Novartis presented the results of the first phase III trial showing significant efficacy of Cosentyx in the treatment of this inflammatory disease.

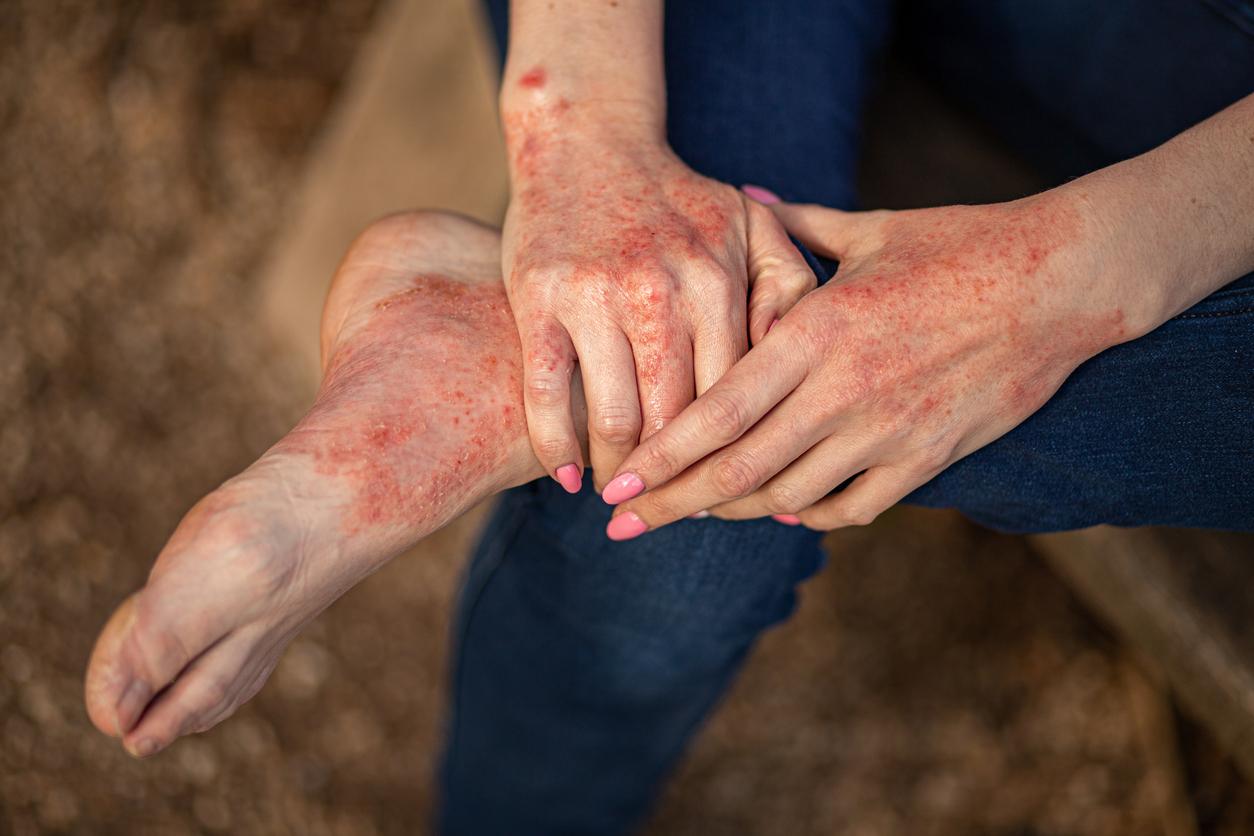
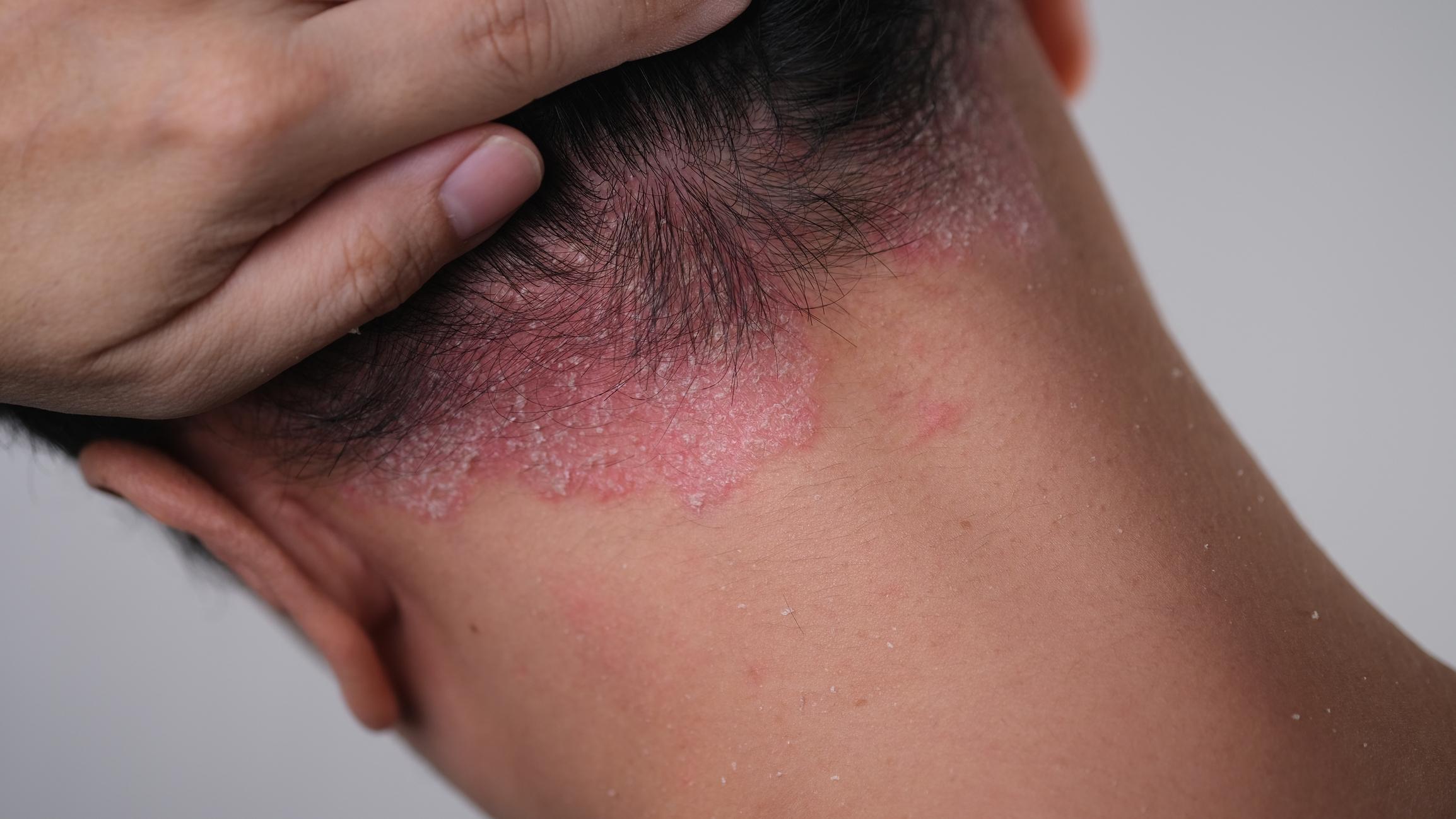
Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory disease affecting the joints. It affects about 30% of patients with psoriasis. A chronic and painful condition against which a monoclonal antibody, secukinumab, would be effective, according to a study published this Monday in the scientific journal The Lancet.
Led by the Novartis laboratory, this randomized, double-blind, phase III clinical trial is the first to show that Cosentyx (secukinumab) is effective in the treatment of rheumatism associated with psoriasis.
Comparing the drug to a placebo in nearly 400 volunteers, the researchers observed that an injection of 300 or 150 mg worked quickly and reduced the signs and symptoms of the disease for more than a year in 64% of patients. In 6 months of study, patients received 9 doses.
Disappearance of plaques
“Secukinumab is the first interleukin 17-A inhibitor to show constant efficacy for one year in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis and ankylosing spondylitis (a rheumatic disease mainly attacking the spine, editor’s note), says Vasant Narasimhan, Global Head of Development at Novartis.
The study confirms that secukinumab considerably improves the symptoms of psoriasis. In 90% of cases, the plaques disappear. A result favorable to the authorization of the American Medicines Agency (FDA) and European last January.

Well tolerated
In addition, the researchers indicate that the benefits of treatment were generally greater in patients who had not yet taken standard therapy. However, the results show that Cosentyx improves signs and symptoms in all patients. It is also very well tolerated. The most common side effects were rhinitis and upper respiratory tract infections.
“The company recently made requests for secukinumab to be prescribed for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis, and we continue to work to bring these important advances to patients,” says Vasant Narasimhan.
For the authors of the study, these encouraging results suggest that this antibody could be a treatment prescribed in first line.
.