Detecting the warning signs of a heart attack with a simple watch would soon be possible thanks to new technology developed by Apple.
The Iwatch, Apple’s connected watch long awaited by the public could be a new ally for our health according to the “San Fransico Chronicles”.
Analyze the sound of blood
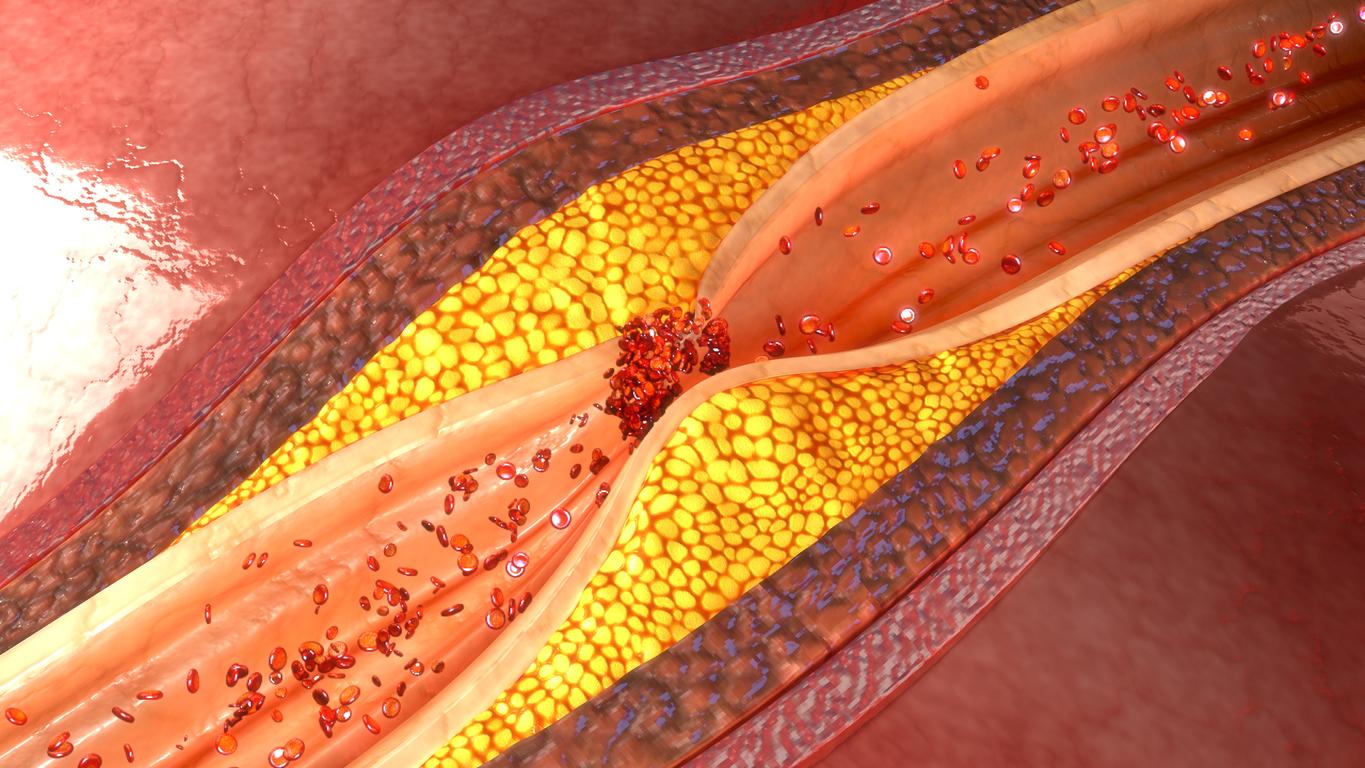
He claims that this watch will be equipped with a system capable of listening and analyzing the sound of blood as it circulates in the arteries and in particular in a blocked artery. So to predict a future heart attack.
In 2011 the American firm Apple hired Tomlinson Holman, a sound specialist and father of THX to improve the sound quality of Iphone.
The daily affirms that this master of the sound would work today to set up the process of listening to the blood.
Faster patient care
Iwatch could therefore become a real tool for prevention and above all for patient care.
Intelligent, she would be able to detect the warning signs of a heart attack, connected, she would reduce the time taken to take charge of the patient.
Because every minute counts. The person in cardiac arrest loses 10% chance of survival for every minute that passes and, in some cases, help can intervene 10 to 20 minutes after the stop.
As 90% of cardiac arrests occur outside a hospital and affect people with healthy hearts, the Iwatch would limit the time it takes for the patient to be taken care of by professionals or by witnesses to the crisis if they are close to a defibrillator.
Cardiac arrest is responsible for 50,000 to 60,000 deaths per year in France, or nearly 200 deaths per day. The survival rate is only 3%, because in the event of cardiac arrest, 40% of witnesses present during cardiac arrest and in the presence of a defibrillatordo not dare to use this object for fear and lack of training.
However, according to Inserm (National Institute of Health and Medical Research), if 30% of the population were trained in first aid, 5,000 people would be saved per year. The survival rate in France is 2 to 4%, when it is 20 to 50% in Anglo-Saxon countries where the population is more widely trained and where the automatic external defibrillator (AED) is more widely used.