kwiatkowski, co-author considers that the reduction in their use will make “make our homes, classrooms, offices and other shared spaces healthier“.

Why is it important to limit the use of these chemicals?
“It’s ironic that the chemicals we deploy in vain for one health crisis actually fuel another.“, believes Erica Hartmann, co-author and professor at Northwestern University. “Antimicrobial resistance was already contributing to millions of deaths a year before the pandemic. Overzealous disinfection, especially with products containing QACs, threatens to worsen the situation.” On the other hand, we should not fear a greater spread of Covid-19, on the contrary, Carol Kwiatkowski, co-author considers that the reduction in their use will make “make our homes, classrooms, offices and other shared spaces healthier“.