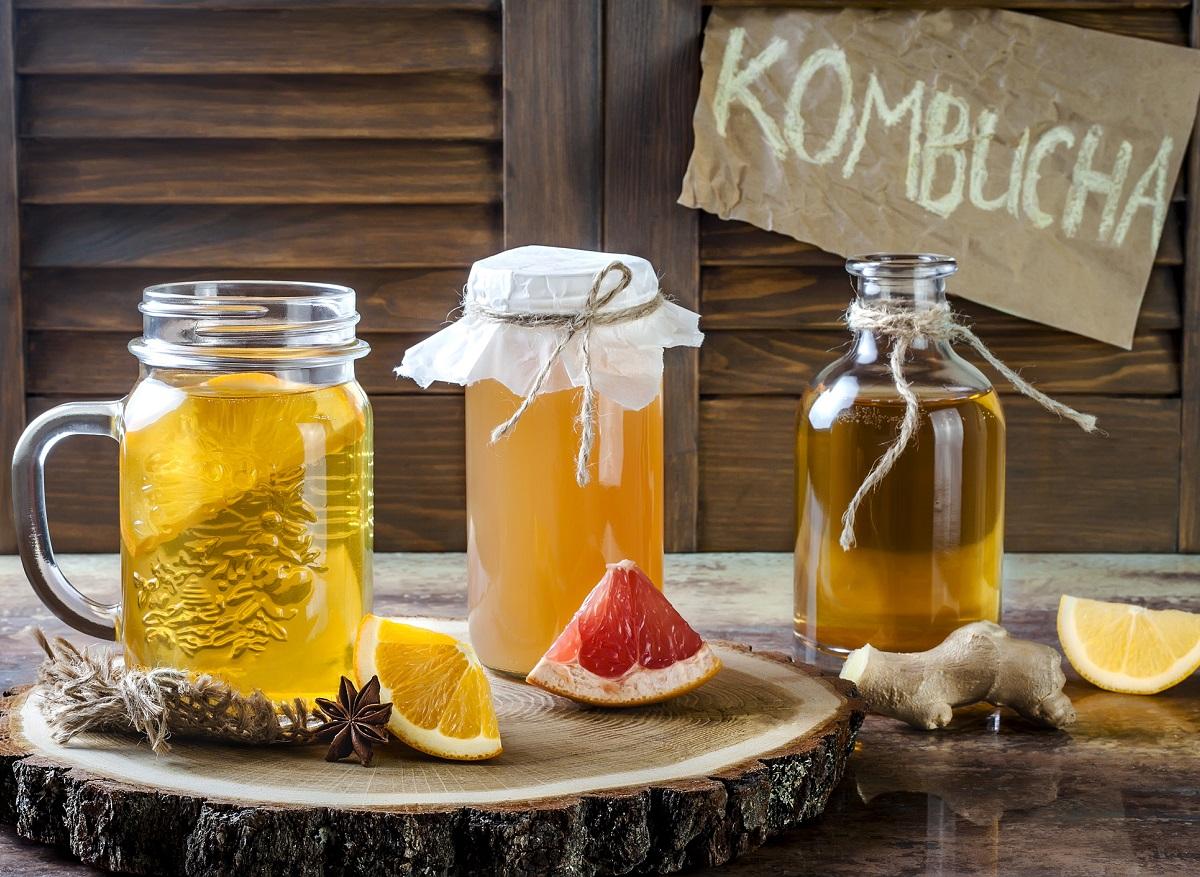
Fermented foods, such as yogurt, kombucha, and kimchi, are enjoying a resurgence in popularity, and for good reason. Packed with probiotics, these foods contribute to a healthy gut microbiome, which is essential for healthy digestion, stronger immunity, and even better mental well-being.

- Fermented foods are rich in probiotics, essential for a healthy and balanced gut microbiota.
- Diversifying probiotic sources with yogurt, kombucha and kimchi is beneficial for digestion and immunity.
- Gradually incorporating fermented foods into your diet can improve your overall well-being.
Find out why these ancient foods have become essential for those looking to improve their overall health by taking care of their gut. Fermented foods are foods that have been transformed by microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast or mold. This fermentation process not only improves the preservation of foods, but it also enriches their content of nutrients and bioactive compounds that are beneficial for health. Yogurt, for example, is a rich source of probiotics, the good bacteria that colonize our intestines and contribute to a balanced microbiota.
A healthy microbiota is crucial for digestion, nutrient absorption, and protection against pathogens. Probiotics found in yogurt and other fermented foods help strengthen the intestinal barrier, reducing the risk of inflammation and infection. In addition, these microorganisms promote the production of anti-inflammatory substances and help balance the immune system.
Kombucha, kimchi and others: diversify your plate to better protect your intestines
Kombucha, a fermented tea drink, and kimchi, a Korean dish made from fermented vegetables, have become stars of modern nutrition. Their popularity is based on their benefits for gut health, while offering a diversity of flavors and nutrients that enrich our daily diets.
Kombucha, in particular, is rich in antioxidants and organic acids that can help detoxify the liver and improve digestion. Kimchi, on the other hand, is a great source of vitamins (like vitamin C and vitamin K), fiber, and probiotics. Fermented foods like these provide a diversity of probiotic strains, which is essential for maintaining a diverse and resilient microbiome.
Diversifying your sources of probiotics by incorporating several types of fermented foods into your diet is an effective strategy to support gut health. Each fermented food provides a unique combination of microorganisms, which enriches the bacterial diversity of the gut and contributes to better digestion and increased resistance to infections.
How to Incorporate Fermented Foods into Your Diet
Incorporating fermented foods into your daily diet is easier than it seems. Start with plain, unsweetened yogurt for breakfast, a great way to feed your microbiome first thing in the morning. For those looking for a plant-based alternative, fermented coconut milk yogurt is also a probiotic-rich option.
Kombucha can replace soda at mealtimes, providing a refreshing and digestive-friendly option. Add kimchi to main dishes, such as salads or rice bowls, for a boost of flavor and nutrients. Finally, fermented pickles and sauerkraut are other easy foods to incorporate into your meals that not only provide health benefits but also provide an interesting variety of flavors.
The important thing is to start gradually, especially if you are not used to fermented foods, to allow your microbiota to adapt. Within a few weeks, you could notice significant improvements in your digestion, energy, and overall well-being.
Fermented foods are not a passing fad, but a rediscovery of ancestral know-how that has tangible effects on our health. By regularly integrating them into your diet, you can support a healthy intestinal microbiota, improve your digestion, strengthen your immune system, and even positively influence your mood. Whether in the form of yogurts, kombucha or kimchi, fermented foods offer a natural and delicious solution to take care of your health from the inside out.