Gout attacks are favored by different factors, in particular a diet rich in purines.

- Gout attacks are inflammatory flare-ups in the joints due to excess uric acid in the blood.
- A diet rich in purines can in particular be a factor favoring gout attacks.
- It is particularly advisable to have a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds to prevent gout attacks.
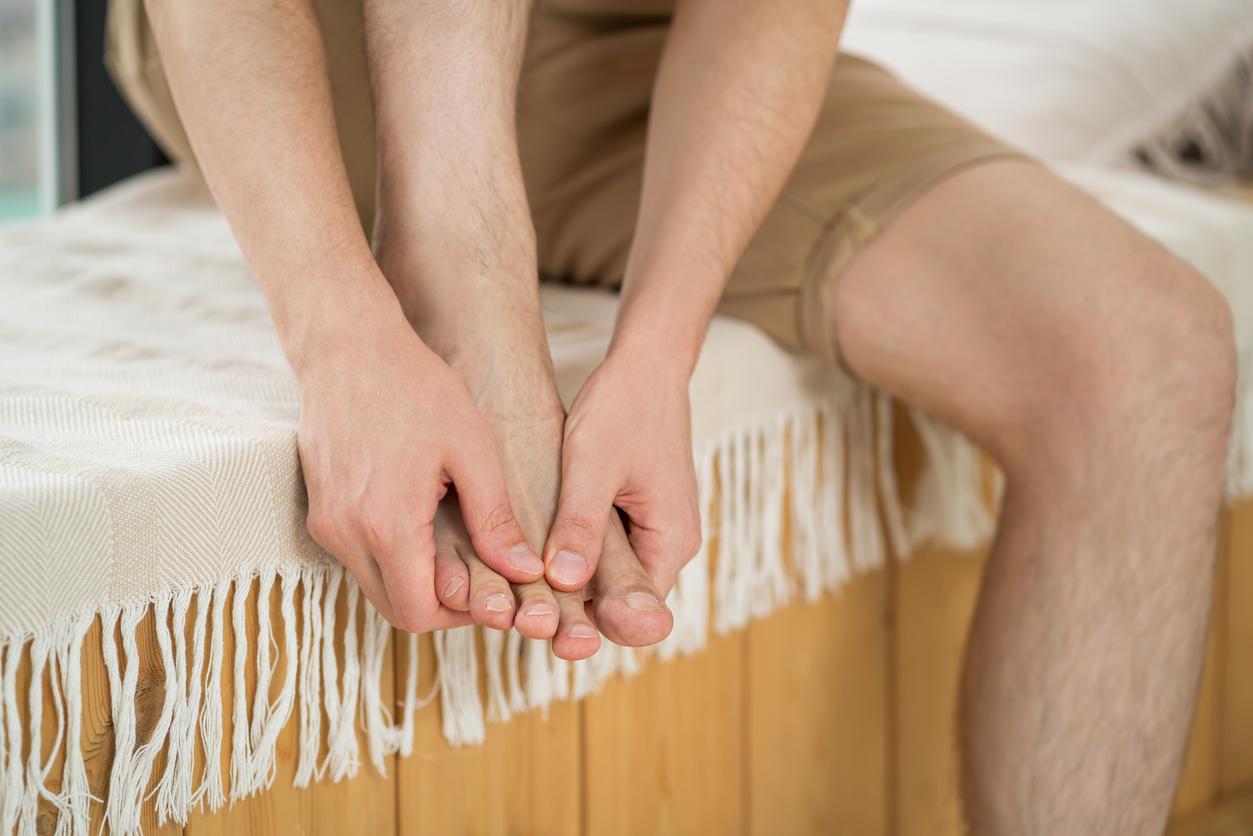
Gout is an inflammatory rheumatic disease, which is characterized by the appearance of joint inflammatory outbreaks called “gout attacks”. This pathology results from an excess of uric acid in the blood.
A diet high in purines promotes gout attacks
The attack of gout generally occurs at night, at rest, and manifests itself by intense pain at the level of a joint, which lasts between six and twelve hours. The affected joint is usually red, swollen, warm and bulky. The skin and subcutaneous tissues often show redness and/or swelling.
Different factors can cause a gout attack such as an episode of stress, taking certain medications, loss of water due to intense physical effort, dehydration or fasting. Certain foods can also promote the appearance of these inflammatory flare-ups, because they induce an increase in uric acid in the body.
Gout attack: what foods to avoid?
In case of gout, it is particularly recommended to avoid:
- meat (pork, chicken, veal, beef, lamb, etc.), which is the main food source of purines, molecules that break down into uric acid during digestion;
- fatty fish (salmon, anchovies, sardines, herring, etc.), which are also rich in animal purines;
- organ meats, which increase uric acid levels in the blood;
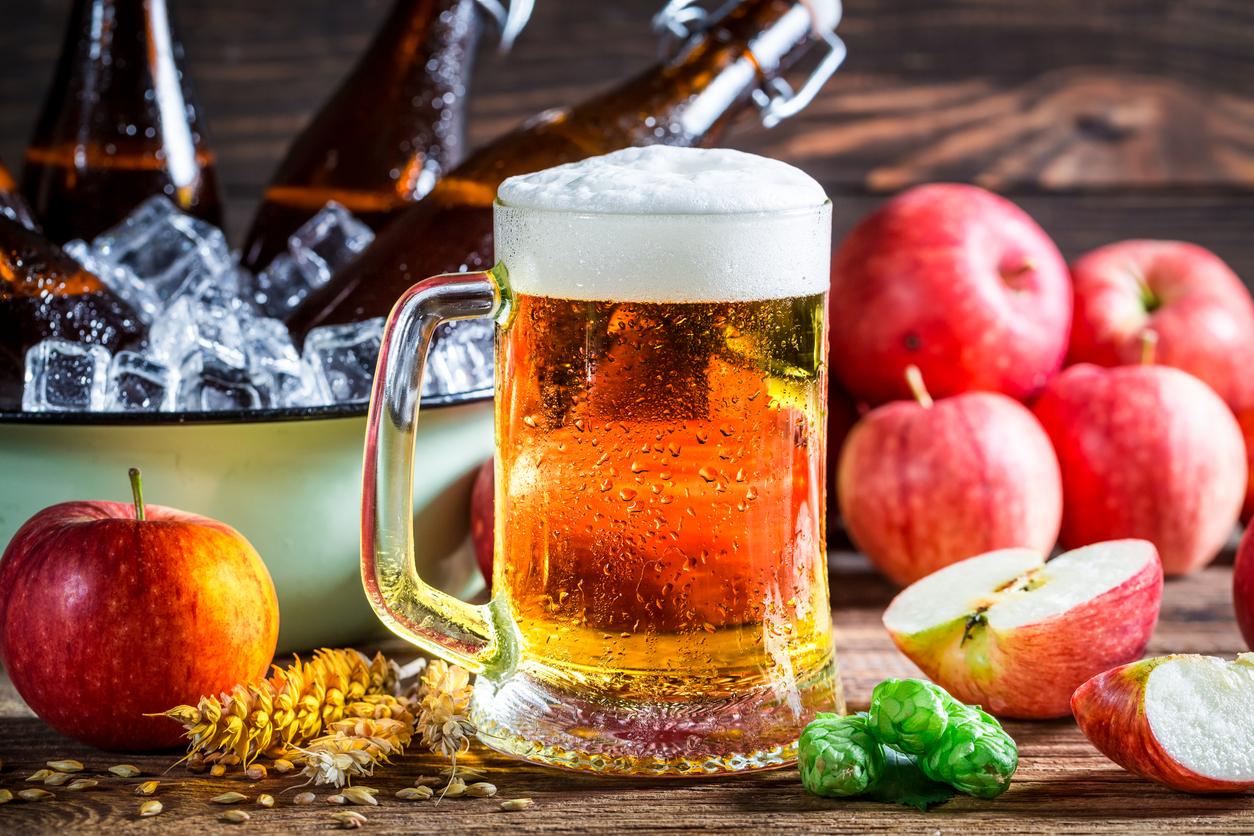
- alcohol, which prevents the renal elimination of uric acid;
- sugary drinks, which contain fructose responsible for increasing the level of uric acid in the body.
However, the frequency and intensity of gout attacks can be reduced with a healthy diet of vegetables, fruits, nuts and seeds. Hydration is also one of the keys to eliminating uric acid and preventing the risk of gout attacks.