There beer, like any alcoholic beverage, should be consumed in moderation. It can have a significant impact on health: in addition to promoting weight gainit is also harmful to the liver, the immune system and increases the risk of cancer.
Indeed, people who tend to consume beer daily (and alcohol in general) are exposed to the risk of liver disease, sleep disorders, increased blood sugar and taking weight.
Michael Masi, CPT, personal trainer certified in the USA has just explained for our American colleagues Eat This, Not ThatTHE effects on the line (and not only that!) in people who drink beer every day.
A grain of significant weight
“ Beer is high in calories and contributes to weight gain “, warns Michael Masi. Another criticism: its carbohydrate content which increases the blood sugar. Beer is associated with obesity and its associated complications.
Dehydration
“ Alcohol is a diureticmeaning it promotes fluid loss and can lead to dehydrationexplains Michael Masi again. This state will play a harmful role and will also hinder your physical performance. “.
Dehydration, caused by alcohol, can lead to headaches, fatigue, excessive thirst and lethargy.
A compromised immune system
Excessive alcohol consumption can hinder immune function, making you more vulnerable to infections. “ Alcohol can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to illness, warns the coach again. It can also hinder recovery efforts in general, leading to a reduction in your abilities if you plan to engage in physical activity “.
A study published in 2017 had also demonstrated the effects of alcohol on immunity. She goes so far as to claim that heavy drinkers are at higher risk of early mortality.
Increased risk of liver disease
Consistent daily beer consumption puts your liver in danger. Excessive alcohol consumption can ultimately lead to liver inflammation, fatty liver and cirrhosis. Please note that alcoholic cirrhosis is the most serious form of alcohol-related liver disease.
Bad sleep
Does beer make you sleepy? Sorry to disappoint you, but in reality, alcohol interferes with sleep quality, leading to frequent awakenings and lack of restorative rest. Over time, this can result in trouble sleeping and fatigue during the day.
“ Alcohol has been shown to reduce the time it takes to fall asleep and increase the amount of deep sleep during the first half of the night. However, this effect reverses during the second half of the night », Explains the coach.
“ Alcohol consumption can lead to more frequent awakenings, reduced REM (rapid eye movement) sleep – crucial for memory and mood regulation – and overall lighter, more fragmented sleep. This disruption can lead to waking up unrested and tired, regardless of sleep duration “.
Nutritional deficiencies
Alcohol can interfere with the absorption of essential vitamins and minerals, thus leading to potential nutritional deficiencies. In particular, you may hinder the absorption of B vitamins, which play an essential role in energy production and overall health.
“ Alcohol can inflame the stomach lining, leading to decreased production of stomach acid, which is essential for digesting certain foods. As the liver is at the heart of nutrient metabolism, damage to this organ will reduce the ability to store and use certain vitamins and minerals. », adds Michael Masi.
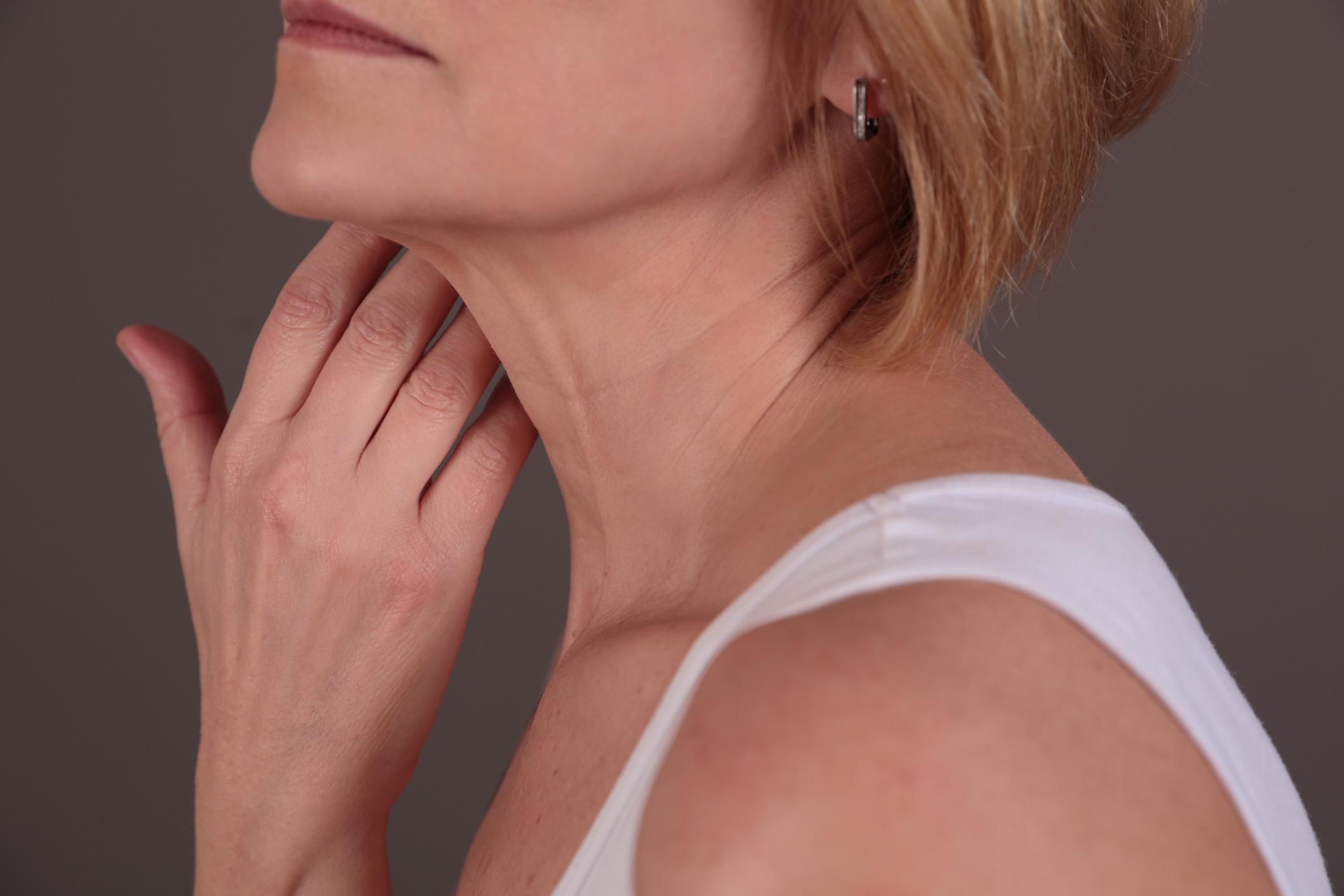
Reduced skin elasticity
Alcohol is dehydrating and chronic dehydration can lead to dry, flaky skin. Additionally, alcohol dilates blood vessels, which can lead to facial redness and broken capillaries.
“Over time, dehydration can reduce skin elasticity and contribute to the development of fine lines and wrinkles. Additionally, since alcohol can interfere with the absorption of nutrients, including essential vitamins like vitamin A and antioxidants, skin health will suffer. “.
Blood sugar spikes
Regular beer consumption may have a impact on blood sugarleading to problems such as insulin resistance and an increased risk of Type 2 diabetes. That’s because the sugar content of certain varieties of beer, as well as alcohol’s effects on insulin regulation, can disrupt your body’s ability to effectively manage blood sugar levels.
“ Additionally, alcohol can alter the body’s hormonal response, impairing insulin secretion from the pancreas. Over time, and with chronic alcohol consumption, these effects can contribute to decreased insulin sensitivity, meaning the body requires more insulin to process glucose effectively. », adds the coach.
Increased risk of cancer
According to the National Cancer Institute, daily beer consumption increases the risk of certain cancers, including cancer of the mouth, throat and esophagus. The ethanol in beer can damage the cells that line these areas, making you susceptible to developing cancer.