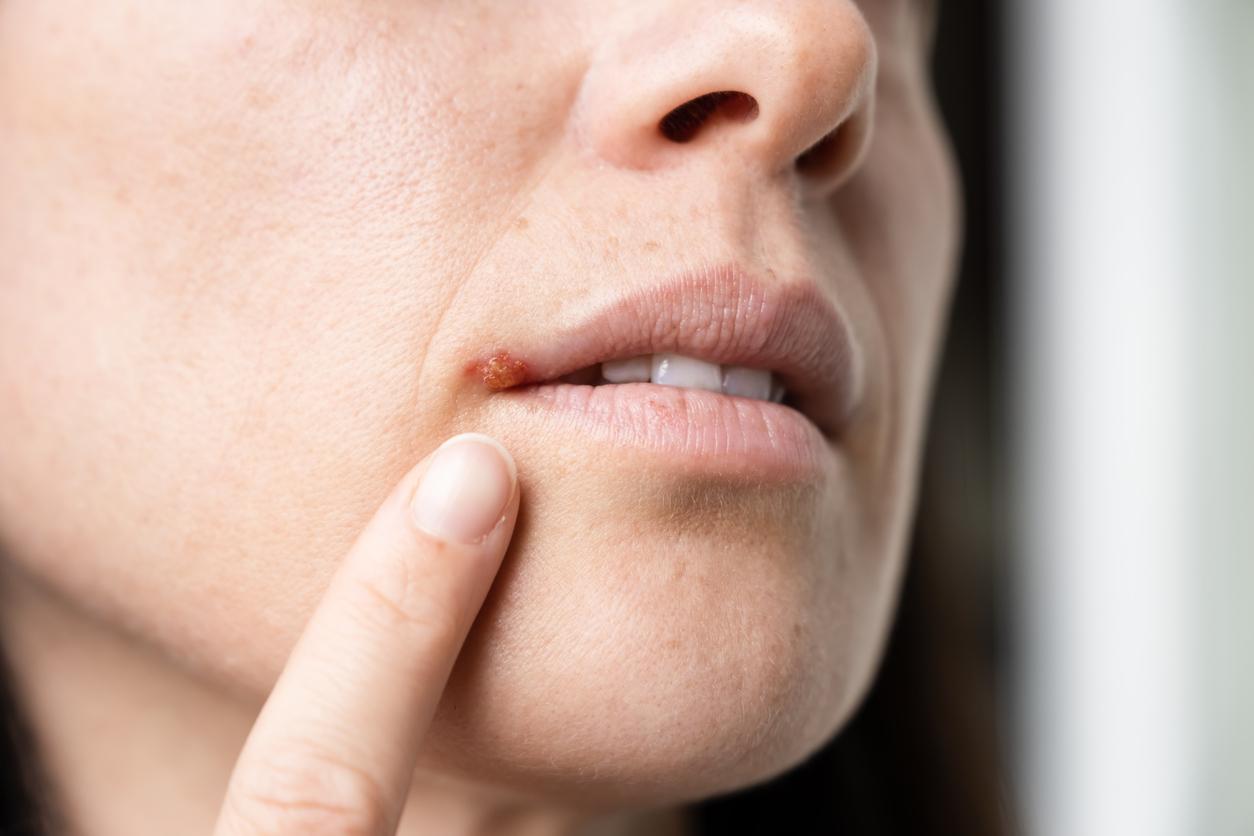
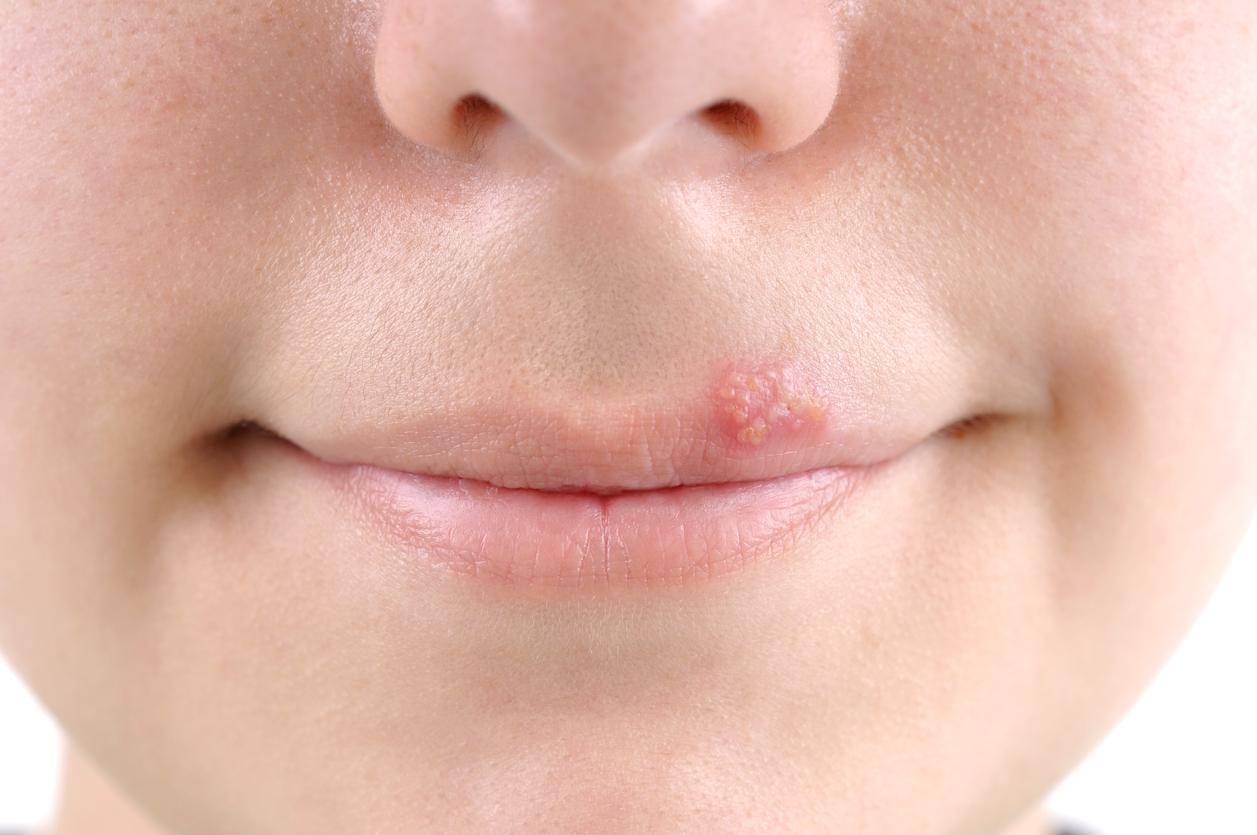
The virus always stays in the body
Genital herpes is an STD, a sexually transmitted disease. It causes burning blisters on the skin and mucous membranes of the penis, vagina and anus.
What is genital herpes?
Genital herpes or genital herpes is an STD. This STI can be transmitted via all mucous membranes, so via the vagina, penis, mouth and anus. It is caused by a virus that stays in your body forever. So you can never get rid of it completely. The herpes simplex virus causes an infection of the skin and mucous membranes.
There are two kinds:
- Type 1: This type of virus usually causes the cold sore around the mouth. It also causes about half of genital herpes cases.
- type 2: this usually only causes genital herpes, there is usually no cold sore to be seen with this form of herpes.
How often and with whom does it occur?
Anyone can get genital herpes. It does require intimate sexual contact. There must be real contact between the rash on the skin and the mucous membranes of the anus, mouth, vagina or penis. The risk of infection is greatest if you have blisters on the mucous membranes. Genital herpes is passed from person to person.
How do you get it?
There is really only one cause of genital herpes and that is sexual contact. If one of the partners is already infected before the sexual contact, he or she can transmit it.
How can you tell if you have genital herpes?
Many people do not even notice that they have contracted genital herpes. Complaints usually arise a week after you have been infected. You feel sick and, for example, get muscle pain and blisters appear. In women these blisters arise on and around the vagina and in and around the anus, in men these blisters develop on the penis, for example on the urethra and also in and around the anus.
How and when is the diagnosis made?
Your doctor will quickly diagnose ‘genital herpes’ if you suffer from many sores on the mucous membranes. But it’s important to do additional research. This can be a blood test or by removing some fluid from a blister with a cotton swab. This is examined in a laboratory and then you know for sure whether you are infected.
Extra risk if you are pregnant
If you are pregnant and contract genital herpes, it can be very dangerous for your baby. Therefore, always consult your gynaecologist or midwife. Sometimes they opt for a delivery via cesarean section to prevent your child from being infected as well.
What can be done?
Treatment is only necessary if there are complaints, because the treatment is not aimed at the condition itself, but against the symptoms. No drugs have yet been found against the herpes itself.
These are the most commonly used treatments for the symptoms of genital herpes:
- Painkillers (for pain when urinating, for example)
- Soothing ointment (also used for pain when e.g. urinating)
- Ice-pack (helps against the burning sensation that the blisters can give)
- Drink a lot (this will reduce the chance of pain)
- Antiviral medicines (stop the virus from growing any further).
Not life-threatening, but lifelong
The herpes simplex virus is certainly not life-threatening, but it remains lifelong. It can also cause complications during pregnancy.
Once you have had an attack of blisters, they can occur more often, usually unexpectedly. This can happen even years after the infection. Nasty complications are more common in women than in men, such as a yeast infection on the vagina or an ascending infection in which the uterus, ovaries and peritoneum can become inflamed. The genitals and the parts around them can also become less sensitive. But you can also suffer from strep throat and muscle pain.
Condom not always enough
A condom does not guarantee you 100 percent safety against genital herpes, the virus can also be transmitted by fingers that have come into contact with an infected mucous membrane or a cold sore. It is best to avoid sexual contact with someone who has blisters. Because that’s when the herpes is most contagious.
Other common STDs
In the Netherlands, besides herpes, these STDs are most common:
- chlamydia
- Genital Warts
- gonorrhea
- hiv
- syphilis
- hepatitis B
These are the characteristics of the various sexually transmitted diseases.
- Add comment