Are you leaving for a sunny destination soon, and you hope to come back with a nice caramelized tan? Warning: according to a new study carried out by the University of Manchester (in England), making the pancake in the sun would be bad for the composition of the skin microbiota, that is to say for the “good” bacteria which naturally cover our skin. skin.
The British researchers carried out an experiment with 21 volunteers: before their holidays, 15 of them had an assumed “tan” objective while the remaining 6 participants had planned to escape the sun as much as possible.
The composition of the cutaneous microbiota of the volunteers was studied before their departure on vacation, then 24 days after their return and again 84 days later: the scientists were (in particular) interested in the 3 main bacterial populations of the skin, that is i.e. actinobacteria, proteobacteria and firmicutes.
Skin microbiota imbalance, a risk factor for certain skin diseases
Verdict? After a week of vacation, the researchers observed a drastic drop in proteobacteria in vacationers who had perfected their tan.
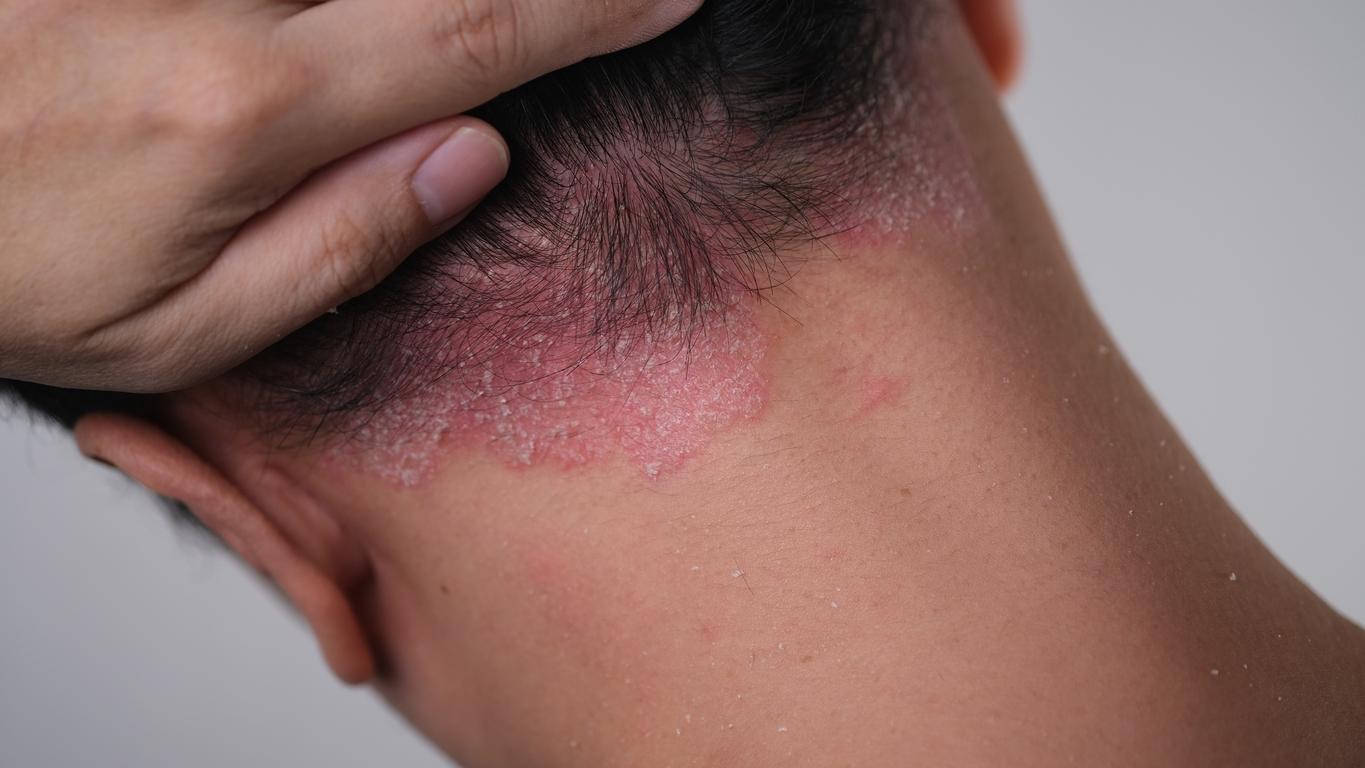
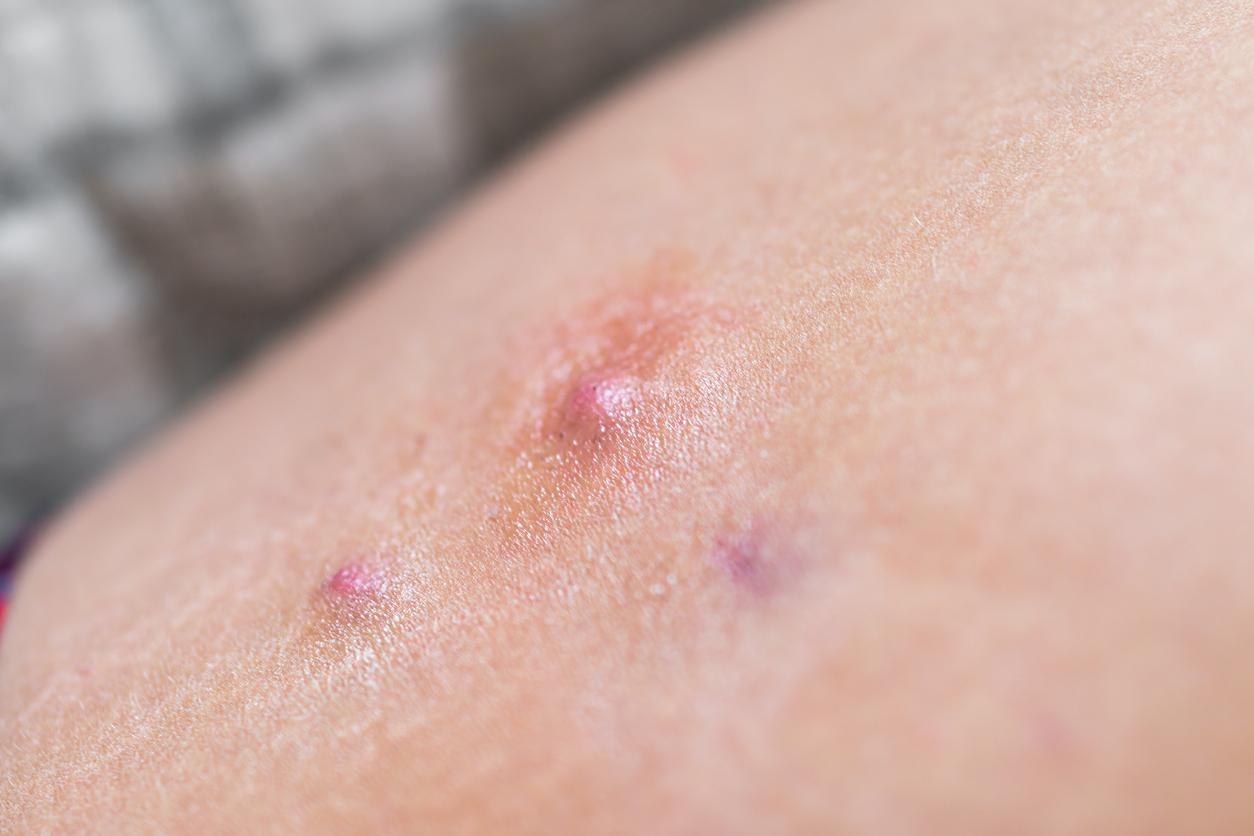
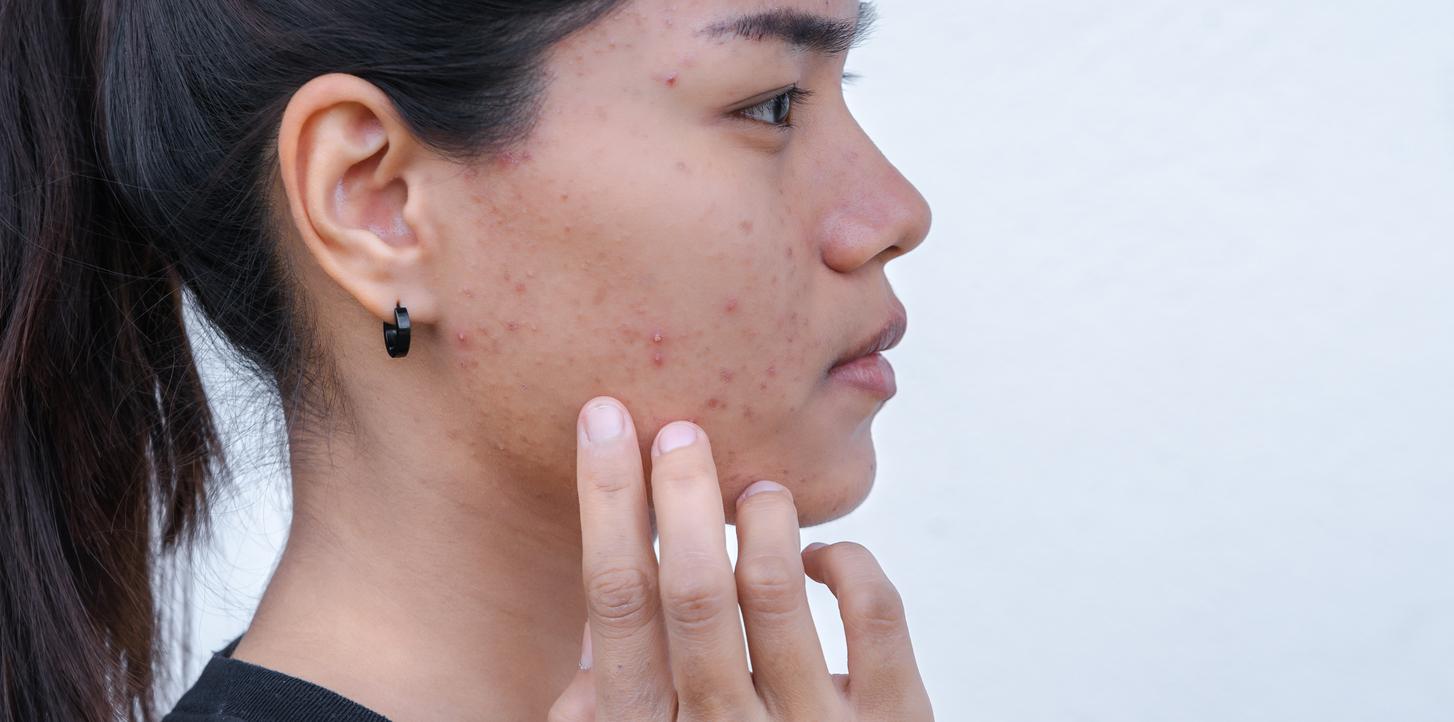
“Exposure to UV rays emitted by the sun therefore seems to be detrimental to the bacterial diversity of the skin microbiota.“analyze the scientists. This microbial imbalance is known to promote the onset of chronic skin diseases – such as atopic dermatitis, eczema or psoriasis, for example.
However, there is no question of panicking: the researchers have indeed observed a reconstitution of the skin microbiota after 28 days after returning from vacation. Phew!
Source :Frontiers in Aging