This practice from Chinese medical tradition helps reduce depressive symptoms.
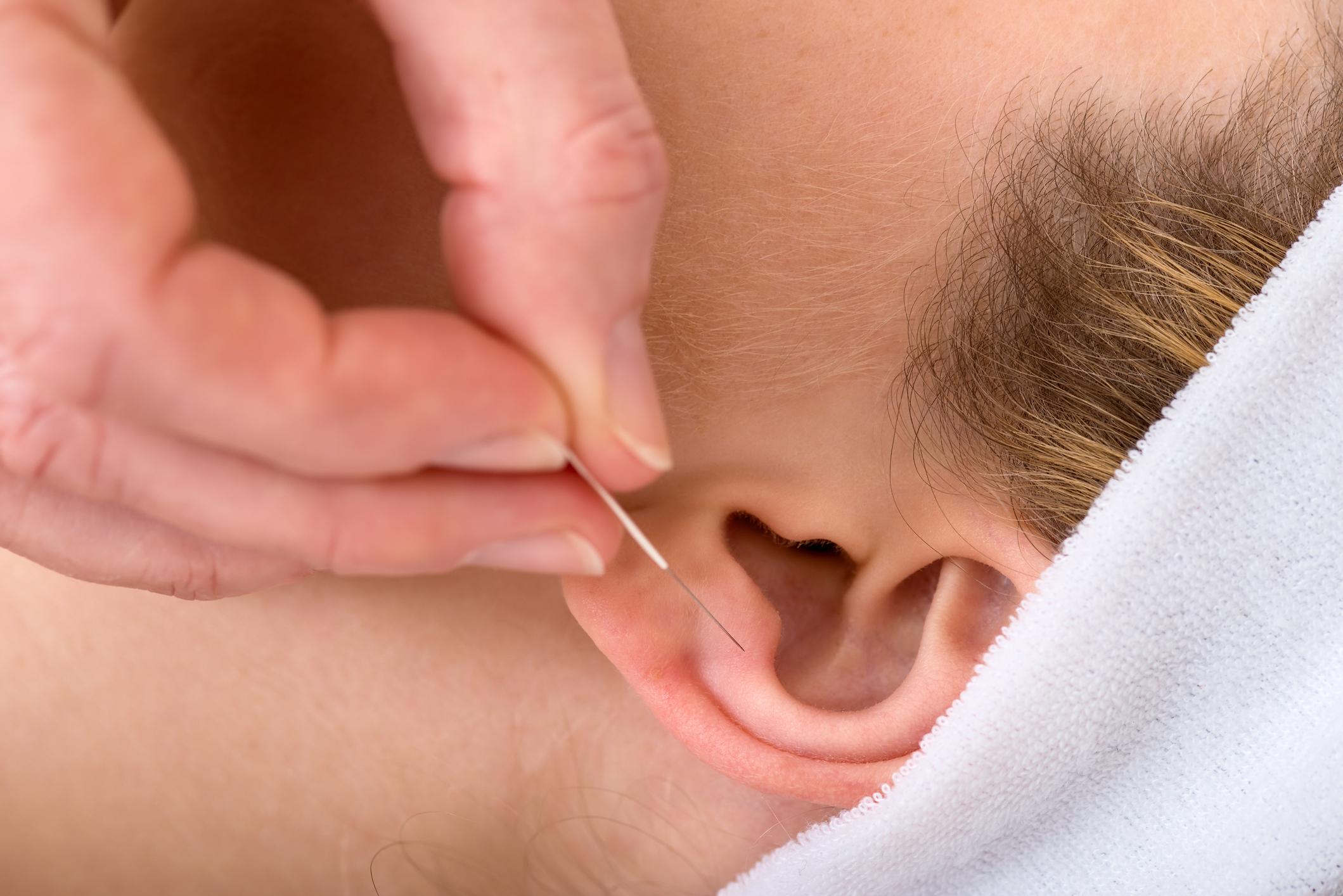
- Auricular acupuncture is a Chinese technique in which fine needles are inserted into points on the outer ear to stimulate various organs.
- In the study, 46% of participants reported a cessation of symptoms, compared to 13% in the group that received the placebo.
- There were no significant differences in serious adverse events between groups, supporting the safety of the intervention.
Is ear acupuncture a safe and effective treatment for depression? This is the question asked by researchers from the universities of São Paulo and Santa Catarina (Brazil). In order to answer this question, they carried out work, the results of which were published in the journal JAMA Network Open.
37 depressed patients benefited from 12 ear acupuncture sessions
For the purposes of their study, the team recruited 74 people, aged approximately 29, whose Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ9) scores indicated moderate or moderately severe depression. They were divided into two groups.
One received 12 15-minute ear acupuncture sessions over a six-week period. As a reminder, this is a practice from Chinese medical tradition, which is based on the idea that health depends on the circulation of energy in the body, according to the Ministry of Health. The latter consists of stimulating points on various locations on the body using techniques that can be physical, such as the implantation of needles, acupressure devices, application of suction cups, magnets, or use of lasers.
The second group received a non-specific treatment using points not associated with symptoms of mental disorders: cheek, face and four points on the helix. “A tracking device was used to confirm which areas had neuroreactive spots,” the scientists clarified. For ethical reasons, all participants continued their usual treatment for depression. The effectiveness and safety of acupuncture were evaluated after four weeks, six weeks and three months.
Depression: 46% of participants “reported a cessation of symptoms”
At the end of the follow-up period, the PHQ9 scores of 58% of patients who received ear acupuncture sessions improved by at least 50%. The proportion for the group that received a placebo was 43%. Despite this difference, which was not considered statistically significant, the authors note that some results were promising. In detail, the proportion of volunteers showing recovery and remission of depression was higher in the group who had auricular acupuncture after four weeks and three months.
“Our results showed that nearly 60% of participants recovered from depression using this quick and simple method. According to other published research on the subject, this rate is similar to the recovery rate for drug treatment. Additionally , 46% of these volunteers reported a cessation of symptoms, compared to 13% in the group who received the placebo. For comparison, the proportion is approximately 35% among patients taking medication. has explained Daniel Mauricio de Oliveira Rodrigueswho led the study.

Auricular acupuncture: absence of serious adverse effects
When it came to serious side effects, the team revealed no significant differences between the intervention group and the control group. A large majority of participants (94%) reported only mild pain at the needle application site. “This proves the safety of the procedure for more than six weeks”said the lead author of the work.
Although these results are encouraging, the researchers say additional research with larger samples and longer interventions is needed to confirm them.















