Reducing abdominal fat could relieve chronic pain in women.
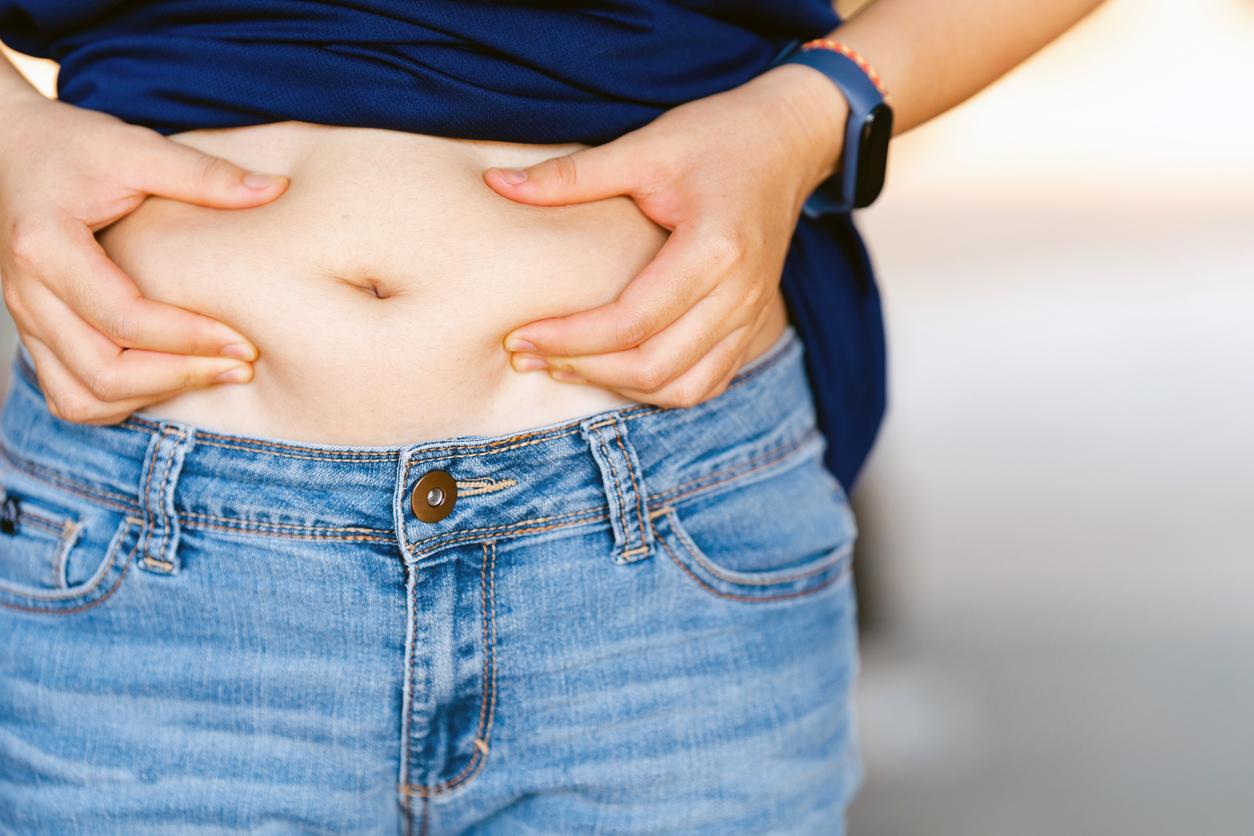

- A new study links excess abdominal fat to chronic pain, particularly in women.
- This link remains constant across the age, size and lifestyles of the participants in this study.
- This work suggests that losing abdominal fat could help manage chronic pain.
A new study recently published in the journal Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine sheds new light on the relationship between chronic pain and abdominal fat in women.
The study, conducted on more than 30,000 participants, the majority of whom were women with an average age of 55, highlighted a significant link between excess abdominal fat and the presence of chronic pain. While obesity was already associated with musculoskeletal pain, this study highlights the specific role of adipose tissue in the occurrence of persistent pain.
A stable link between pain and abdominal fat outside of other factors
Researchers have observed that reducing abdominal fat may help reduce the intensity of chronic pain in women. This correlation remains stable and does not appear to depend on factors such as age, size, physical activity, alcohol or tobacco consumption.
To accurately quantify visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue, UK Biobank study participants underwent abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measurements, providing rich data to study the relationship between abdominal fat and chronic pain.
Towards new strategies for preventing chronic pain
Although significant links were found, the researchers emphasize that this study remains observational and does not establish a direct cause and effect between excess abdominal fat and chronic pain. Further investigations will be necessary to further explore this complex relationship and better understand the underlying mechanisms.
By highlighting the link between abdominal fat and chronic pain, this study could, however, pave the way for new strategies for preventing and managing these public health issues, with an emphasis on weight management and promoting a healthy lifestyle. “Reducing abdominal adiposity can be considered a goal for the management of chronic pain, suggesting that excessive fat deposition may be involved in the pathogenesis of widespread musculoskeletal pain”the researchers point out.