On the occasion of World Herpes Day this November 20, 2023, Why Doctor reviews the measures to avoid cold sores, better known as cold sores.
- Herpes labialis is caused by the Herpes simplex virus 1 virus.
- It is particularly contagious during outbreaks of cold sores.
- Several measures allow you to avoid contagions, such as avoiding kissing loved ones at the first symptoms of a cold sore.
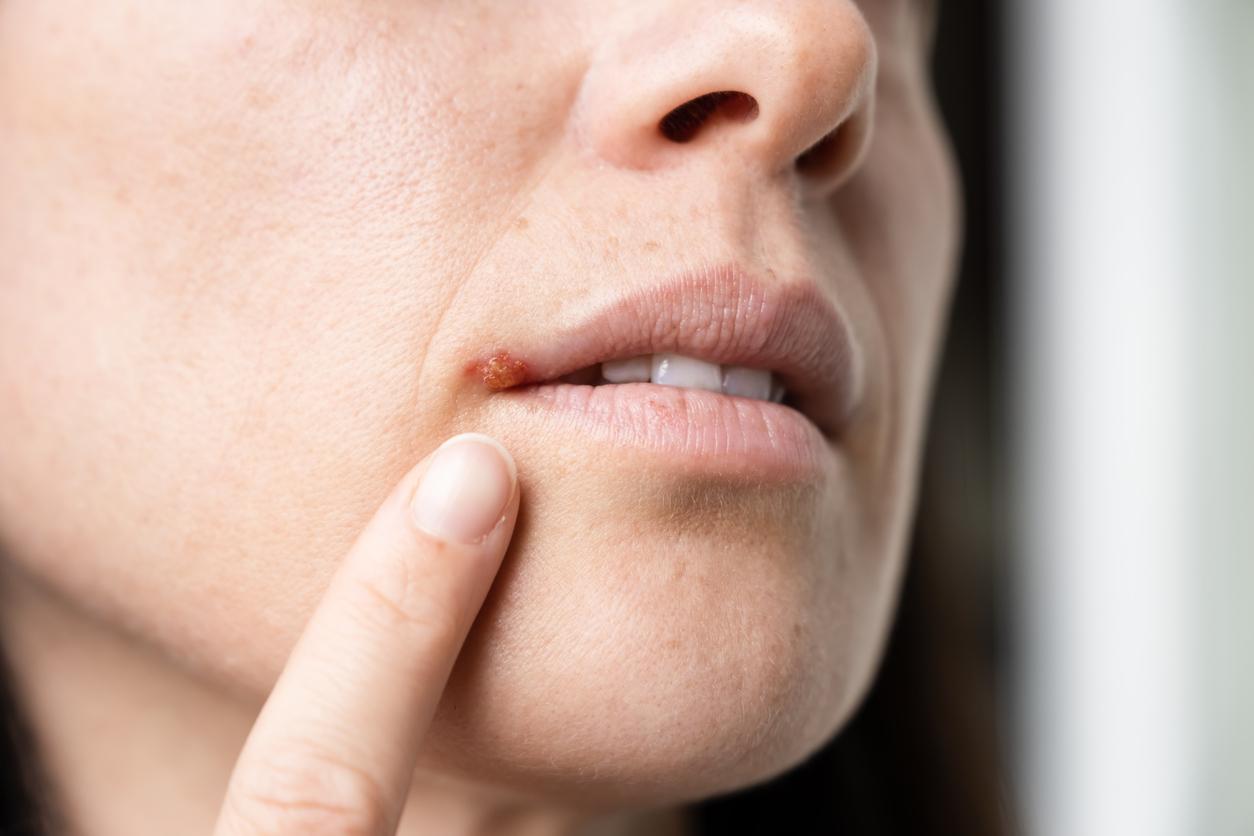
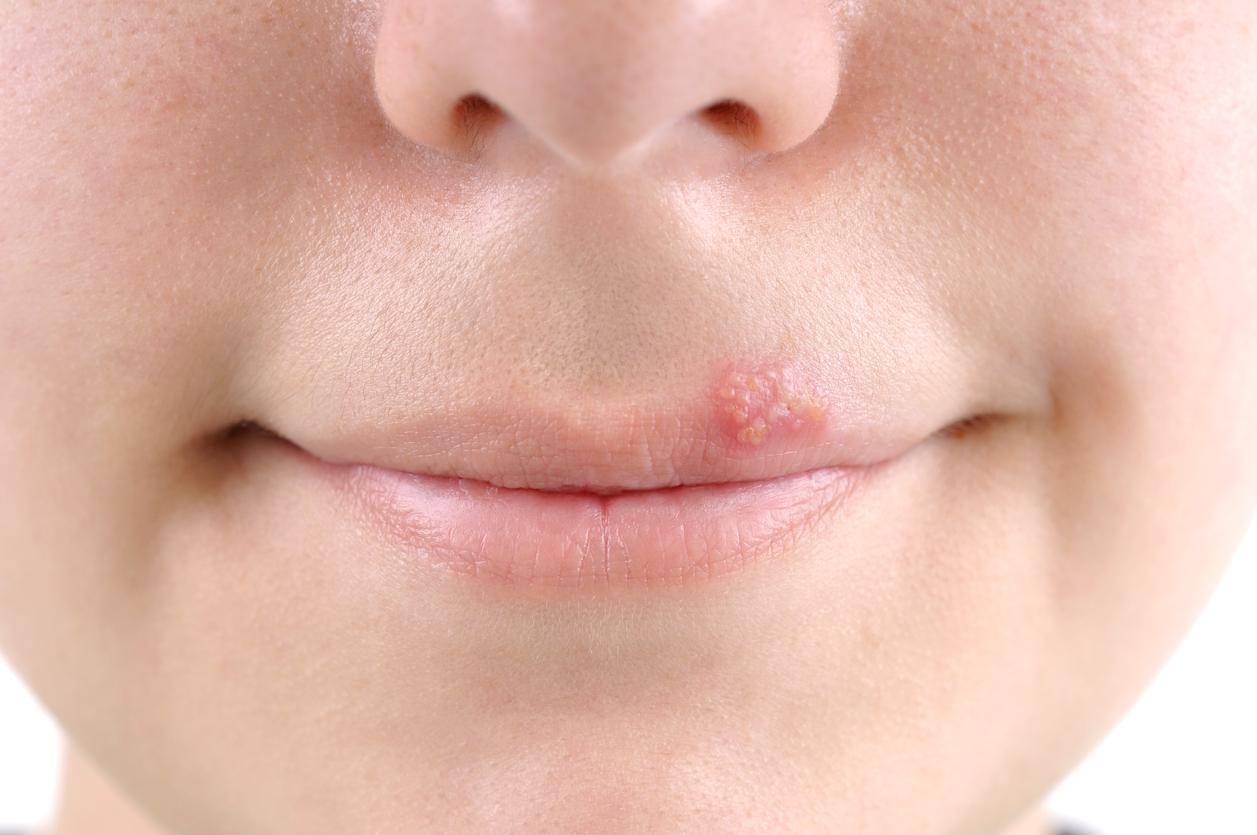
Herpes labialis, better known as cold sores, is characterized by the appearance of small vesicles on a lip at the junction between the skin and the mucous membrane. The offending ? Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV1). According to WHO estimates3.7 billion people under the age of 50 worldwide are infected with the latter. Several measures make it possible to limit the transmission and appearance of this particularly contagious infection.
Sore : the right actions to take to avoid infection
Cold sores can be transmitted by direct contact with the lesions and saliva of the infected individual. Contagion is possible from the warning signs of the rash (redness, tingling, itching of the lips) until crusts appear.
To avoid transmitting the virus HSV1 to loved ones, it is recommended to avoid having contact during an outbreak of cold sores:
- Don’t kiss your loved ones: it is important to avoid contact with young children and immunocompromised people who can develop significant complications.
- Limit contact sports like karate, football or rugby.
- Avoid oral sex while pushing: “these reports putting in contact the mouth with sex can be the cause of transmission of the virus present on the lips to the genitals of the partner. Likewise, a finger that touches a cold sore can carry the virus to other parts of the body.warnsHealth Insurance on its website.
It is also important to be vigilant in respecting hygiene rules. It’s necessary :
- se wash hands after touching the lesion;
- to use their own bath towels and washcloths;
- Do not share balms and lipsticks, cutlery or even razors.

Cold sore: how to avoid an outbreak of cold sores?
The Herpes simplex virus 1 virus does not disappear from the body once the primary infection has passed, generally in childhood. It settles in a nerve ganglion where it can remain “asleep”. Certain factors can favor its reactivation:
- fever: this is one of the most common factors;
- exposure to the sun or cold;
- tiredness ;
- the stress ;
- periods for women;
- during trauma;
- after surgery or illness;
- certain treatments such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants.