With the arrival of sunny days, it is essential to use effective sun protection. Why Doctor explains to you how to choose it well so that it is adapted to your skin type.

- 80,000 skin cancers are screened each year in France
- Ultraviolet (UV) rays are a risk factor
- The choice of sun protection depends on the amount of sunshine and the phototype
The beautiful days are coming and with them, this irresistible desire to be exposed to the sun. Only here, this kind of behavior considerably increases the risk of developing skin cancer.
Risky behaviors
Approximately 80,000 new cases are diagnosed each year in France, of which 90% are cutaneous carcinomas and 10% cutaneous melanomas. The first type includes basal cell and epidermoid forms: the first does not metastasize, unlike the second which can invade the lymph nodes and metastasize.
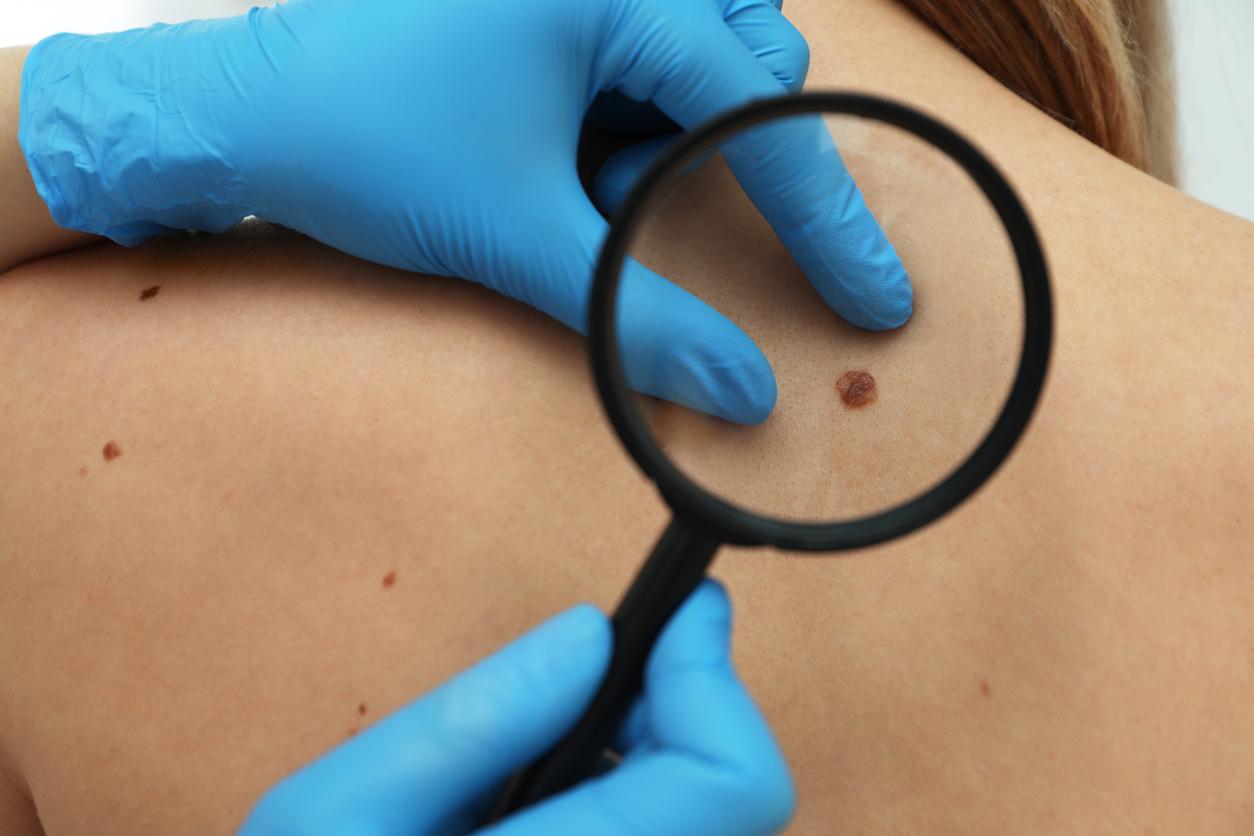
Finally, melanoma can appear on healthy skin or from the malignant transformation of a mole (nevus) and can spread rapidly to ganglionic relays and other organs if it is not detected early. .
The incidence of melanoma, which kills nearly 2,000 people each year, has increased in recent decades, in particular due to exposure to ultraviolet rays from tanning machines and the sun. However, in the long term, prolonged exposure of unprotected skin can lead to an allergy to the sun (lucitis), premature skin aging and the occurrence of melanoma. It is therefore essential to protect yourself from the sun, in particular by applying an effective sunscreen… But how to choose it?
The rays of the sun
The sun emits ultraviolet (UV) rays, which are divided into three categories according to their range: UVA (400-315 nm), UVB (315-280 nm) and UVC (280-100 nm). UVB rays are the most dangerous rays since they are the ones that burn the skin and cause sunburn. They are also responsible for 90% of melanomas. Also beware of UVA rays which cause destruction of collagen fibers and destroy the tone of the skin.
According to European regulations, a sunscreen must guarantee UVA protection at least equal to one third of UVB protection (eg: for a protection factor of 30 for UVB, the UVA ratio will be at least 10).
skin type
Each skin is different and knowing its “phototype”, ie its level of sensitivity to the sun, is essential to choose an appropriate sunscreen. There are 6 different phototypes:
– Phototype 0 : skin that easily gets sunburned without tanning, that has freckles and that generally should avoid exposure to the sun (albinos, population without melanocytes).
– Phototype 1 : very fair skin that quickly sunburns or develops freckles in case of exposure.
These phototypes are what are called “melano-compromises”: they easily get sunburn and require a very high protection cream.
– Phototype 2 : very fair skin that can become tanned with the sun, but burns easily or freckles quickly when exposed.
– Phototype 3 : medium skin, with few or no freckles, rarely sunburns and tans.
– Phototype 4 : Dark skin, rarely sunburns and tans easily.
These phototypes are “melano-competent”: they are sensitive to the sun but can tan. They need a very high or high sun protection cream.
– Phototype 5 : dark skin, naturally pigmented, tans quickly and easily.
– Phototype 6 : black skin, does not sunburn.
These “melano-protected” produce a lot of eumelanins (black melanins) and tan easily without burning.
Family history (if there have been skin cancers in the family), number and size of moles, and condition of the skin (if it has ever suffered from numerous sunburns that caused it weakened for example) are also factors to be taken into account.
sunscreen protection factor
The protection index of your sunscreen will therefore depend on your skin, but also on the conditions of sunshine and the exposure you envisage: hiking in the mountains, for example, will not have the same repercussions as prolonged exposure on the beach between 12 p.m. and 4 p.m.
There are 4 indices of protection:
– Weak protection: 6 or 10
– Average protection: 15, 20 or 25
– High protection: 30 or 50
– Very high protection: 50+
Be careful, it is more effective to apply a medium protection sunscreen several times a day than a very high protection cream only once.
Of course, the best protection is not to be exposed to the sun and/or to wear loose clothing to block its radiation. Dark colors in particular prevent UV rays from passing through. As well as dry clothes, unlike humidity.
.