A new study confirms that the incidence of autism spectrum disorder is high in children exposed to topiramate, valproate or lamotrigine before birth.
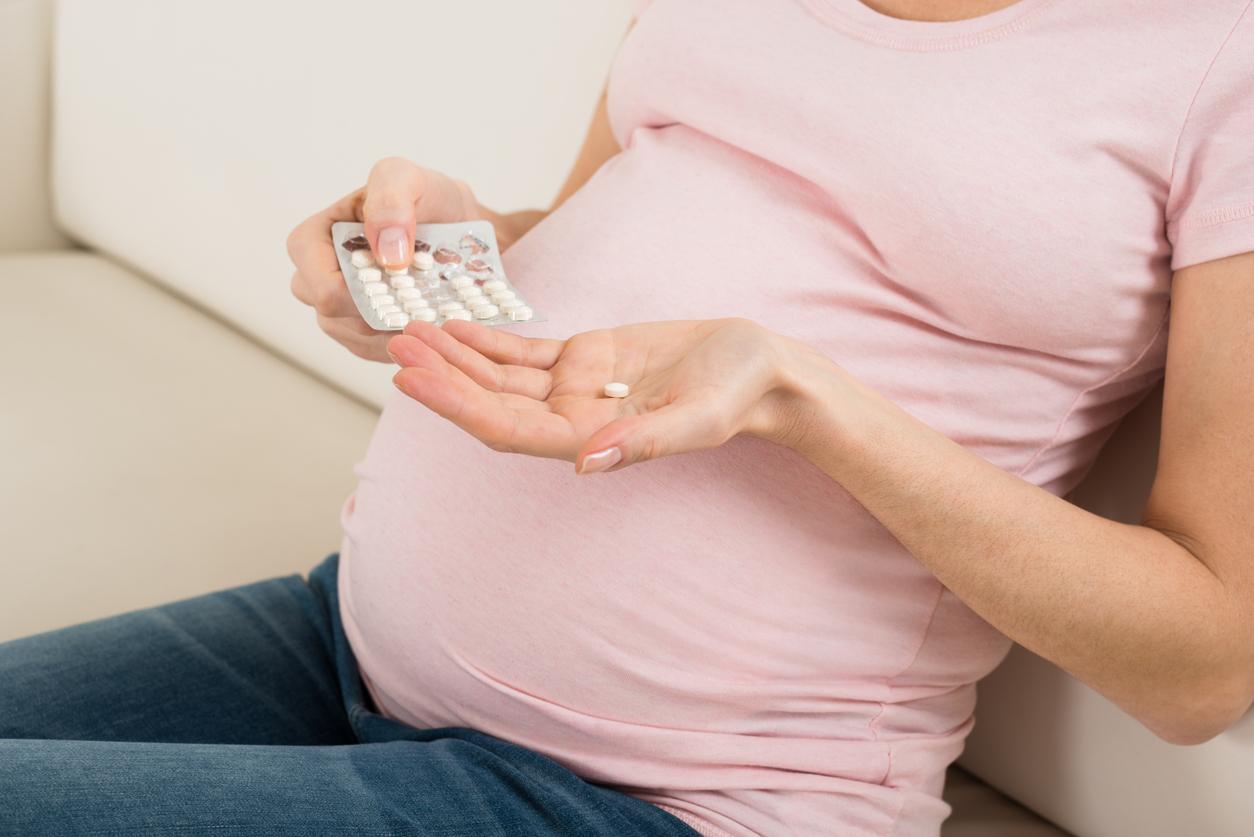

- In the study, at the age of eight, the risk of developing autism spectrum disorders was 1.9% for the 4,199,796 children not exposed to antiepileptic drugs.
- For toddlers born to mothers with epilepsy, the incidence was 6.2% with exposure to topiramate, 10.5% with exposure to valproate, and 4.1% with exposure to lamotrigine.
- “The association was significantly attenuated for topiramate and lamotrigine, whereas an increased risk remained for valproate,” according to the authors.
Maternal use of certain antiepileptic treatments during pregnancy has been associated with an increased risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in unborn children. Among the disorders, we find “the disruption of brain development, which can lead to an intelligence quotient lower than that observed in the general population, a delay in learning, and autism-like disorders”according to the ANSM. In a recent study, researchers from Harvard TH Chan School of Public Health in Boston confirmed that the risk of developing autism spectrum disorder was increased for children exposed to epilepsy medications while in the womb. of their mother.
Studying the exposure of babies to antiepileptic drugs in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy
To reach this conclusion, scientists identified a cohort of pregnant women and their children in two American databases. Information was collected from 2000 to 2020. Exposure to specific antiepileptic treatments was defined based on prescriptions filled from the 19th week of pregnancy until delivery. Children who were exposed to topiramate during the second half of pregnancy were compared to those who were not exposed to any antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy for the risk of autism spectrum disorder.

ASD: more risks when the mother took valproate
According to the results, published in the journal New England Journal of Medicine, at age eight, the estimated cumulative incidence of autism spectrum disorder was 1.9% for the 4,199,796 children who had not been exposed to antiepileptic medications. In contrast, for children whose mothers suffered from epilepsy, the incidence was 4.2% without exposure to antiepileptic drugs (8,815 children), 6.2% with exposure to topiramate (1,030 children), 10 .5% with exposure to valproate (800 children) and 4.1% having been exposed to lamotrigine (4,205 children)
“After adjusting for indication and other confounding factors, the association was significantly attenuated for topiramate and lamotrigine, whereas an increased risk remained for valproate,” reported the authors in the conclusions of the work.