These three common drugs, used against gastroesophageal reflux (heartburn, regurgitation) have just been associated with an increased risk of kidney failure.

Prilosec, Nexium, Prevacid… These common drugs, used against gastroesophageal reflux (heartburn, regurgitation) have just been combined in a new study at an increased risk of kidney failure. Renal failure results from the progressive and irreversible destruction of the kidneys, and results in the death of the patient if no treatment is applied.
Prefer Zantac and Pepcid
The research team focused on 43,000 patients who were taking these drugs and nothing else, and compared their medical records to 8,000 controls, this time taking Zantac and Pepcid, another class of treatment intended for them. also to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Result: patients who took Prilosec, Nexium or Prevacid were 28.4 times more likely to develop chronic renal failure, acute kidney injury (4.2 times more likely) or end-stage renal failure (35 .5 times more likely). Kidney-related adverse reactions were also 5.6% more frequent in this group than the other (0.7%).
Alcohol, tobacco and overweight
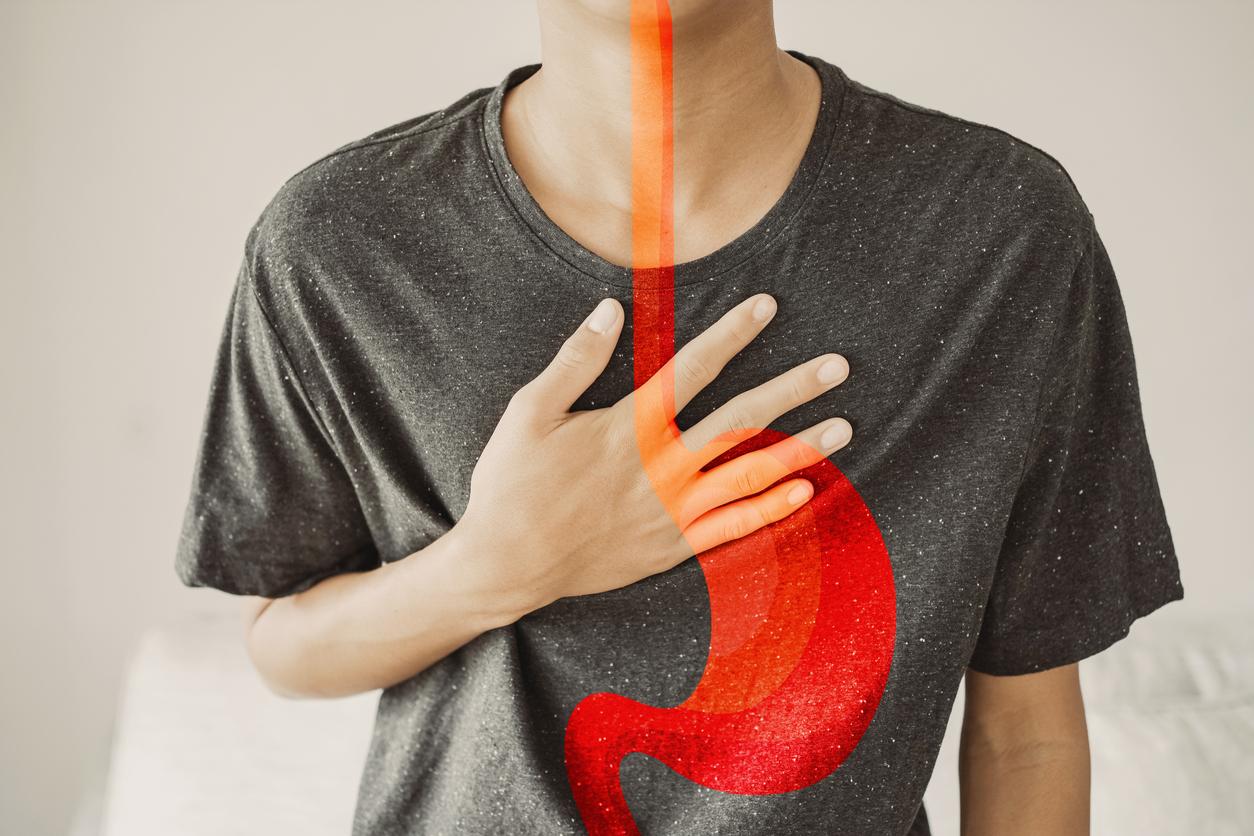
The overall prevalence (regardless of the frequency of symptoms) of gastroesophageal reflux disease in France is 31.3%, mainly in people over 50 years old. Gastroesophageal reflux, or “GERD”, is the rise of part of the contents of the stomach into the esophagus, linked to a failure of the muscle closing this part of the digestive tract. It is favored by the excessive consumption of alcohol, tobacco and by being overweight.
Gastroesophageal reflux is manifested by several symptoms that occur more readily after meals, when leaning forward or lying down. Most often, it causes burning starting from the epigastric region and going up behind the sternum, acid regurgitation (food returning to the mouth), occurring without nausea or vomiting, hiccups, belching or pain in the of the abdomen.
.