If the first suns often seem less dangerous for health than those of summer, it is not so.

As an early heat wave hits all of France, here are some tips for enjoying it without putting your health at risk.
1/Do not expose yourself between 12 p.m. and 4 p.m.
We tend to think that the first suns are less violent than the others, which is not true. To avoid getting sunburn and thus increasing the risk of developing skin cancer, avoid exposure to the hottest hours of the day, between 12 p.m. and 4 p.m.
2/ Put on sunscreen
For the same reason as the one mentioned above, when you decide to sunbathe in May, you must put on sunscreen at least every four hours, taking care to choose a protection factor adapted to your skin. type of skin, age or possible pathologies (melasma, lupus, etc.).
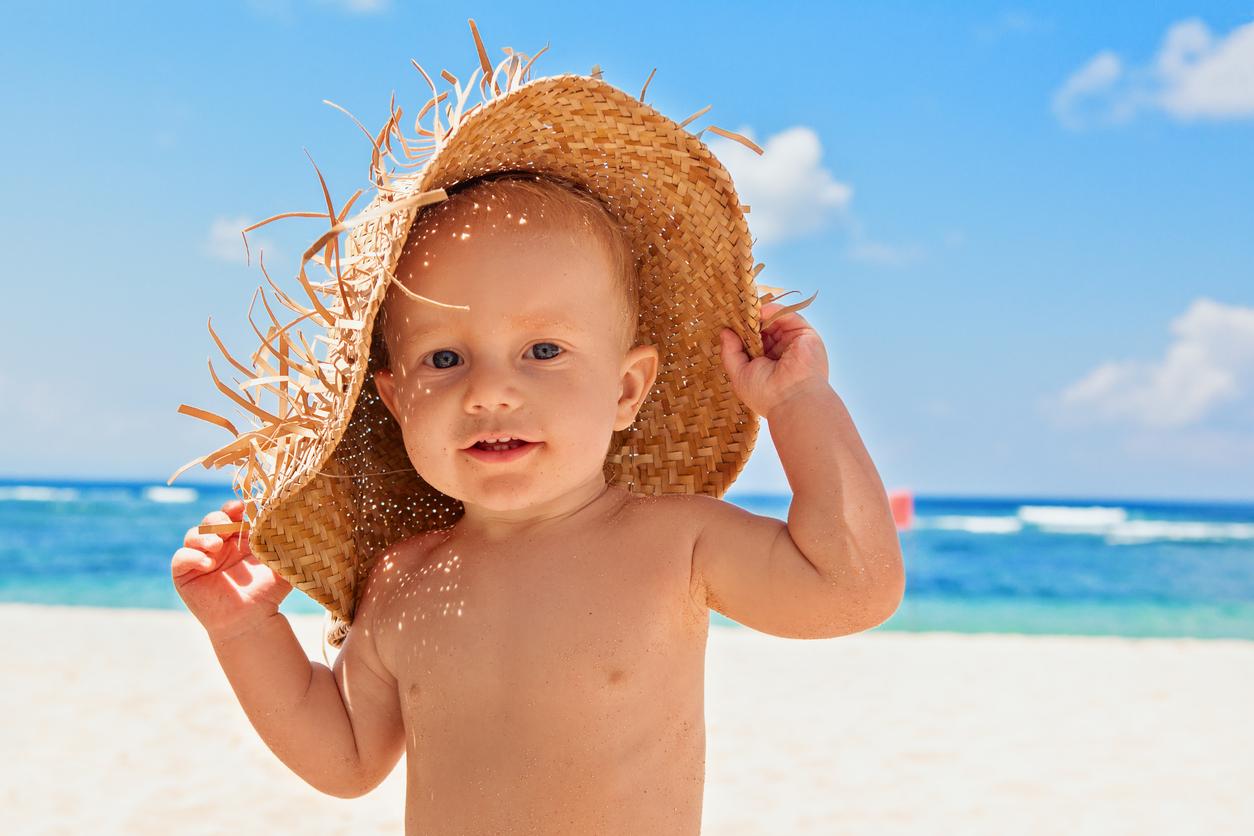
3/Cover fragile areas
It is also recommended to cover with clothes, hats and glasses the most fragile areas of the body in case of prolonged exposure to the spring sun. We will think here particularly of the ears, the feet, the eyes, the head and the face.
4/ Stay hydrated
Admittedly, we are not yet in summer temperatures, but 25 degrees are enough to make the body sweat more, so to have to drink more water than usual, or/and to consume more fresh fruits and vegetables with moisturizing properties. .
5/ Pay attention to children and the elderly
The current sun and heat, while not extreme, can be particularly dangerous for children and the elderly, who are at greater risk of dehydration and sunstroke. All the advice mentioned above must therefore be particularly applied to them.
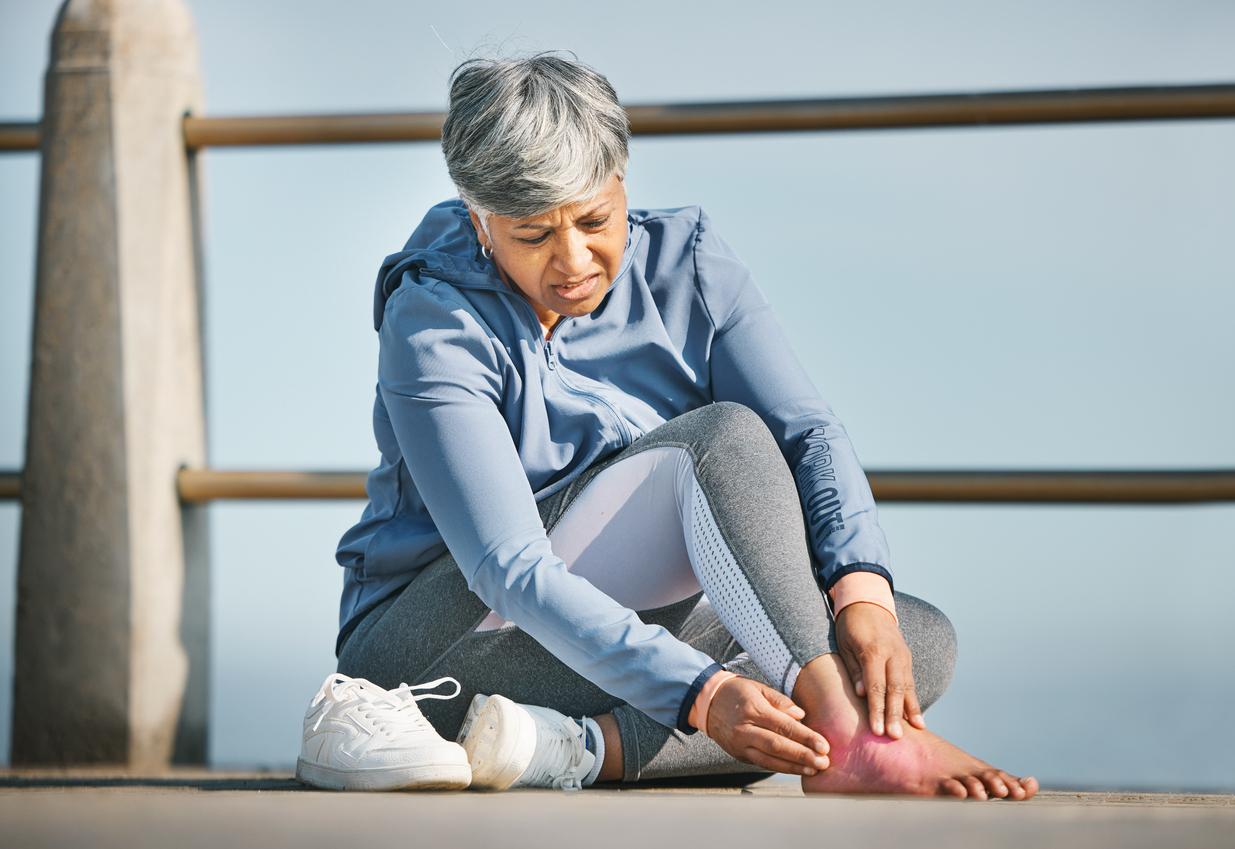
6/ Resume sport gradually
The first suns are often synonymous with the resumption of sport, sometimes neglected during the short, cold winter days. If the intention is excellent for health, be careful however not to resume an activity too intensively: you risk injuring yourself.
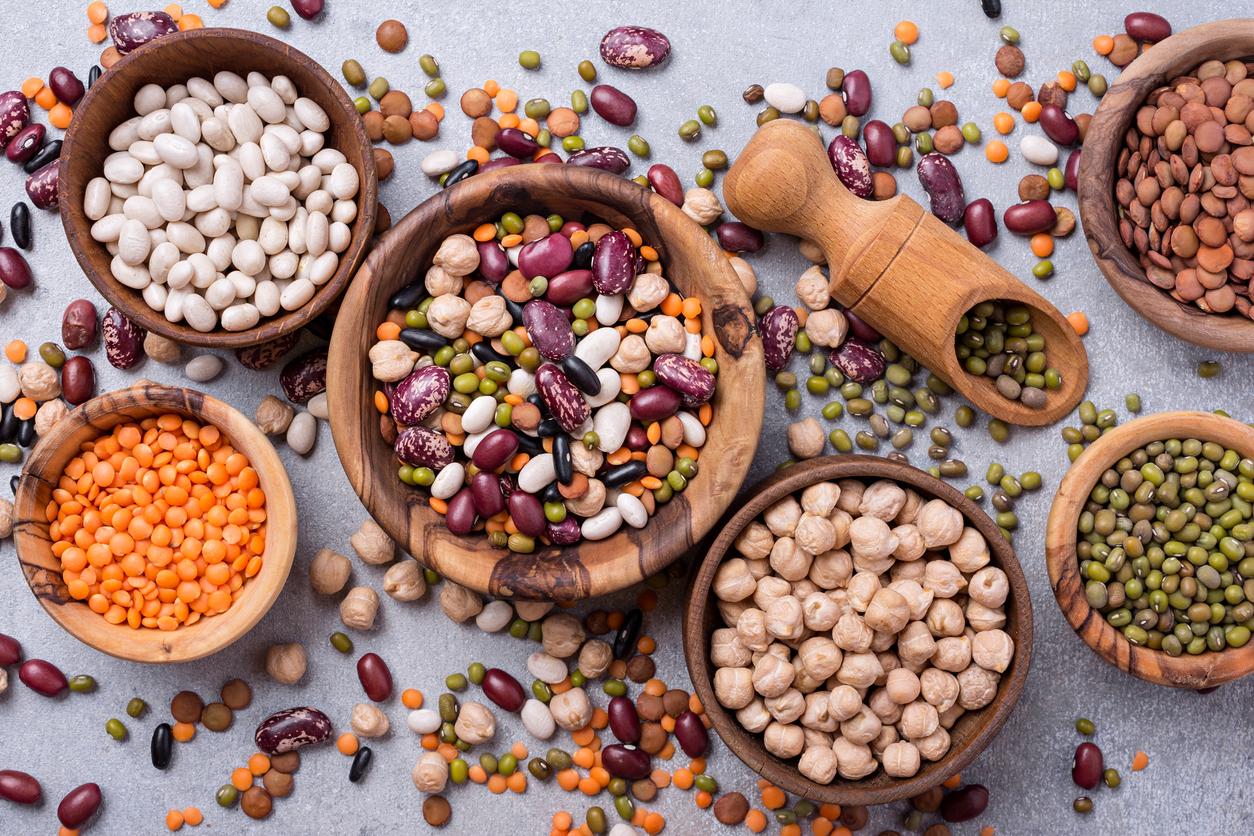
7/Do not go on an extreme diet
Finally, if the return of sunny days motivates you to lose a few pounds before the summer holidays, be careful not to set up a diet that is too restrictive. In addition to triggering a potential “yoyo effect”, it can generate nutritional deficiencies that are dangerous to health.
ncc