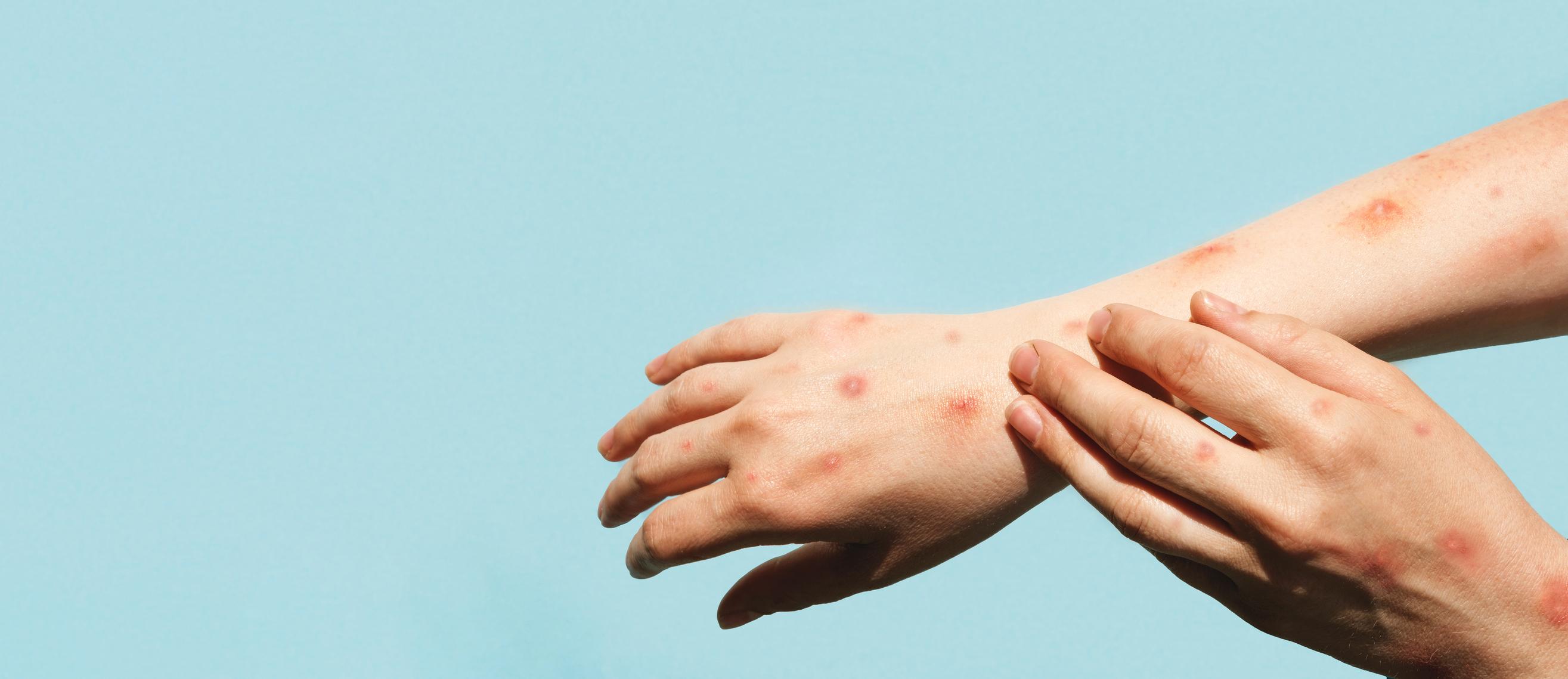
Men who have sex with men (MSM) are most affected by the monkeypox virus.

- Monkeypox was first identified in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- As of July 23, more than 16,000 cases and 5 deaths related to monkeypox have been recorded worldwide.
- In July 2022, the World Health Organization issued its highest level of alert over the rise in the number of monkeypox cases.
Since May, numerous cases of contamination by monkey pox have been reported around the world. In France, 2,601 cases have been confirmed, according to data from Public Health France, published on August 9. In the scientific journal The Lancet, researchers publish the conclusions of a study carried out in Spain, between June 11 and 29.
Frequent skin lesions
In Madrid and Barcelona, scientists recruited 181 patients, whose infection with monkeypox was confirmed during medical analyses. 92% of them said they were homosexual or bisexual, and 8% were heterosexual women or men. All presented skin lesions, particularly in the anogenital and oral areas. “In our cohort, monkeypox caused genital, perianal, and oral lesions and complications, including proctitis and tonsillitis.”, explain the authors. Proctitis is an inflammation of the rectum, and tonsillitis, an infection of the tonsils.
A “close contact” with an infected person
“Almost all participants had previous sexual exposure to someone known to have monkeypox or had risk factors for sexually transmitted diseases, such as multiple sexual partners in the 12 weeks prior to their diagnosis of monkeypox or recreational drug use during sex, note the researchers. The analysis of the samples taken from the lesions showed that the viral loads in these areas were three times higher, compared to the respiratory samples. “This observation, together with lesion location, individual exposure history, and concurrent sexually transmitted infections, suggests that close contact during sexual intercourse is the dominant form of monkeypox transmission in the current epidemic.”they conclude.
An evolution of measures?
According to them, public health messages must target populations at risk and “must be adapted to highlight the risk of transmission linked to close contact, skin to skin”. The scientists also recommend further research on viral load, at the level of lesions and in throat swabs, to find out if respiratory transmission is plausible, and therefore “whether respiratory isolation at home is necessary”. In France, infected people must remain isolated for three weeks, from the first symptoms. “This isolation, after medical advice, can be lifted after 14 days in the event of healing (healing of all the vesicles with the fall of the scabs)”noted ARS Ile-de-France. At the same time, the High Council for Public Health recommends using a condom during sexual intercourse of all types up to 8 weeks after the end of the period of contagiousness.